Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00362)
| Name |
Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
ENX-1; Enhancer of zeste homolog 2; Lysine N-methyltransferase 6; KMT6
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
EZH2
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr7:148807257-148884321[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MGQTGKKSEKGPVCWRKRVKSEYMRLRQLKRFRRADEVKSMFSSNRQKILERTEILNQEW
KQRRIQPVHILTSVSSLRGTRECSVTSDLDFPTQVIPLKTLNAVASVPIMYSWSPLQQNF MVEDETVLHNIPYMGDEVLDQDGTFIEELIKNYDGKVHGDRECGFINDEIFVELVNALGQ YNDDDDDDDGDDPEEREEKQKDLEDHRDDKESRPPRKFPSDKIFEAISSMFPDKGTAEEL KEKYKELTEQQLPGALPPECTPNIDGPNAKSVQREQSLHSFHTLFCRRCFKYDCFLHPFH ATPNTYKRKNTETALDNKPCGPQCYQHLEGAKEFAAALTAERIKTPPKRPGGRRRGRLPN NSSRPSTPTINVLESKDTDSDREAGTETGGENNDKEEEEKKDETSSSSEANSRCQTPIKM KPNIEPPENVEWSGAEASMFRVLIGTYYDNFCAIARLIGTKTCRQVYEFRVKESSIIAPA PAEDVDTPPRKKKRKHRLWAAHCRKIQLKKDGSSNHVYNYQPCDHPRQPCDSSCPCVIAQ NFCEKFCQCSSECQNRFPGCRCKAQCNTKQCPCYLAVRECDPDLCLTCGAADHWDSKNVS CKNCSIQRGSKKHLLLAPSDVAGWGIFIKDPVQKNEFISEYCGEIISQDEADRRGKVYDK YMCSFLFNLNNDFVVDATRKGNKIRFANHSVNPNCYAKVMMVNGDHRIGIFAKRAIQTGE ELFFDYRYSQADALKYVGIEREMEIP Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Polycomb group (PcG) protein. Catalytic subunit of the PRC2/EED-EZH2 complex, which methylates 'Lys-9' (H3K9me) and 'Lys-27' (H3K27me) of histone H3, leading to transcriptional repression of the affected target gene. Able to mono-, di- and trimethylate 'Lys-27' of histone H3 to form H3K27me1, H3K27me2 and H3K27me3, respectively. Displays a preference for substrates with less methylation, loses activity when progressively more methyl groups are incorporated into H3K27, H3K27me0 > H3K27me1 > H3K27me2. Compared to EZH1-containing complexes, it is more abundant in embryonic stem cells and plays a major role in forming H3K27me3, which is required for embryonic stem cell identity and proper differentiation. The PRC2/EED-EZH2 complex may also serve as a recruiting platform for DNA methyltransferases, thereby linking two epigenetic repression systems. Genes repressed by the PRC2/EED-EZH2 complex include HOXC8, HOXA9, MYT1, CDKN2A and retinoic acid target genes. EZH2 can also methylate non-histone proteins such as the transcription factor GATA4 and the nuclear receptor RORA. Regulates the circadian clock via histone methylation at the promoter of the circadian genes. Essential for the CRY1/2-mediated repression of the transcriptional activation of PER1/2 by the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer; involved in the di and trimethylation of 'Lys-27' of histone H3 on PER1/2 promoters which is necessary for the CRY1/2 proteins to inhibit transcription.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
7 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.60E-184 Fold-change: 6.37E-01 Z-score: 4.69E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | CASC9 is upregulated in breast cancer tissues and breast cancer drug-resistant cell lines and overexpressed CASC9 may significantly increase the protein expression of EZH2. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [13] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 |
| SGC7901/VCR cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VU58 | |
| SGC7901/ADR cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VU57 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Caspase3/7 activity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-126 increases chemosensitivity in drug-resistant gastric cancer cells by targeting EZH2. | |||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [14] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | |
| SNU182 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0090 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-101-mediated EZH2 silencing sensitized hepatoblastoma cells to 5-FU- and doxorubicin-induced apoptosis, whereas antagomiR-mediated downregulation of endogenous miR-101 reversed the pro-apoptotic effect. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovarian tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.10E-06 Fold-change: 5.88E-01 Z-score: 1.13E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | We found that EZH2 was overexpressed in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells compared with cisplatin-sensitive cells. Knockdown of EZH2 by RNA interference (RNAi) resensitized drug-resistant ovarian cancer A2780/DDP cells to cisplatin and decreased the level of H3K27 trimethylation (H3K27me3). | |||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [3], [4], [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.56E-02 Fold-change: 5.80E-01 Z-score: 3.18E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| Epithelial mesenchymal transition signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01521 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | ||
| Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04310 | ||
| In Vitro Model | BGC-823 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3360 |
| MGC-803 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5334 | |
| SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 | |
| In Vivo Model | Balb/c athymic nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RIP experiments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Knockdown of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer cells through inhibiting the PI3k/Akt and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways by up-regulating miR34a. | |||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Melanoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Skin | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.38E-01 Fold-change: 1.02E-02 Z-score: 2.07E-01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 |
| Sk-Mel28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpressed 211 could enhance the anticancer effect of cisplatin and restoration of miR-211 rendered susceptibility to cisplatin in cisplatin-resistant cells.miR-211 could be transcriptionally repressed by EZH2 mediated promoter methylation. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell colony | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| c-Myc/miR137/EZH2 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | PEO1 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2686 |
| PEO4 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2690 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse xenograft mode | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SRB assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In resistant cells c-Myc enhances the expression of EZH2 by directly suppressing miR-137 that targets EZH2 mRNA, and increased expression of EZH2 activates cellular survival pathways, resulting in the resistance to cisplatin. | |||
| Disease Class: Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C23.10] | [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C23.10] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HEp-2 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1906 |
| AMC-HN-8 cells | Larynx | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5966 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | HOTAIR and EZH2 were over-expressed in LSCC tissue. The higher expression was significantly related to T phase, pathological grades, and risk of lymphatic metastasis of LSCC. Suppressing HOTAIR expression stimulated EZH2 expressing, promoted the proliferation of AMC-HN8 cells, and increased the sensitivity to cis-platinum of the LSCC cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Epithelial ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | [10] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Epithelial ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 | |
| ES2 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_AX39 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of let-7e by transfection of agomir could resensitize A2780/CP and reduce the expression of cisplatin-resistant-related proteins enhancer of zeste 2 (EZH2) and cyclin D1 (CCND1), whereas let-7e inhibitors increased resistance to cisplatin in parental A2780 cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | [11] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| miR138/EZH2 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | MG63 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0426 |
| SAOS-2 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0548 | |
| U2OS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0042 | |
| HOS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0312 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Flow cytometric assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-138 acts as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma, inhibiting cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by downregulating EZH2 expression. Mir-138 overexpression also enhances osteosarcoma cell chemosensitivity to cisplatin by targeting EZH2. | |||
| Disease Class: Epithelial ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | [12] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Epithelial ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; BrdU assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-101 overexpression decreased the expression of EZH2, reduced proliferation and migration of ovarian cancer cells, and resensitized drug-resistant cancer cells to cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [15], [16] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell metastasis | Activation | hsa05205 | |
| NF-kB signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04218 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HT29 Cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A8EZ |
| SW480 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0546 | |
| FHC cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3688 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RIP experiments | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | HOTAIR directly recruits EZH2 and subsequently suppresses miR-218 expression by binding to its promoter and contributes to 5FU resistance through activating NF-kB/TS Signaling in colorectal cancer. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [14] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | |
| SNU182 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0090 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-101-mediated EZH2 silencing sensitized hepatoblastoma cells to 5-FU- and doxorubicin-induced apoptosis, whereas antagomiR-mediated downregulation of endogenous miR-101 reversed the pro-apoptotic effect. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [17] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Oxaliplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HT29 Cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A8EZ |
| SW480 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0546 | |
| FHC cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3688 | |
| SW620 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0547 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Boyden chambers cell migration and invasion assays | |||
| Mechanism Description | MALAT1 tethers EZH2 to CDH1 promoter and suppresses miR218 during oxaliplatin treatment, which finally promotes colorectal cancer cell EMT, metastasis, and chemoresistance. MALAT1 mediates oxaliplatin-induced EMT through EZH2 and interacts with miR218. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: ER positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.6] | [18] | |||
| Resistant Disease | ER positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.6] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| MCF-7R cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_Y493 | |
| ZR-75-1R cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Annexin V apoptosis assay; Fow cytometry analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | H19 was confirmed to suppress the promoter activity of BIk by recruiting EZH2 and by trimethylating the histone H3 at lysine 27. H19 bound to EZH2 in breast cancer cells, epigenetic silencing of BIk by H19 was dependent on EZH2. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [19] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Tazemetostat | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y111D (c.331T>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HEK293 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0045 |
| Pfeiffer cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3326 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay | |||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [20] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Tazemetostat | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Complex-indel | p.T678_R679delinsKK (c.2032_2037delinsAAGAAG) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | RN2c cells | Blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | N.A. |
| RN2 cells | Blood | Mus musculus (Mouse) | N.A. | |
| Plat-E cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B488 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90- 2A85] | [21] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90- 2A85] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Tazemetostat | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y646F (c.1937A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CRL-2959 cells | Peritoneal effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2206 |
| CRL-2632 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3326 | |
| CRL-2631 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3611 | |
| CRL-2630 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3302 | |
| CRL-2261 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1660 | |
| ACC-576 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1889 | |
| ACC-575 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1902 | |
| ACC-528 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1878 | |
| ACC-32 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1325 | |
| In Vivo Model | Sprague-Dawley rat model | Rattus norvegicus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ChIP-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell Titer Glo assay; Tumor volume measurement assay; Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [13] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Vincristine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 |
| SGC7901/VCR cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VU58 | |
| SGC7901/ADR cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VU57 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Caspase3/7 activity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | microRNA-126 increases chemosensitivity in drug-resistant gastric cancer cells by targeting EZH2. | |||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [19] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | GSK126 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y111D (c.331T>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HEK293 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0045 |
| Pfeiffer cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3326 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay | |||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | [22] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | GSK126 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y641S (c.1922A>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Propidium-iodide cell cycle analysis; BrdU-PI cell cycle analysis | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [23] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | GSK126 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y641S (c.1922A>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Skin sample | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; BCA assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | EZH2 activation by mutations, gene amplification and increased transcription occurred in about 20% of the cohort. These alterations were associated with significant hypermethylation of DNA and significant downregulation of 11% of transcripts in patient RNASeq data. | |||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [23] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | GSK126 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y641N (c.1921T>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Skin sample | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; BCA assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | EZH2 activation by mutations, gene amplification and increased transcription occurred in about 20% of the cohort. These alterations were associated with significant hypermethylation of DNA and significant downregulation of 11% of transcripts in patient RNASeq data. | |||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [23] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | GSK126 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y641H (c.1921T>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Skin sample | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; BCA assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | EZH2 activation by mutations, gene amplification and increased transcription occurred in about 20% of the cohort. These alterations were associated with significant hypermethylation of DNA and significant downregulation of 11% of transcripts in patient RNASeq data. | |||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [24] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | GSK126 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y646N (c.1936T>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SKMEL-28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 |
| MM386 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2607 | |
| MM200 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C836 | |
| MEL-RM cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D548 | |
| MEL-JD cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_BS80 | |
| ME4405 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C680 | |
| ME1007 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C668 | |
| IGR1 Mel-RMU cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_S994 | |
| HEM cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| HDF cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| C001 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B4K8 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay | |||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [24] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | GSK126 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y646N (c.1936T>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SKMEL-28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 |
| MM386 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2607 | |
| MM200 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C836 | |
| MEL-RM cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D548 | |
| MEL-JD cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_BS80 | |
| ME4405 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C680 | |
| ME1007 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C668 | |
| IGR1 Mel-RMU cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_S994 | |
| HEM cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| HDF cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| C001 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B4K8 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay | |||
Preclinical Drug(s)
5 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | [22] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | ACY-957/DZNEP | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y641S (c.1922A>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Propidium-iodide cell cycle analysis; BrdU-PI cell cycle analysis | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | [22] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | ACY-957/GSK126 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y641N (c.1921T>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Propidium-iodide cell cycle analysis; BrdU-PI cell cycle analysis | |||
| Disease Class: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | [22] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | ACY-957/GSK126 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y641N (c.1921T>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Propidium-iodide cell cycle analysis; BrdU-PI cell cycle analysis | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | [25] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | EED226 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y646F (c.1937A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | WSU-DLCL2 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1902 |
| Toledo cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3611 | |
| SU-DHL6 cells | Peritoneal effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2206 | |
| SU-DHL4 cells | Peritoneal effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0539 | |
| OCI-LY19 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1878 | |
| Karpas422 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1325 | |
| GA10 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1222 | |
| DB cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1168 | |
| AZ_521 cells | Small intestine | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2862 | |
| In Vivo Model | Female athymic balb/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
LC-MS assay; Vi-CELL assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In contrast to SAM-competitive inhibitors, EED226 acts through a distinct allosteric mechanism via direct binding to the H3K27me3 pocket of EED. We further demonstrated that EED226 regulates histone H3K27 methylation and PRC2 target gene expression in cells. EED226 effectively induced tumor regression in a mouse xenograft model. Our work demonstrates that allosteric inhibition of PRC2 by targeting EED is a promising approach for developing effective cancer therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | [25] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | EED226 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y641N (c.1921T>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | WSU-DLCL2 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1902 |
| Toledo cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3611 | |
| SU-DHL6 cells | Peritoneal effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2206 | |
| SU-DHL4 cells | Peritoneal effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0539 | |
| OCI-LY19 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1878 | |
| Karpas422 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1325 | |
| GA10 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1222 | |
| DB cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1168 | |
| AZ_521 cells | Small intestine | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2862 | |
| In Vivo Model | Female athymic balb/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
LC-MS assay; Vi-CELL assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In contrast to SAM-competitive inhibitors, EED226 acts through a distinct allosteric mechanism via direct binding to the H3K27me3 pocket of EED. We further demonstrated that EED226 regulates histone H3K27 methylation and PRC2 target gene expression in cells. EED226 effectively induced tumor regression in a mouse xenograft model. Our work demonstrates that allosteric inhibition of PRC2 by targeting EED is a promising approach for developing effective cancer therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | [25] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | EED226 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y646N (c.1936T>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | WSU-DLCL2 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1902 |
| Toledo cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3611 | |
| SU-DHL6 cells | Peritoneal effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2206 | |
| SU-DHL4 cells | Peritoneal effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0539 | |
| OCI-LY19 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1878 | |
| Karpas422 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1325 | |
| GA10 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1222 | |
| DB cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1168 | |
| AZ_521 cells | Small intestine | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2862 | |
| In Vivo Model | Female athymic balb/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
LC-MS assay; Vi-CELL assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In contrast to SAM-competitive inhibitors, EED226 acts through a distinct allosteric mechanism via direct binding to the H3K27me3 pocket of EED. We further demonstrated that EED226 regulates histone H3K27 methylation and PRC2 target gene expression in cells. EED226 effectively induced tumor regression in a mouse xenograft model. Our work demonstrates that allosteric inhibition of PRC2 by targeting EED is a promising approach for developing effective cancer therapy. | |||
| Disease Class: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | [25] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | EED226 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y646S (c.1937A>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | WSU-DLCL2 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1902 |
| Toledo cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3611 | |
| SU-DHL6 cells | Peritoneal effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2206 | |
| SU-DHL4 cells | Peritoneal effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0539 | |
| OCI-LY19 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1878 | |
| Karpas422 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1325 | |
| GA10 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1222 | |
| DB cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1168 | |
| AZ_521 cells | Small intestine | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2862 | |
| In Vivo Model | Female athymic balb/c nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
LC-MS assay; Vi-CELL assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In contrast to SAM-competitive inhibitors, EED226 acts through a distinct allosteric mechanism via direct binding to the H3K27me3 pocket of EED. We further demonstrated that EED226 regulates histone H3K27 methylation and PRC2 target gene expression in cells. EED226 effectively induced tumor regression in a mouse xenograft model. Our work demonstrates that allosteric inhibition of PRC2 by targeting EED is a promising approach for developing effective cancer therapy. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90- 2A85] | [21] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90- 2A85] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | EZH2 inhibitors | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y641F (c.1922A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | CRL-2959 cells | Peritoneal effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2206 |
| CRL-2632 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3326 | |
| CRL-2631 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3611 | |
| CRL-2630 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3302 | |
| CRL-2261 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1660 | |
| ACC-576 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1889 | |
| ACC-575 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1902 | |
| ACC-528 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1878 | |
| ACC-32 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1325 | |
| In Vivo Model | Sprague-Dawley rat model | Rattus norvegicus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ChIP-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell Titer Glo assay; Tumor volume measurement assay; Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Disease Class: Lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90- 2A85] | [26] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90- 2A85] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | EZH2 inhibitors | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A677G (c.2030C>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | 293 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Determination of inhibitor IC50 values in the PMT panel assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.A677G (c.2030C>G) in gene EZH2 cause the sensitivity of EZH2 inhibitors by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | [27] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | UNC1999 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y641N (c.1921T>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF10A cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0598 |
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Y641N (c.1921T>A) in gene EZH2 cause the sensitivity of UNC1999 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
Investigative Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | [22] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | 3-Deazaneplanocin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y641N (c.1921T>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Propidium-iodide cell cycle analysis; BrdU-PI cell cycle analysis | |||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: cancer [ICD-11: 2D4Z] | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | cancer [ICD-11: 2D4Z] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | 3-Deazaneplanocin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | B16 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_F936 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The?protein expression?of the?enhancer of zeste homolog 2?(EZH2),?histone methyltransferase?and its target?histone H3?trimethylation at lysine 27 (H3K27Me3) level increased under hypoxia. The induction of H3K27Me3 under hypoxia was suppressed by EZH2?siRNA?and 3-deazaneplanocin A (DZNep), an EZH2 inhibitor. Furthermore, both EZH2?siRNA?and DZNep significantly reduced the?cell viability?after SN-38 treatment and improved the chemoresistance to SN-38 under hypoxia. These results indicated that the chemoresistance to SN-38 under hypoxia would arise from epigenetic mechanism, H3K27Me3 elevation due to EZH2 induction. In conclusion, a?histone methyltransferase?EZH2 inhibitor, DZNep was capable of tackling acquired chemoresistance via the suppression of?histone methylation?induced under hypoxic?tumor microenvironment. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90- 2A85] | [26] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90- 2A85] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | EPZ005687 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y641F (c.1922A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | 293 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Determination of inhibitor IC50 values in the PMT panel assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Y641F (c.1922A>T) in gene EZH2 cause the sensitivity of EPZ005687 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [28] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Platinum | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | A2780_CR5 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| A2780p cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 | |
| KURAMOCHI cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1345 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblot assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Caspase 3/7 cleavage assays; Aldefluor assay; MTS assay; Flow cytometric analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Blocking the EZH2-interactiing domain of HOTAIR and disrupting the HOTAIR-EZH2 interaction resensitizes cancer cells to clinically relevant cytotoxic chemotherapies, reduces cell invasion and decreases NF-kB transcriptional activity and IL-6 and MMP-9 expression in vivo. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Bone marrow | |
| The Specified Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.84E-11; Fold-change: -4.39E-01; Z-score: -6.93E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Tonsil tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Lymphoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.73E-01; Fold-change: 2.56E-01; Z-score: 8.10E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.56E-02; Fold-change: 2.42E+00; Z-score: 1.87E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 5.88E-03; Fold-change: 8.98E-01; Z-score: 1.14E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
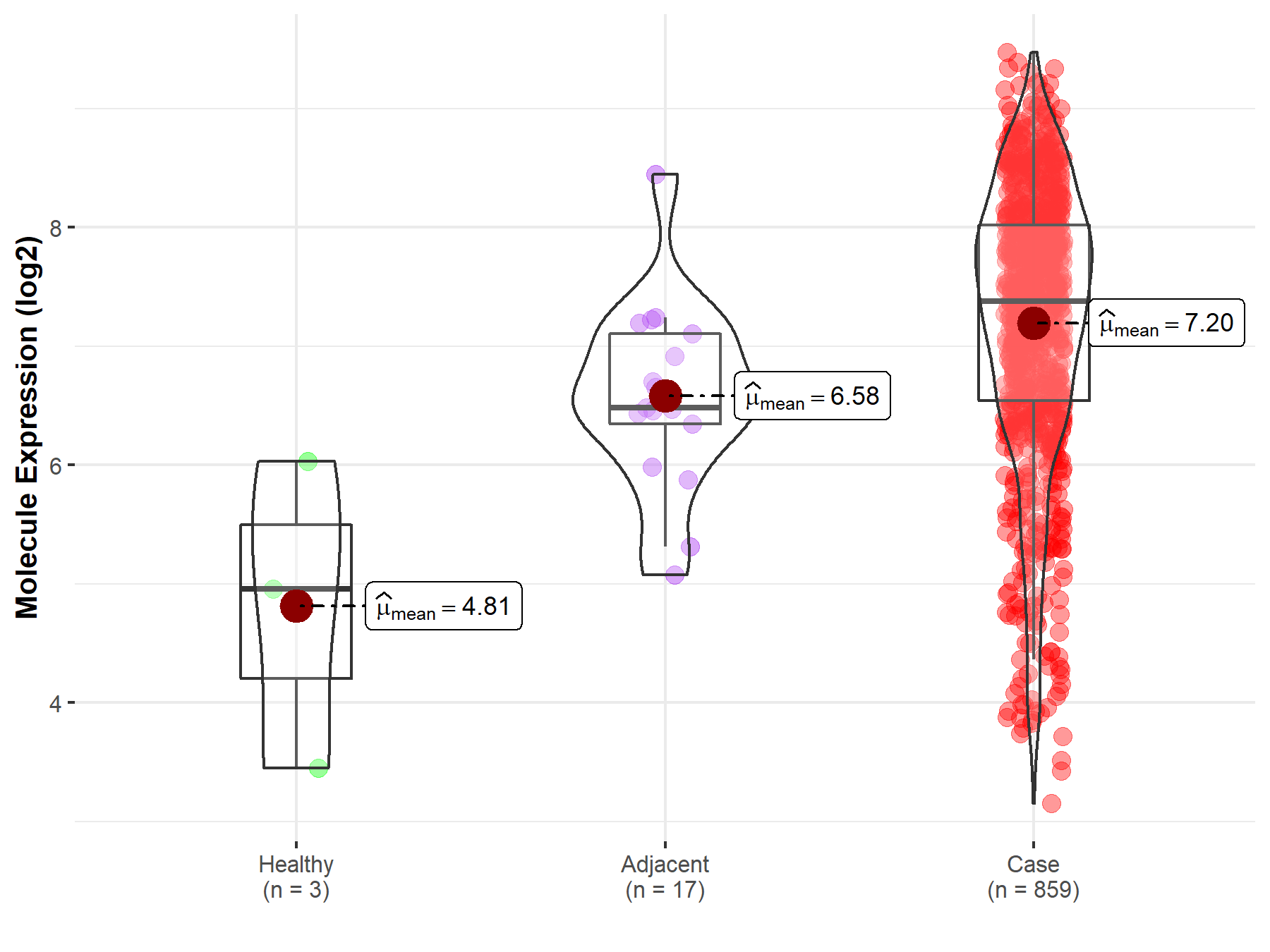
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.04E-20; Fold-change: 2.39E+00; Z-score: 2.83E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.06E-61; Fold-change: 1.53E+00; Z-score: 2.00E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 3.20E-04; Fold-change: 2.42E+00; Z-score: 7.21E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
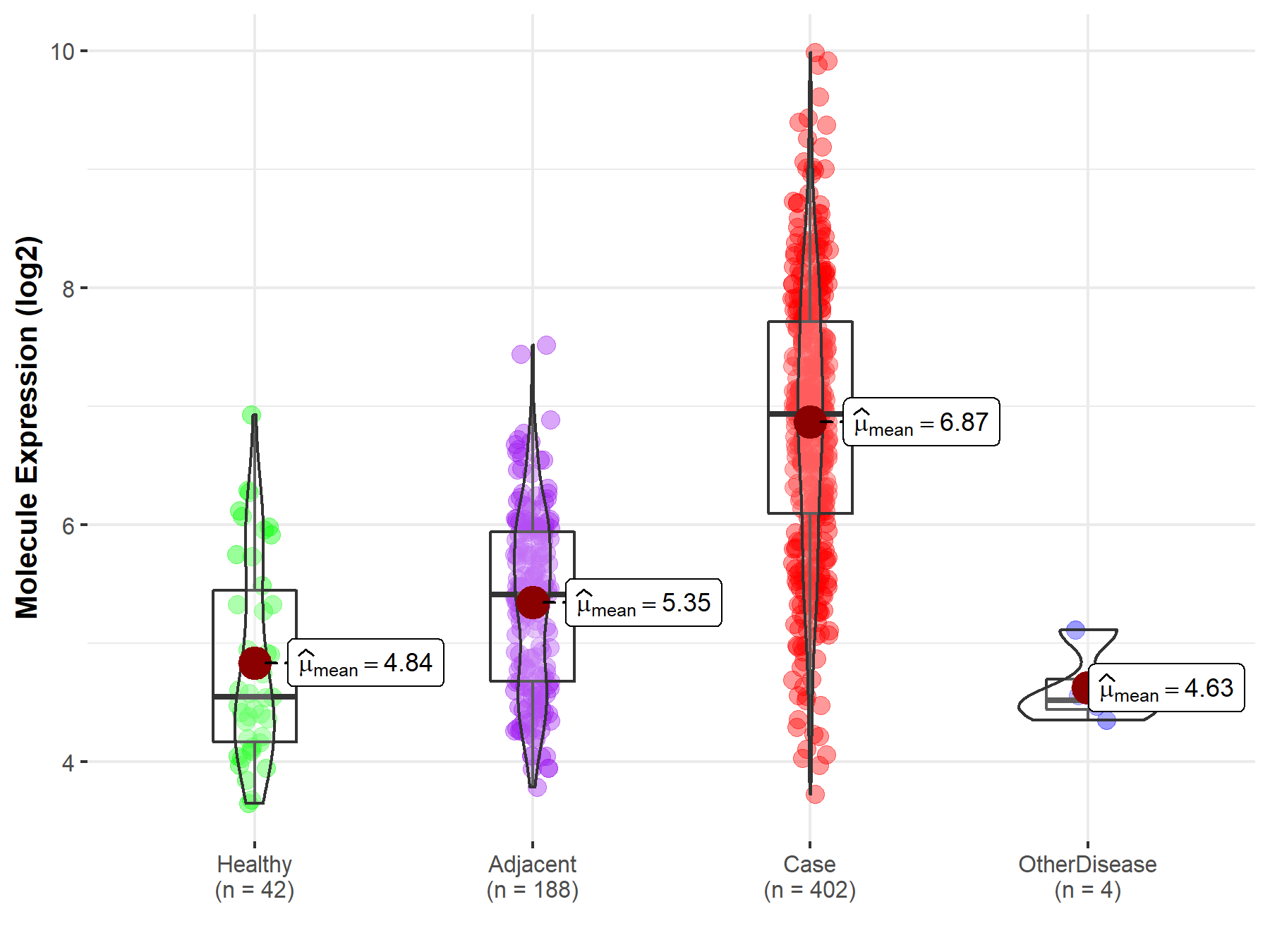
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Skin | |
| The Specified Disease | Melanoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.38E-01; Fold-change: -5.97E-01; Z-score: -3.99E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
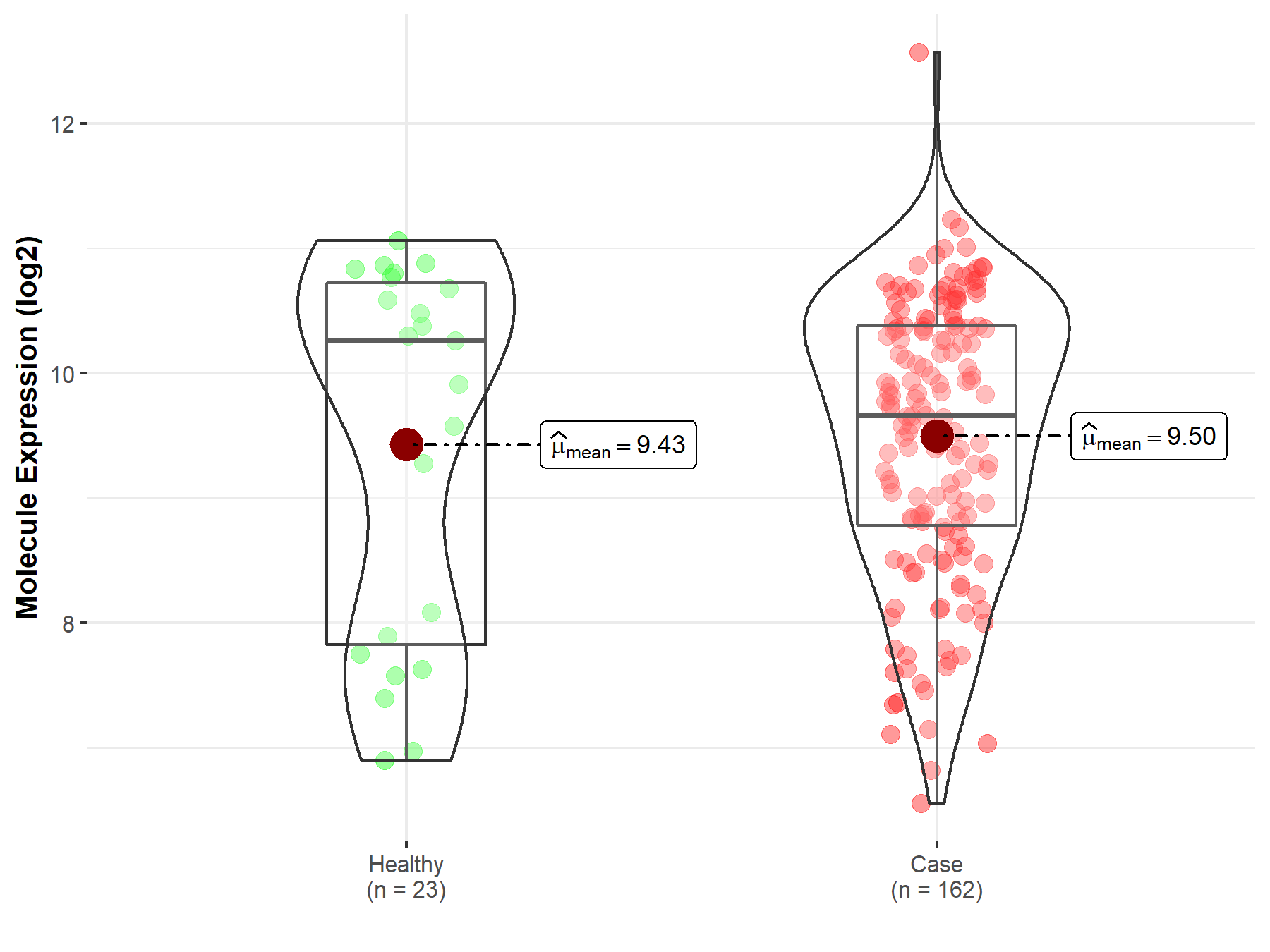
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.60E-184; Fold-change: 3.09E+00; Z-score: 3.63E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 7.99E-16; Fold-change: 2.13E+00; Z-score: 1.85E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.10E-06; Fold-change: 2.59E+00; Z-score: 3.86E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 6.57E-02; Fold-change: 6.98E-01; Z-score: 6.65E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
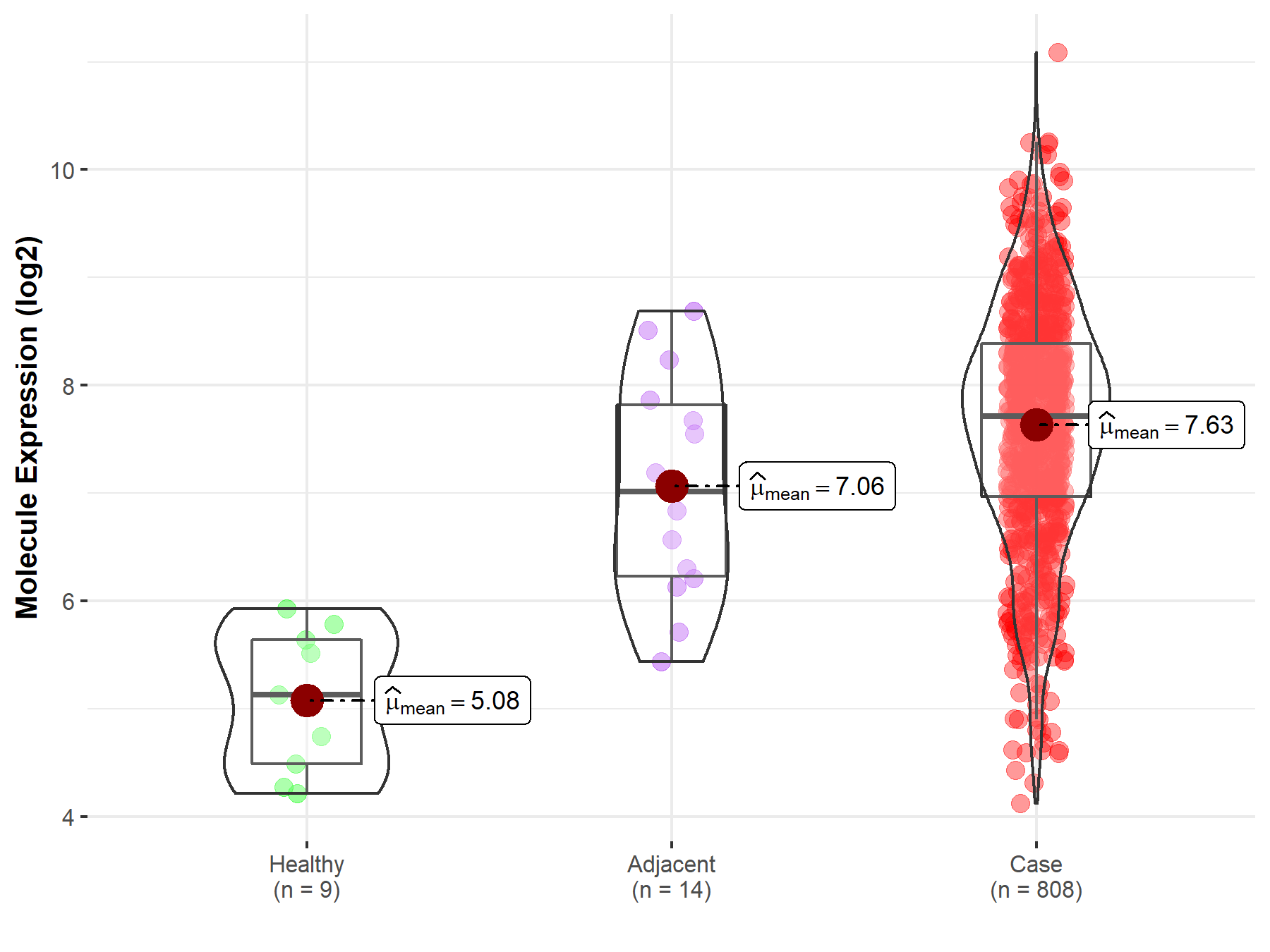
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

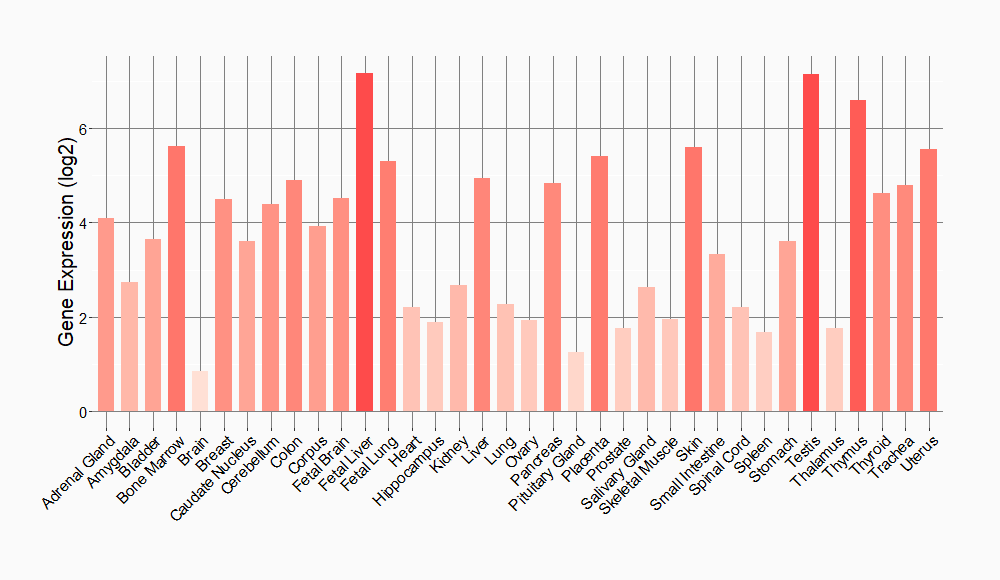
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
