Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00550) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Infigratinib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
NVP-BGJ398; Infigratinib; 872511-34-7; BGJ398; BGJ-398; BGJ 398; Infigratinib free base; 3-(2,6-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(6-((4-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)phenyl)amino)pyrimidin-4-yl)-1-methylurea; UNII-A4055ME1VK; BGJ398 (NVP-BGJ398); MVP-BGJ398; A4055ME1VK; CHEBI:63451; 872511-34-7 (free base); 3-(2,6-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(6-{[4-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)phenyl]amino}pyrimidin-4-yl)-1-methylurea; 3-(2,6-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(6-(4-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)phenylamino)pyrimidin-4-yl)-1-methylurea; 3-(2,6-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-[6-[4-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)anilino]pyrimidin-4-yl]-1-methylurea; C26H31Cl2N7O3; Truseltiq; CHEMBL1834657; 3-(2,6-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(6-((4-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)phenyl)amino)pyrimidin-4-yl)-1-methylurea.; 3-(2,6-Dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-[6-[[4-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)phenyl]amino]pyrimidin-4-yl]-1-methylurea; Infigratinib [INN]; Infigratinib [USAN]; Infigratinib (BGJ398); Infigratinib (USAN/INN); Infigratinib [USAN:INN]; NVP-BGJ389; NVP-BGJ398(Infigratinib); MLS006010953; SCHEMBL374435; GTPL7877; QCR-48; CHEMBL1852688; DTXSID70236238; EX-A057; SYN1152; BGJ398, BGJ-398; HMS3295O21; AMY10737; AOB87703; BCP03602; BGJ398 - NVP-BGJ398; BDBM50355393; FD5035; MFCD22123241; NSC764487; s2183; WHO 10032; ZINC72105034; AKOS025149513; AKOS032949944; BCP9000399; CS-0586; DB11886; NSC-764487; SB16612; NCGC00274030-01; NCGC00274030-11; 3-(2,6-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(6-(4-(4-ethylpiperazin-1-yl)-phenylamino)pyrimidin-4-yl)-1-methylurea; AC-28417; AS-16290; HY-13311; SMR004702757; Urea, N'-(2,6-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N-(6-((4-(4-ethyl-1-piperazinyl)phenyl)amino)-4-pyrimidinyl)-N-methyl-; BCP0726000187; FT-0699366; Y0313; D11589; J-510477; BRD-K42728290-001-01-8; Q27075200; 07J; 3-(2,6-Dichloro-3,5-dimethoxy-phenyl)-1-{6-[4-(4-ethyl-piperazin-1-yl)-phenylamino]-pyrimidin-4-yl}-1-methyl-urea
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 2 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
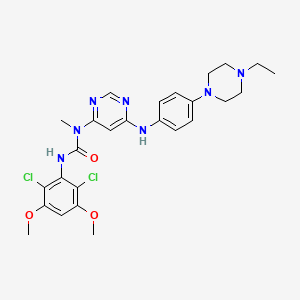
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(4 diseases)
[2]
[1]
[3]
[4]
|
||||
| Target | Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) | FGFR1_HUMAN | [1] | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C26H31Cl2N7O3
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CCN1CCN(CC1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)NC3=CC(=NC=N3)N(C)C(=O)NC4=C(C(=CC(=C4Cl)OC)OC)Cl
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C26H31Cl2N7O3/c1-5-34-10-12-35(13-11-34)18-8-6-17(7-9-18)31-21-15-22(30-16-29-21)33(2)26(36)32-25-23(27)19(37-3)14-20(38-4)24(25)28/h6-9,14-16H,5,10-13H2,1-4H3,(H,32,36)(H,29,30,31)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
QADPYRIHXKWUSV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K650E (c.1948A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.53 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.34 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
G
-
S
-
S
-
H
440
|
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
S
-
Q
G
D
S
P
H
P
450
|
M
T
L
L
A
A
G
N
V
V
S
S
E
E
Y
L
E
E
L
L
460
|
P
P
E
A
D
D
P
P
K
K
W
W
E
E
F
L
P
S
R
R
470
|
D
A
K
R
L
L
T
T
L
L
G
G
K
K
P
P
L
L
G
G
480
|
E
E
G
G
C
A
F
F
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
M
M
A
A
490
|
E
E
A
A
I
I
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
D
D
R
R
A
A
500
|
A
A
K
K
P
P
V
V
T
T
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
510
|
L
L
K
K
D
D
D
D
A
A
T
T
D
D
K
K
D
D
L
L
520
|
S
S
D
D
L
L
V
V
S
S
E
E
M
M
E
E
M
M
M
M
530
|
K
K
M
M
I
I
G
G
K
K
H
H
K
K
N
N
I
I
I
I
540
|
N
N
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
G
G
G
G
550
|
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
V
V
L
L
V
V
E
E
Y
Y
A
A
A
A
560
|
K
K
G
G
N
N
L
L
R
R
E
E
F
F
L
L
R
R
A
A
570
|
R
R
R
R
P
P
P
P
G
G
L
L
D
D
Y
Y
S
S
F
F
580
|
D
D
T
T
C
S
K
K
P
P
P
P
E
E
E
E
Q
Q
L
L
590
|
T
T
F
F
K
K
D
D
L
L
V
V
S
S
C
C
A
A
Y
Y
600
|
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
R
R
G
G
M
M
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
A
A
610
|
S
S
Q
Q
K
K
C
C
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
620
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
T
T
E
E
D
D
N
N
630
|
V
V
M
M
K
K
I
I
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
640
|
R
R
D
D
V
V
H
H
N
N
L
L
D
D
Y
Y
Y
Y
K
K
650
|
K
E
T
T
T
T
N
N
G
G
R
R
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
660
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
P
P
E
E
A
A
L
L
F
F
D
D
R
R
670
|
V
V
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
680
|
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
T
T
690
|
L
L
G
G
G
G
S
S
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
G
G
I
I
P
P
700
|
V
V
E
E
E
E
L
L
F
F
K
K
L
L
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
G
G
H
H
R
R
M
M
D
D
K
K
P
P
A
A
N
N
C
C
720
|
T
T
H
H
D
D
L
L
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
R
R
E
E
730
|
C
C
W
W
H
H
A
A
A
A
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
740
|
T
T
F
F
K
K
Q
Q
L
L
V
V
E
E
D
D
L
L
D
D
750
|
R
R
V
V
L
L
T
T
V
V
T
T
S
S
T
T
D
D
E
E
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Gallbladder | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Targeted sequencing of tumor tissue assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.K650E (c.1948A>G) in gene FGFR3 cause the resistance of Infigratinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V555M (c.1663G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.53 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.35 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
S
-
H
-
450
|
M
-
L
-
A
-
G
-
V
M
S
S
E
E
Y
L
E
E
L
L
460
|
P
P
E
A
D
D
P
P
K
K
W
W
E
E
F
L
P
S
R
R
470
|
D
A
K
R
L
L
T
T
L
L
G
G
K
K
P
P
L
L
G
G
480
|
E
E
G
G
C
C
F
F
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
M
M
A
A
490
|
E
E
A
A
I
I
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
D
D
R
R
A
A
500
|
A
A
K
K
P
P
V
V
T
T
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
510
|
L
L
K
K
D
D
D
D
A
A
T
T
D
D
K
K
D
D
L
L
520
|
S
S
D
D
L
L
V
V
S
S
E
E
M
M
E
E
M
M
M
M
530
|
K
K
M
M
I
I
G
G
K
K
H
H
K
K
N
N
I
I
I
I
540
|
N
N
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
G
G
G
G
550
|
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
V
V
L
L
V
M
E
E
Y
Y
A
A
A
A
560
|
K
K
G
G
N
N
L
L
R
R
E
E
F
F
L
L
R
R
A
A
570
|
R
R
R
R
P
S
P
G
G
-
L
-
D
-
Y
-
S
-
F
-
580
|
D
-
T
-
C
-
K
-
P
-
P
-
E
E
E
E
Q
Q
L
L
590
|
T
T
F
F
K
K
D
D
L
L
V
V
S
S
C
C
A
A
Y
Y
600
|
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
R
R
G
G
M
M
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
A
A
610
|
S
S
Q
Q
K
K
C
C
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
620
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
T
T
E
E
D
D
N
N
630
|
V
V
M
M
K
K
I
I
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
640
|
R
R
D
D
V
V
H
H
N
N
L
L
D
D
Y
Y
Y
Y
K
K
650
|
K
K
T
T
T
T
N
N
G
G
R
R
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
660
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
P
P
E
E
A
A
L
L
F
F
D
D
R
R
670
|
V
V
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
680
|
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
T
T
690
|
L
L
G
G
G
G
S
S
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
G
G
I
I
P
P
700
|
V
V
E
E
E
E
L
L
F
F
K
K
L
L
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
G
G
H
H
R
R
M
M
D
D
K
K
P
P
A
A
N
N
C
C
720
|
T
T
H
H
D
D
L
L
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
R
R
E
E
730
|
C
C
W
W
H
H
A
A
A
A
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
740
|
T
T
F
F
K
K
Q
Q
L
L
V
V
E
E
D
D
L
L
D
D
750
|
R
R
V
V
L
L
T
T
V
V
T
T
S
S
T
H
D
H
E
H
760
|
-
H
-
H
-
H
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Gallbladder | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Targeted sequencing of tumor tissue assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.V555M (c.1663G>A) in gene FGFR3 cause the resistance of Infigratinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V564F (c.1690G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.22 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
-
400
|
G
-
S
-
S
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
S
-
410
|
Q
-
D
-
P
-
P
-
A
-
V
-
H
-
K
-
L
-
T
-
420
|
K
-
R
-
I
-
P
-
L
-
R
-
R
-
Q
-
V
-
T
-
430
|
V
-
S
-
A
-
E
-
S
-
S
-
S
-
S
-
M
-
N
-
440
|
S
-
N
-
T
-
P
-
L
-
V
-
R
-
I
-
T
-
T
-
450
|
R
-
L
-
S
-
S
-
T
-
A
-
D
-
T
-
P
-
M
-
460
|
L
-
A
A
G
G
V
V
S
S
E
E
Y
Y
E
E
L
L
P
P
470
|
E
E
D
D
P
P
K
K
W
W
E
E
F
F
P
P
R
R
D
D
480
|
K
K
L
L
T
T
L
L
G
G
K
K
P
P
L
L
G
G
E
E
490
|
G
G
C
C
F
F
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
M
M
A
A
E
E
500
|
A
A
V
V
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
D
D
K
K
P
P
K
K
510
|
E
E
A
A
V
V
T
T
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
L
L
520
|
K
K
D
D
D
D
A
A
T
T
E
E
K
K
D
D
L
L
S
S
530
|
D
D
L
L
V
V
S
S
E
E
M
M
E
E
M
M
M
M
K
K
540
|
M
M
I
I
G
G
K
K
H
H
K
K
N
N
I
I
I
I
N
N
550
|
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
G
G
P
P
560
|
L
L
Y
Y
V
V
I
I
V
F
E
E
Y
Y
A
A
S
S
K
K
570
|
G
G
N
N
L
L
R
R
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
R
R
A
A
R
R
580
|
R
R
P
P
P
P
G
G
M
M
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
Y
Y
D
D
590
|
I
I
N
N
R
R
V
V
P
P
E
E
E
E
Q
Q
M
M
T
T
600
|
F
F
K
K
D
D
L
L
V
V
S
S
C
C
T
T
Y
Y
Q
Q
610
|
L
L
A
A
R
R
G
G
M
M
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
620
|
Q
Q
K
K
C
C
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
630
|
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
T
T
E
E
N
N
N
N
V
V
640
|
M
M
K
K
I
I
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
650
|
D
D
I
I
N
N
N
N
I
I
D
D
Y
Y
Y
Y
K
K
K
K
660
|
T
T
T
T
N
N
G
G
R
R
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
670
|
M
M
A
A
P
P
E
E
A
A
L
L
F
F
D
D
R
R
V
V
680
|
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
690
|
G
G
V
V
L
L
M
M
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
T
T
L
L
700
|
G
G
G
G
S
S
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
G
G
I
I
P
P
V
V
710
|
E
E
E
E
L
L
F
F
K
K
L
L
L
L
K
K
E
E
G
G
720
|
H
H
R
R
M
M
D
D
K
K
P
P
A
A
N
N
C
C
T
T
730
|
N
N
E
E
L
L
Y
Y
M
M
M
M
M
M
R
R
D
D
C
C
740
|
W
W
H
H
A
A
V
V
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
T
T
750
|
F
F
K
K
Q
Q
L
L
V
V
E
E
D
D
L
L
D
D
R
R
760
|
I
I
L
L
T
T
L
L
T
T
T
T
N
N
E
E
E
E
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Gallbladder | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Targeted sequencing of tumor tissue assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.V564F (c.1690G>T) in gene FGFR2 cause the resistance of Infigratinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N540K (c.1620C>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Gallbladder | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Targeted sequencing of tumor tissue assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.N540K (c.1620C>G) in gene FGFR3 cause the resistance of Infigratinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V555L (c.1663G>C) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Gallbladder | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Targeted sequencing of tumor tissue assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.V555L (c.1663G>C) in gene FGFR3 cause the resistance of Infigratinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L608V (c.1822T>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Gallbladder | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Targeted sequencing of tumor tissue assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.L608V (c.1822T>G) in gene FGFR3 cause the resistance of Infigratinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K660E (c.1978A>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| NIH-3T3 cells | Embryo | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0594 | |
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Soft-agar colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.K660E (c.1978A>G) in gene FGFR2 cause the sensitivity of Infigratinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K660N (c.1980G>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| NIH-3T3 cells | Embryo | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0594 | |
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Soft-agar colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.K660N (c.1980G>C) in gene FGFR2 cause the sensitivity of Infigratinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.W290C (c.870G>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| NIH-3T3 cells | Embryo | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0594 | |
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Soft-agar colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.W290C (c.870G>T) in gene FGFR2 cause the sensitivity of Infigratinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R248C (c.742C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| NIH-3T3 cells | Embryo | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0594 | |
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Soft-agar colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.R248C (c.742C>T) in gene FGFR3 cause the sensitivity of Infigratinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S249C (c.746C>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| NIH-3T3 cells | Embryo | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0594 | |
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Soft-agar colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.S249C (c.746C>G) in gene FGFR3 cause the sensitivity of Infigratinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.S267_D273 (c.799_819) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NIH-3T3 cells | Embryo | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0594 |
| In Vivo Model | Nu/Nu mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Soft-agar colony formation assay | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Complex-indel | p.W290_I291delinsC (c.870_872delGAT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NIH-3T3 cells | Embryo | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0594 |
| In Vivo Model | Nu/Nu mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Soft-agar colony formation assay | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Amplification |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MET signalling pathway | Activation | hsa04020 | |
| ERK/MAPK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04210 | ||
| In Vitro Model | DMS114 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1174 |
| Mechanism Description | Upregulation of the MET signalling pathway leading to re-activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway was observed in conjunction with the development of resistance to infigratinib in FGFR1-amplified DMS114 lung cancer cells. | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Amplification |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MET signalling pathway | Activation | hsa04020 | |
| ERK/MAPK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04210 | ||
| In Vitro Model | DMS114 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1174 |
| Mechanism Description | Upregulation of the MET signalling pathway leading to re-activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway was observed in conjunction with the development of resistance to infigratinib in FGFR1-amplified DMS114 lung cancer cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G370C (c.1108G>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y373C (c.1118A>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R248C (c.742C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S371C (c.1111A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G380R (c.1138G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S249C (c.746C>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Synonymous | p.K650K (c.1950G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [9] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Urinary system cancer [ICD-11: 2C95.Y] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S249C (c.746C>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | FGF/FGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H716 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1581 |
| NCI-H520 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1566 | |
| RT112 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1670 | |
| BaF3 cells | Bone | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0161 | |
| KG-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0374 | |
| KATO-3 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0371 | |
| UMUC14 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2747 | |
| SNU16 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0076 | |
| OPM2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1625 | |
| NCI-H2444 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1552 | |
| NCI-H1581 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1479 | |
| MFM-223 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1408 | |
| DMS-114 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1174 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Mechanism Description | c-Myc functioned as the key downstream effector that preceded FGFR-MEK/ERK signaling in FGFR aberrant cancer. Disruption of c-Myc overrode the cell proliferation driven by constitutively active FGFR. FGFR inhibition in FGFR-addicted cancer facilitated c-Myc degradation via phosphorylating c-Myc at threonine 58. Ectopic expression of undegradable c-Myc mutant conferred resistance to FGFR inhibition both in vitro and in vivo. c-Myc level alteration stringently determined the response to FGFR inhibitors, as demonstrated in FGFR-responsive cancer subset, as well as cancers bearing acquired or de novo resistance to FGFR inhibition. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Transitional cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C9Z.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V555M (c.1663G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.53 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.35 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
S
-
H
-
450
|
M
-
L
-
A
-
G
-
V
M
S
S
E
E
Y
L
E
E
L
L
460
|
P
P
E
A
D
D
P
P
K
K
W
W
E
E
F
L
P
S
R
R
470
|
D
A
K
R
L
L
T
T
L
L
G
G
K
K
P
P
L
L
G
G
480
|
E
E
G
G
C
C
F
F
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
M
M
A
A
490
|
E
E
A
A
I
I
G
G
I
I
D
D
K
K
D
D
R
R
A
A
500
|
A
A
K
K
P
P
V
V
T
T
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
510
|
L
L
K
K
D
D
D
D
A
A
T
T
D
D
K
K
D
D
L
L
520
|
S
S
D
D
L
L
V
V
S
S
E
E
M
M
E
E
M
M
M
M
530
|
K
K
M
M
I
I
G
G
K
K
H
H
K
K
N
N
I
I
I
I
540
|
N
N
L
L
L
L
G
G
A
A
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
G
G
G
G
550
|
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
V
V
L
L
V
M
E
E
Y
Y
A
A
A
A
560
|
K
K
G
G
N
N
L
L
R
R
E
E
F
F
L
L
R
R
A
A
570
|
R
R
R
R
P
S
P
G
G
-
L
-
D
-
Y
-
S
-
F
-
580
|
D
-
T
-
C
-
K
-
P
-
P
-
E
E
E
E
Q
Q
L
L
590
|
T
T
F
F
K
K
D
D
L
L
V
V
S
S
C
C
A
A
Y
Y
600
|
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
R
R
G
G
M
M
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
A
A
610
|
S
S
Q
Q
K
K
C
C
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
620
|
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
L
L
V
V
T
T
E
E
D
D
N
N
630
|
V
V
M
M
K
K
I
I
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
640
|
R
R
D
D
V
V
H
H
N
N
L
L
D
D
Y
Y
Y
Y
K
K
650
|
K
K
T
T
T
T
N
N
G
G
R
R
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
660
|
W
W
M
M
A
A
P
P
E
E
A
A
L
L
F
F
D
D
R
R
670
|
V
V
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
680
|
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
T
T
690
|
L
L
G
G
G
G
S
S
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
G
G
I
I
P
P
700
|
V
V
E
E
E
E
L
L
F
F
K
K
L
L
L
L
K
K
E
E
710
|
G
G
H
H
R
R
M
M
D
D
K
K
P
P
A
A
N
N
C
C
720
|
T
T
H
H
D
D
L
L
Y
Y
M
M
I
I
M
M
R
R
E
E
730
|
C
C
W
W
H
H
A
A
A
A
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
740
|
T
T
F
F
K
K
Q
Q
L
L
V
V
E
E
D
D
L
L
D
D
750
|
R
R
V
V
L
L
T
T
V
V
T
T
S
S
T
H
D
H
E
H
760
|
-
H
-
H
-
H
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2D42.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S131L (c.392C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SCC25 cells | Oral | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1682 |
| HSC3 cells | Tongue | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1288 | |
| FaDu cells | Pharynx | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1218 | |
| HN cells | Cervical lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1283 | |
| Detroit 562 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1171 | |
| 584-A2 cells | Larynx | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_V278 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemical staining assay; qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In vitro, FGFR3 overexpression led to increased proliferation, whereas migration was not altered. Moreover, FGFR3-overexpressing cells were more sensitive to BGJ398. Cells overexpressing FGFR3 mutant versions showed increased proliferation compared to wild-type FGFR3 under serum-reduced conditions and were largely as sensitive as the wild-type protein to BGJ398. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
