Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01594) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
AZD-4547
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
AZD4547; 1035270-39-3; AZD-4547; AZD 4547; UNII-2167OG1EKJ; N-(5-(3,5-dimethoxyphenethyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-4-((3S,5R)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl)benzamide; 2167OG1EKJ; CHEBI:63453; rel-N-[5-[2-(3,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]-1H-pyrazol-3-yl]-4-[(3R,5S)-3,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl]benzamide; N-{3-[2-(3,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]-1h-Pyrazol-5-Yl}-4-[(3r,5s)-3,5-Dimethylpiperazin-1-Yl]benzamide; N-{5-[2-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]-1H-pyrazol-3-yl}-4-(cis-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl)benzamide; N-{5-[2-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]-1H-pyrazol-3-yl}-4-[(3R,5S)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl]benzamide; 66T; KB-74810; N-[5-[2-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]-1H-pyrazol-3-yl]-4-[(3R,5S)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl]benzamide; SCHEMBL63884; N-(5-(3,5-Dimethoxyphenethyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-4-((3R,5S)-rel-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl)benzamide; GTPL7707; QCR-89; SCHEMBL15250892; DTXSID80145887; AMY16612; AOB87745; EX-A1578; 2240AH; MFCD22580423; NSC764239; NSC765338; NSC799346; s2801; ZINC95616598; AKOS024464898; BCP9000364; CCG-269382; CS-0971; DB12247; NSC-764239; NSC-765338; NSC-799346; NCGC00346713-01; NCGC00346713-05; AC-28442; AS-17054; HY-13330; rel-N-(5-(3,5-Dimethoxyphenethyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-4-((3R,5S)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl)benzamide; SW219341-1; J-000994; J-524217; Q27074746; N-(5-(3,5-dimethoxyphenethyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-4-((3R,5S)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl)benzamide, rel-; N-(5-(3,5-Dimethoxyphenethyl)-4H-pyrazol-3-yl)-4-((3S,5R)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl)benzamide; N-[5-[2-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]-1H-pyrazol-3-yl]-4-[(3R,5S)-3,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl]-Benzamide; N-[5-[2-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]-1H-pyrazol-3-yl]-4-[(3S,5R)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl]benzamide; N-[5-[2-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]-2H-pyrazol-3-yl]-4-[(3R,5S)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin -1-yl]benzamide; N-[5-[2-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]-2H-pyrazol-3-yl]-4-[(3R,5S)-3,5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl]benzamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 2 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
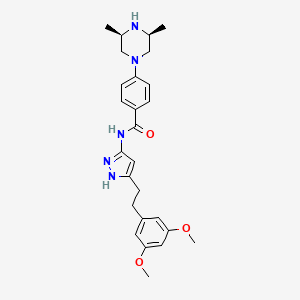
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[2]
[3]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[4]
[5]
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Erbb2 tyrosine kinase receptor (HER2) | ERBB2_HUMAN | [2] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
8
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C[C@@H]1CN(C[C@@H](N1)C)C2=CC=C(C=C2)C(=O)NC3=NNC(=C3)CCC4=CC(=CC(=C4)OC)OC
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C26H33N5O3/c1-17-15-31(16-18(2)27-17)22-9-6-20(7-10-22)26(32)28-25-13-21(29-30-25)8-5-19-11-23(33-3)14-24(12-19)34-4/h6-7,9-14,17-18,27H,5,8,15-16H2,1-4H3,(H2,28,29,30,32)/t17-,18+
|
||||
| InChIKey |
VRQMAABPASPXMW-HDICACEKSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K650E (c.1948A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.53 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.34 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
G
-
S
-
S
-
H
440
|
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
S
-
Q
G
D
S
P
H
P
450
|
M
T
L
L
A
A
G
N
V
V
S
S
E
E
Y
L
E
E
L
L
460
|
P
P
E
A
D
D
P
P
K
K
W
W
E
E
F
L
P
S
R
R
470
|
D
A
K
R
L
L
T
T
L
L
G
G
K
K
P
P
L
L
G
G
480
|
E
E
G
G
C
A
F
F
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
M
M
A
A
490
|
E
E
A
A
I
I
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
D
D
R
R
A
A
500
|
A
A
K
K
P
P
V
V
T
T
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
510
|
L
L
K
K
D
D
D
D
A
A
T
T
D
D
K
K
D
D
L
L
520
|
S
S
D
D
L
L
V
V
S
S
E
E
M
M
E
E
M
M
M
M
530
|
K
K
M
M
I
I
G
G
K
K
H
H
K
K
N
N
I
I
I
I
540
|
N
N
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
G
G
G
G
550
|
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
V
V
L
L
V
V
E
E
Y
Y
A
A
A
A
560
|
K
K
G
G
N
N
L
L
R
R
E
E
F
F
L
L
R
R
A
A
570
|
R
R
R
R
P
P
P
P
G
G
L
L
D
D
Y
Y
S
S
F
F
580
|
D
D
T
T
C
S
K
K
P
P
P
P
E
E
E
E
Q
Q
L
L
590
|
T
T
F
F
K
K
D
D
L
L
V
V
S
S
C
C
A
A
Y
Y
600
|
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
R
R
G
G
M
M
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
A
A
610
|
S
S
Q
Q
K
K
C
C
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
620
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
T
T
E
E
D
D
N
N
630
|
V
V
M
M
K
K
I
I
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
640
|
R
R
D
D
V
V
H
H
N
N
L
L
D
D
Y
Y
Y
Y
K
K
650
|
K
E
T
T
T
T
N
N
G
G
R
R
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
660
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
P
P
E
E
A
A
L
L
F
F
D
D
R
R
670
|
V
V
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
680
|
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
T
T
690
|
L
L
G
G
G
G
S
S
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
G
G
I
I
P
P
700
|
V
V
E
E
E
E
L
L
F
F
K
K
L
L
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
G
G
H
H
R
R
M
M
D
D
K
K
P
P
A
A
N
N
C
C
720
|
T
T
H
H
D
D
L
L
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
R
R
E
E
730
|
C
C
W
W
H
H
A
A
A
A
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
740
|
T
T
F
F
K
K
Q
Q
L
L
V
V
E
E
D
D
L
L
D
D
750
|
R
R
V
V
L
L
T
T
V
V
T
T
S
S
T
T
D
D
E
E
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V555M (c.1663G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.53 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.35 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
S
-
H
-
450
|
M
-
L
-
A
-
G
-
V
M
S
S
E
E
Y
L
E
E
L
L
460
|
P
P
E
A
D
D
P
P
K
K
W
W
E
E
F
L
P
S
R
R
470
|
D
A
K
R
L
L
T
T
L
L
G
G
K
K
P
P
L
L
G
G
480
|
E
E
G
G
C
C
F
F
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
M
M
A
A
490
|
E
E
A
A
I
I
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
D
D
R
R
A
A
500
|
A
A
K
K
P
P
V
V
T
T
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
510
|
L
L
K
K
D
D
D
D
A
A
T
T
D
D
K
K
D
D
L
L
520
|
S
S
D
D
L
L
V
V
S
S
E
E
M
M
E
E
M
M
M
M
530
|
K
K
M
M
I
I
G
G
K
K
H
H
K
K
N
N
I
I
I
I
540
|
N
N
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
G
G
G
G
550
|
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
V
V
L
L
V
M
E
E
Y
Y
A
A
A
A
560
|
K
K
G
G
N
N
L
L
R
R
E
E
F
F
L
L
R
R
A
A
570
|
R
R
R
R
P
S
P
G
G
-
L
-
D
-
Y
-
S
-
F
-
580
|
D
-
T
-
C
-
K
-
P
-
P
-
E
E
E
E
Q
Q
L
L
590
|
T
T
F
F
K
K
D
D
L
L
V
V
S
S
C
C
A
A
Y
Y
600
|
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
R
R
G
G
M
M
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
A
A
610
|
S
S
Q
Q
K
K
C
C
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
620
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
T
T
E
E
D
D
N
N
630
|
V
V
M
M
K
K
I
I
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
640
|
R
R
D
D
V
V
H
H
N
N
L
L
D
D
Y
Y
Y
Y
K
K
650
|
K
K
T
T
T
T
N
N
G
G
R
R
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
660
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
P
P
E
E
A
A
L
L
F
F
D
D
R
R
670
|
V
V
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
680
|
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
T
T
690
|
L
L
G
G
G
G
S
S
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
G
G
I
I
P
P
700
|
V
V
E
E
E
E
L
L
F
F
K
K
L
L
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
G
G
H
H
R
R
M
M
D
D
K
K
P
P
A
A
N
N
C
C
720
|
T
T
H
H
D
D
L
L
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
R
R
E
E
730
|
C
C
W
W
H
H
A
A
A
A
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
740
|
T
T
F
F
K
K
Q
Q
L
L
V
V
E
E
D
D
L
L
D
D
750
|
R
R
V
V
L
L
T
T
V
V
T
T
S
S
T
H
D
H
E
H
760
|
-
H
-
H
-
H
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Gallbladder | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Targeted sequencing of tumor tissue assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.V555M (c.1663G>A) in gene FGFR3 cause the resistance of AZD-4547 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V564F (c.1690G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.22 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
-
400
|
G
-
S
-
S
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
S
-
410
|
Q
-
D
-
P
-
P
-
A
-
V
-
H
-
K
-
L
-
T
-
420
|
K
-
R
-
I
-
P
-
L
-
R
-
R
-
Q
-
V
-
T
-
430
|
V
-
S
-
A
-
E
-
S
-
S
-
S
-
S
-
M
-
N
-
440
|
S
-
N
-
T
-
P
-
L
-
V
-
R
-
I
-
T
-
T
-
450
|
R
-
L
-
S
-
S
-
T
-
A
-
D
-
T
-
P
-
M
-
460
|
L
-
A
A
G
G
V
V
S
S
E
E
Y
Y
E
E
L
L
P
P
470
|
E
E
D
D
P
P
K
K
W
W
E
E
F
F
P
P
R
R
D
D
480
|
K
K
L
L
T
T
L
L
G
G
K
K
P
P
L
L
G
G
E
E
490
|
G
G
C
C
F
F
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
M
M
A
A
E
E
500
|
A
A
V
V
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
D
D
K
K
P
P
K
K
510
|
E
E
A
A
V
V
T
T
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
L
L
520
|
K
K
D
D
D
D
A
A
T
T
E
E
K
K
D
D
L
L
S
S
530
|
D
D
L
L
V
V
S
S
E
E
M
M
E
E
M
M
M
M
K
K
540
|
M
M
I
I
G
G
K
K
H
H
K
K
N
N
I
I
I
I
N
N
550
|
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
G
G
P
P
560
|
L
L
Y
Y
V
V
I
I
V
F
E
E
Y
Y
A
A
S
S
K
K
570
|
G
G
N
N
L
L
R
R
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
R
R
A
A
R
R
580
|
R
R
P
P
P
P
G
G
M
M
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
Y
Y
D
D
590
|
I
I
N
N
R
R
V
V
P
P
E
E
E
E
Q
Q
M
M
T
T
600
|
F
F
K
K
D
D
L
L
V
V
S
S
C
C
T
T
Y
Y
Q
Q
610
|
L
L
A
A
R
R
G
G
M
M
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
620
|
Q
Q
K
K
C
C
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
630
|
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
T
T
E
E
N
N
N
N
V
V
640
|
M
M
K
K
I
I
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
650
|
D
D
I
I
N
N
N
N
I
I
D
D
Y
Y
Y
Y
K
K
K
K
660
|
T
T
T
T
N
N
G
G
R
R
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
670
|
M
M
A
A
P
P
E
E
A
A
L
L
F
F
D
D
R
R
V
V
680
|
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
690
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
M
M
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
T
T
L
L
700
|
G
G
G
G
S
S
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
G
G
I
I
P
P
V
V
710
|
E
E
E
E
L
L
F
F
K
K
L
L
L
L
K
K
E
E
G
G
720
|
H
H
R
R
M
M
D
D
K
K
P
P
A
A
N
N
C
C
T
T
730
|
N
N
E
E
L
L
Y
Y
M
M
M
M
M
M
R
R
D
D
C
C
740
|
W
W
H
H
A
A
V
V
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
T
T
750
|
F
F
K
K
Q
Q
L
L
V
V
E
E
D
D
L
L
D
D
R
R
760
|
I
I
L
L
T
T
L
L
T
T
T
T
N
N
E
E
E
E
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | 327 cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female BALB-nu/nu mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L608V (c.1822T>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Gallbladder | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Targeted sequencing of tumor tissue assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.L608V (c.1822T>G) in gene FGFR3 cause the resistance of AZD-4547 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N540K (c.1620C>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NIH3T3 cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0594 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.W290C (c.870G>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| NIH-3T3 cells | Embryo | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0594 | |
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Soft-agar colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.W290C (c.870G>T) in gene FGFR2 cause the sensitivity of AZD-4547 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K660E (c.1978A>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| NIH-3T3 cells | Embryo | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0594 | |
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Soft-agar colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.K660E (c.1978A>G) in gene FGFR2 cause the sensitivity of AZD-4547 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K660N (c.1980G>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| NIH-3T3 cells | Embryo | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0594 | |
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Soft-agar colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.K660N (c.1980G>C) in gene FGFR2 cause the sensitivity of AZD-4547 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) | [5] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glucose metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A90.5] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | The 6 to 8-week-old NCG mice, with Jurkat-luciferase cell | Mice | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cd7 antibody assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanistically, we found that FGFR1 inhibitors markedly increased the expression of ATF4, which was a major initiator for T-ALL resistance to FGFR1 inhibitors. We further revealed that FGFR1 inhibitors induced expression of ATF4 through enhancing chromatin accessibility combined with translational activation via the GCN2-eIF2alpha pathway. Subsequently, ATF4 remodeled the amino acid metabolism by stimulating the expression of multiple metabolic genes ASNS, ASS1, PHGDH and SLC1A5, maintaining the activation of mTORC1, which contributed to the drug resistance in T-ALL cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V561M (c.1681G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.63 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
G
V
A
A
G
G
460
|
V
V
S
S
E
E
Y
Y
E
E
L
L
P
P
E
E
D
D
P
P
470
|
R
R
W
W
E
E
L
L
P
P
R
R
D
D
R
R
L
L
V
V
480
|
L
L
G
G
K
K
P
P
L
L
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
F
F
490
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
L
L
A
A
E
E
A
A
I
I
G
G
500
|
L
L
D
D
K
K
D
D
K
K
P
P
N
N
R
R
V
V
T
T
510
|
K
K
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
L
L
K
K
S
S
D
D
520
|
A
A
T
T
E
E
K
K
D
D
L
L
S
S
D
D
L
L
I
I
530
|
S
S
E
E
M
M
E
E
M
M
M
M
K
K
M
M
I
I
G
G
540
|
K
K
H
H
K
K
N
N
I
I
I
I
N
N
L
L
L
L
G
G
550
|
A
A
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
G
G
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
V
V
560
|
I
I
V
M
E
E
Y
Y
A
A
S
S
K
K
G
G
N
N
L
L
570
|
R
R
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
Q
Q
A
A
R
R
R
R
P
P
P
P
580
|
G
G
L
L
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
S
S
H
H
590
|
N
N
P
P
E
E
E
E
Q
Q
L
L
S
S
S
S
K
K
D
D
600
|
L
L
V
V
S
S
C
C
A
A
Y
Y
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
R
R
610
|
G
G
M
M
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
C
C
620
|
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
630
|
L
L
V
V
T
T
E
E
D
D
N
N
V
V
M
M
K
K
I
I
640
|
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
H
H
650
|
H
H
I
I
D
D
Y
Y
Y
Y
K
K
K
K
T
T
T
T
N
N
660
|
G
G
R
R
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
A
A
P
P
670
|
E
E
A
A
L
L
F
F
D
D
R
R
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
680
|
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
690
|
L
L
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
T
T
L
L
G
G
G
G
S
S
700
|
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
G
G
V
V
P
P
V
V
E
E
E
E
L
L
710
|
F
F
K
K
L
L
L
L
K
K
E
E
G
G
H
H
R
R
M
M
720
|
D
D
K
K
P
P
S
S
N
N
C
C
T
T
N
N
E
E
L
L
730
|
Y
Y
M
M
M
M
M
M
R
R
D
D
C
C
W
W
H
H
A
A
740
|
V
V
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
T
T
F
F
K
K
Q
Q
750
|
L
L
V
V
E
E
D
D
L
L
D
D
R
R
I
I
V
V
A
A
760
|
L
L
T
T
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | STAT3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04550 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | L6 cells | Skeletal muscle | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | CVCL_0385 | |||||||||
| H1581 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1479 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Transwell migration assay; Matrigel invasion assay; Proliferation assay; MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The V561M mutation biases cells towards a more mesenchymal phenotype, including increased levels of proliferation, migration, invasion and anchorage-independent growth, which was confirmed using CyTOF, a novel single cell analysis tool. Using shRNA knockdown, loss of STAT3 restored sensitivity of cancer cells expressing V561M FGFR1 to AZD4547. Thus, the data demonstrate that combination therapies including FGFR and STAT3 may overcome V561M FGFR1 driven drug resistance in the clinic. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Endometrial adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C76.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S252W (c.755C>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.88 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.70 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
-
N
N
S
S
N
N
150
|
N
N
K
K
R
R
A
A
P
P
Y
Y
W
W
T
T
N
N
T
T
160
|
E
E
K
K
M
M
E
E
K
K
R
R
L
L
H
H
A
A
V
V
170
|
P
P
A
A
A
A
N
N
T
T
V
V
K
K
F
F
R
R
C
C
180
|
P
P
A
A
G
G
G
G
N
N
P
P
M
M
P
P
T
T
M
M
190
|
R
R
W
W
L
L
K
K
N
N
G
G
K
K
E
E
F
F
K
K
200
|
Q
Q
E
E
H
H
R
R
I
I
G
G
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
V
V
210
|
R
R
N
N
Q
Q
H
H
W
W
S
S
L
L
I
I
M
M
E
E
220
|
S
S
V
V
V
V
P
P
S
S
D
D
K
K
G
G
N
N
Y
Y
230
|
T
T
C
C
V
V
V
V
E
E
N
N
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
S
S
240
|
I
I
N
N
H
H
T
T
Y
Y
H
H
L
L
D
D
V
V
V
V
250
|
E
E
R
R
S
W
P
P
H
H
R
R
P
P
I
I
L
L
Q
Q
260
|
A
A
G
G
L
L
P
P
A
A
N
N
A
A
S
S
T
T
V
V
270
|
V
V
G
G
G
G
D
D
V
V
E
E
F
F
V
V
C
C
K
K
280
|
V
V
Y
Y
S
S
D
D
A
A
Q
Q
P
P
H
H
I
I
Q
Q
290
|
W
W
I
I
K
K
H
H
V
V
E
E
K
K
N
N
G
G
S
S
300
|
K
K
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
D
D
G
G
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
L
L
310
|
K
K
V
V
L
L
K
K
A
A
A
A
G
G
V
V
N
N
T
T
320
|
T
T
D
D
K
K
E
E
I
I
E
E
V
V
L
L
Y
Y
I
I
330
|
R
R
N
N
V
V
T
T
F
F
E
E
D
D
A
A
G
G
E
E
340
|
Y
Y
T
T
C
C
L
L
A
A
G
G
N
N
S
S
I
I
G
G
350
|
I
I
S
S
F
F
H
H
S
S
A
A
W
W
L
L
T
T
V
V
360
|
L
L
P
P
A
A
P
P
G
G
R
R
E
E
L
-
E
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HEK293T cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | |||||||||
| U2OS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0042 | ||||||||||
| Ishikawa cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2529 | ||||||||||
| HEC1A cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0293 | ||||||||||
| MV4-11 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0064 | ||||||||||
| TT cells | Thyroid gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1774 | ||||||||||
| MOLM-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2188 | ||||||||||
| MFE296 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1406 | ||||||||||
| MFE296 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1406 | ||||||||||
| MFE280 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1405 | ||||||||||
| MFE280 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1405 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female balb/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Phospho-kinase array analysis; Reporter gene assay; Microarray analysis; RT-PCR; Gene set enrichment analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Soft-agar colony assay | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Endometrial adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C76.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N550K (c.1650T>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HEK293T cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | |||||||||
| U2OS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0042 | ||||||||||
| Ishikawa cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2529 | ||||||||||
| HEC1A cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0293 | ||||||||||
| MV4-11 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0064 | ||||||||||
| TT cells | Thyroid gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1774 | ||||||||||
| MOLM-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2188 | ||||||||||
| MFE296 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1406 | ||||||||||
| MFE296 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1406 | ||||||||||
| MFE280 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1405 | ||||||||||
| MFE280 cells | Endometrium | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1405 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female balb/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Phospho-kinase array analysis; Reporter gene assay; Microarray analysis; RT-PCR; Gene set enrichment analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Soft-agar colony assay | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S249C (c.746C>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [9] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Synonymous | p.K650K (c.1950G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G370C (c.1108G>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y373C (c.1118A>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R248C (c.742C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [9] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S371C (c.1111A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [9] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G380R (c.1138G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [10] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Urinary system cancer [ICD-11: 2C95.Y] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S249C (c.746C>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | FGF/FGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H716 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1581 |
| NCI-H520 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1566 | |
| RT112 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1670 | |
| BaF3 cells | Bone | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0161 | |
| KG-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0374 | |
| KATO-3 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0371 | |
| UMUC14 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2747 | |
| SNU16 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0076 | |
| OPM2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1625 | |
| NCI-H2444 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1552 | |
| NCI-H1581 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1479 | |
| MFM-223 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1408 | |
| DMS-114 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1174 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Mechanism Description | c-Myc functioned as the key downstream effector that preceded FGFR-MEK/ERK signaling in FGFR aberrant cancer. Disruption of c-Myc overrode the cell proliferation driven by constitutively active FGFR. FGFR inhibition in FGFR-addicted cancer facilitated c-Myc degradation via phosphorylating c-Myc at threonine 58. Ectopic expression of undegradable c-Myc mutant conferred resistance to FGFR inhibition both in vitro and in vivo. c-Myc level alteration stringently determined the response to FGFR inhibitors, as demonstrated in FGFR-responsive cancer subset, as well as cancers bearing acquired or de novo resistance to FGFR inhibition. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
