Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01652) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
PRN1371
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
PRN1371; 1802929-43-6; PRN-1371; 8-(3-(4-acryloylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl)-6-(2,6-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7(8H)-one; UNII-S3OPE9IA3Q; S3OPE9IA3Q; 6-(2,6-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)-8-[3-(4-prop-2-enoylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-one; GTPL9788; CHEMBL4068509; SCHEMBL16993012; US9567334, Example 6; BDBM286984; BCP20493; EX-A2927; NSC801089; s8578; CCG-270053; CS-7485; NSC-801089; compound 34 [PMID: 28665128]; BP179867; HY-101768; J3.662.238E; C92492; A936037; Q29213602
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 3 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
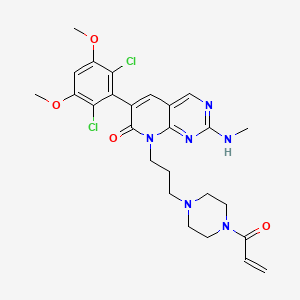
|
||||
| Target | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) | PGFRA_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
9
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CNC1=NC=C2C=C(C(=O)N(C2=N1)CCCN3CCN(CC3)C(=O)C=C)C4=C(C(=CC(=C4Cl)OC)OC)Cl
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C26H30Cl2N6O4/c1-5-20(35)33-11-9-32(10-12-33)7-6-8-34-24-16(15-30-26(29-2)31-24)13-17(25(34)36)21-22(27)18(37-3)14-19(38-4)23(21)28/h5,13-15H,1,6-12H2,2-4H3,(H,29,30,31)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
PUIXMSRTTHLNKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V561M (c.1681G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.63 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.96 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
G
V
A
A
G
G
460
|
V
V
S
S
E
E
Y
Y
E
E
L
L
P
P
E
E
D
D
P
P
470
|
R
R
W
W
E
E
L
L
P
P
R
R
D
D
R
R
L
L
V
V
480
|
L
L
G
G
K
K
P
P
L
L
G
G
E
E
G
G
A
A
F
F
490
|
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
V
V
L
L
A
A
E
E
A
A
I
I
G
G
500
|
L
L
D
D
K
K
D
D
K
K
P
P
N
N
R
R
V
V
T
T
510
|
K
K
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
L
L
K
K
S
S
D
D
520
|
A
A
T
T
E
E
K
K
D
D
L
L
S
S
D
D
L
L
I
I
530
|
S
S
E
E
M
M
E
E
M
M
M
M
K
K
M
M
I
I
G
G
540
|
K
K
H
H
K
K
N
N
I
I
I
I
N
N
L
L
L
L
G
G
550
|
A
A
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
G
G
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
V
V
560
|
I
I
V
M
E
E
Y
Y
A
A
S
S
K
K
G
G
N
N
L
L
570
|
R
R
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
Q
Q
A
A
R
R
R
R
P
P
P
P
580
|
G
G
L
L
E
E
Y
Y
S
S
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
S
S
H
H
590
|
N
N
P
P
E
E
E
E
Q
Q
L
L
S
S
S
S
K
K
D
D
600
|
L
L
V
V
S
S
C
C
A
A
Y
Y
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
R
R
610
|
G
G
M
M
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
A
A
S
S
K
K
K
K
C
C
620
|
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
V
V
630
|
L
L
V
V
T
T
E
E
D
D
N
N
V
V
M
M
K
K
I
I
640
|
A
A
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
H
H
650
|
H
H
I
I
D
D
Y
Y
Y
Y
K
K
K
K
T
T
T
T
N
N
660
|
G
G
R
R
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
A
A
P
P
670
|
E
E
A
A
L
L
F
F
D
D
R
R
I
I
Y
Y
T
T
H
H
680
|
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
690
|
L
L
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
T
T
L
L
G
G
G
G
S
S
700
|
P
P
Y
Y
P
P
G
G
V
V
P
P
V
V
E
E
E
E
L
L
710
|
F
F
K
K
L
L
L
L
K
K
E
E
G
G
H
H
R
R
M
M
720
|
D
D
K
K
P
P
S
S
N
N
C
C
T
T
N
N
E
E
L
L
730
|
Y
Y
M
M
M
M
M
M
R
R
D
D
C
C
W
W
H
H
A
A
740
|
V
V
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
R
R
P
P
T
T
F
F
K
K
Q
Q
750
|
L
L
V
V
E
E
D
D
L
L
D
D
R
R
I
I
V
V
A
A
760
|
L
L
T
T
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | FGF/FGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |||||||||
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | ||||||||||
| RT4 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0036 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H716 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1581 | ||||||||||
| RT112 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1670 | ||||||||||
| AN3CA cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0028 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| SNU878 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5102 | ||||||||||
| SNU16 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0076 | ||||||||||
| OPM2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1625 | ||||||||||
| LI7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3840 | ||||||||||
| JHH7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2805 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | PRN1371 exhibits potent and durable pathway inhibition, and robust antiproliferative activity. PRN1371 demonstrates prolonged FGFR inhibition in vivo. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N550K (c.1650T>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | FGF/FGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |||||||||
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | ||||||||||
| RT4 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0036 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H716 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1581 | ||||||||||
| RT112 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1670 | ||||||||||
| AN3CA cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0028 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| SNU878 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5102 | ||||||||||
| SNU16 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0076 | ||||||||||
| OPM2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1625 | ||||||||||
| LI7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3840 | ||||||||||
| JHH7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2805 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | PRN1371 exhibits potent and durable pathway inhibition, and robust antiproliferative activity. PRN1371 demonstrates prolonged FGFR inhibition in vivo. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K660E (c.1978A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | FGF/FGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |||||||||
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | ||||||||||
| RT4 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0036 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H716 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1581 | ||||||||||
| RT112 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1670 | ||||||||||
| AN3CA cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0028 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| SNU878 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5102 | ||||||||||
| SNU16 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0076 | ||||||||||
| OPM2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1625 | ||||||||||
| LI7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3840 | ||||||||||
| JHH7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2805 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | PRN1371 exhibits potent and durable pathway inhibition, and robust antiproliferative activity. PRN1371 demonstrates prolonged FGFR inhibition in vivo. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K660N (c.1980G>C) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | FGF/FGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |||||||||
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | ||||||||||
| RT4 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0036 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H716 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1581 | ||||||||||
| RT112 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1670 | ||||||||||
| AN3CA cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0028 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| SNU878 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5102 | ||||||||||
| SNU16 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0076 | ||||||||||
| OPM2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1625 | ||||||||||
| LI7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3840 | ||||||||||
| JHH7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2805 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | PRN1371 exhibits potent and durable pathway inhibition, and robust antiproliferative activity. PRN1371 demonstrates prolonged FGFR inhibition in vivo. | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K650M (c.1949A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | FGF/FGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |||||||||
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | ||||||||||
| RT4 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0036 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H716 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1581 | ||||||||||
| RT112 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1670 | ||||||||||
| AN3CA cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0028 | ||||||||||
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | ||||||||||
| SNU878 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5102 | ||||||||||
| SNU16 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0076 | ||||||||||
| OPM2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1625 | ||||||||||
| LI7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3840 | ||||||||||
| JHH7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2805 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | PRN1371 exhibits potent and durable pathway inhibition, and robust antiproliferative activity. PRN1371 demonstrates prolonged FGFR inhibition in vivo. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Endometrial adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C76.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N549K (c.1647T>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | FGF/FGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | |
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 |
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | |
| RT4 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0036 | |
| NCI-H716 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1581 | |
| RT112 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1670 | |
| AN3CA cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0028 | |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| SNU878 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5102 | |
| SNU16 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0076 | |
| OPM2 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1625 | |
| LI7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3840 | |
| JHH7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2805 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | PRN1371 exhibits potent and durable pathway inhibition, and robust antiproliferative activity. PRN1371 demonstrates prolonged FGFR inhibition in vivo. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
