Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01618) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
GSK126
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
GSK126; 1346574-57-9; GSK-126; GSK 126; GSK2816126; (S)-1-(sec-Butyl)-N-((4,6-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)methyl)-3-methyl-6-(6-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-3-yl)-1H-indole-4-carboxamide; EZH2 inhibitor; UNII-W4OGW9QZ97; GSK-2816126; W4OGW9QZ97; CHEMBL3287735; 1-[(2S)-butan-2-yl]-N-[(4,6-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)methyl]-3-methyl-6-[6-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-3-yl]-1H-indole-4-carboxamide; 1-[(2S)-butan-2-yl]-N-[(4,6-dimethyl-2-oxo-1H-pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-3-methyl-6-(6-piperazin-1-ylpyridin-3-yl)indole-4-carboxamide; A9G; N-((1,2-Dihydro-4,6-dimethyl-2-oxo-3-pyridinyl)methyl)-3-methyl-1-((1S)-1-methylpropyl)-6-(6-(1-piperazinyl)-3-pyridinyl)-1H-indole-4-carboxamide; N-[(1,2-Dihydro-4,6-dimethyl-2-oxo-3-pyridinyl)methyl]-3-methyl-1-[(1S)-1-methylpropyl]-6-[6-(1-piperazinyl)-3-pyridinyl]-1H-indole-4-carboxamide; GSK126 HCl; GSK-126 HCl; MLS006010251; GTPL7012; SCHEMBL12180401; AOB1764; EX-A499; SYN5012; CHEBI:124921; BCP06129; BDBM50017293; GSK-2816126A; NSC780041; NSC789702; s7061; ZINC72318146; AKOS027322309; CCG-269895; CS-1401; NSC-780041; NSC-789702; QC-9703; NCGC00347286-01; 1H-Indole-4-carboxamide, N-((1,2-dihydro-4,6-dimethyl-2-oxo-3-pyridinyl)methyl)-3-methyl-1-((1S)-1-methylpropyl)-6-(6-(1-piperazinyl)-3-pyridinyl)-; AS-16379; HY-13470; SMR004701327; X5824; Q27077865; EZH2 inhibitor;GSK-126;GSK 126;GSK2816126A;GSK-2816126A;GSK 2816126A; (S)-1-sec-butyl-N-((4,6-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)methyl)-3-methyl-6-(6-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-3-yl)-1H-indole-4-carboxamide; N-[(4,6-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3-pyridinyl)methyl]-3-methyl-1-[(1S)-1-methylpropyl]-6-[6-(1-piperazinyl)-3-pyridinyl]-1H-indole-4-carboxamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 4 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
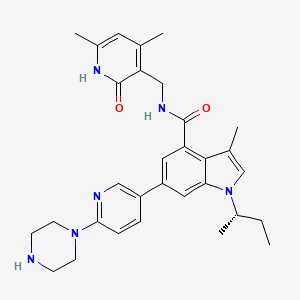
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[1]
[2]
|
||||
| Target | ALK tyrosine kinase receptor (ALK) | ALK_HUMAN | [3] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
7
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC[C@H](C)N1C=C(C2=C(C=C(C=C21)C3=CN=C(C=C3)N4CCNCC4)C(=O)NCC5=C(C=C(NC5=O)C)C)C
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C31H38N6O2/c1-6-22(5)37-18-20(3)29-25(30(38)34-17-26-19(2)13-21(4)35-31(26)39)14-24(15-27(29)37)23-7-8-28(33-16-23)36-11-9-32-10-12-36/h7-8,13-16,18,22,32H,6,9-12,17H2,1-5H3,(H,34,38)(H,35,39)/t22-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
FKSFKBQGSFSOSM-QFIPXVFZSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y111D (c.331T>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HEK293 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0045 |
| Pfeiffer cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3326 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y641S (c.1922A>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Propidium-iodide cell cycle analysis; BrdU-PI cell cycle analysis | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2) | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y641S (c.1922A>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Skin sample | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; BCA assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | EZH2 activation by mutations, gene amplification and increased transcription occurred in about 20% of the cohort. These alterations were associated with significant hypermethylation of DNA and significant downregulation of 11% of transcripts in patient RNASeq data. | |||
| Key Molecule: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2) | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y641N (c.1921T>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Skin sample | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; BCA assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | EZH2 activation by mutations, gene amplification and increased transcription occurred in about 20% of the cohort. These alterations were associated with significant hypermethylation of DNA and significant downregulation of 11% of transcripts in patient RNASeq data. | |||
| Key Molecule: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2) | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y641H (c.1921T>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Skin sample | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; BCA assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | EZH2 activation by mutations, gene amplification and increased transcription occurred in about 20% of the cohort. These alterations were associated with significant hypermethylation of DNA and significant downregulation of 11% of transcripts in patient RNASeq data. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2) | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y646N (c.1936T>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SKMEL-28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 |
| MM386 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2607 | |
| MM200 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C836 | |
| MEL-RM cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D548 | |
| MEL-JD cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_BS80 | |
| ME4405 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C680 | |
| ME1007 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C668 | |
| IGR1 Mel-RMU cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_S994 | |
| HEM cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| HDF cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| C001 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B4K8 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay | |||
| Key Molecule: Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 (EZH2) | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y646N (c.1936T>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SKMEL-28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 |
| MM386 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2607 | |
| MM200 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C836 | |
| MEL-RM cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D548 | |
| MEL-JD cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_BS80 | |
| ME4405 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C680 | |
| ME1007 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C668 | |
| IGR1 Mel-RMU cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_S994 | |
| HEM cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| HDF cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| C001 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B4K8 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
