Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00279)
| Name |
G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 (CCND1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
B-cell lymphoma 1 protein; BCL-1; BCL-1 oncogene; PRAD1 oncogene; BCL1; PRAD1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
CCND1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr11:69641156-69654474[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MEHQLLCCEVETIRRAYPDANLLNDRVLRAMLKAEETCAPSVSYFKCVQKEVLPSMRKIV
ATWMLEVCEEQKCEEEVFPLAMNYLDRFLSLEPVKKSRLQLLGATCMFVASKMKETIPLT AEKLCIYTDNSIRPEELLQMELLLVNKLKWNLAAMTPHDFIEHFLSKMPEAEENKQIIRK HAQTFVALCATDVKFISNPPSMVAAGSVVAAVQGLNLRSPNNFLSYYRLTRFLSRVIKCD PDCLRACQEQIEALLESSLRQAQQNMDPKAAEEEEEEEEEVDLACTPTDVRDVDI Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Regulatory component of the cyclin D1-CDK4 (DC) complex that phosphorylates and inhibits members of the retinoblastoma (RB) protein family including RB1 and regulates the cell-cycle during G(1)/S transition. Phosphorylation of RB1 allows dissociation of the transcription factor E2F from the RB/E2F complex and the subsequent transcription of E2F target genes which are responsible for the progression through the G(1) phase. Hypophosphorylates RB1 in early G(1) phase. Cyclin D-CDK4 complexes are major integrators of various mitogenenic and antimitogenic signals. Also substrate for SMAD3, phosphorylating SMAD3 in a cell-cycle-dependent manner and repressing its transcriptional activity. Component of the ternary complex, cyclin D1/CDK4/CDKN1B, required for nuclear translocation and activity of the cyclin D-CDK4 complex. Exhibits transcriptional corepressor activity with INSM1 on the NEUROD1 and INS promoters in a cell cycle-independent manner.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
10 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: ER positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.6] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | ER positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.6] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Arzoxifene | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.07E-09 Fold-change: 5.12E-02 Z-score: 6.18E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SW620 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0547 |
| MDA PCa 2b cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4748 | |
| Prolactinoma samples | N.A. | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Casy model TT cell counter | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of a regular component of the ERalpha transcription factor complex, cyclin D1, which occurs in approximately 40% of breast cancer patients, renders cells resistant to the new promising antiestrogen, arzoxifene. Overexpression of cyclin D1 alters the conformation of ERalpha in the presence of arzoxifene. In this altered conformation, ERalpha still recruits RNA polymerase II to an estrogen response element-containing promoter, inducing transcription of an ERalpha-dependent reporter gene and of endogenous pS2, and promoting arzoxifene-stimulated growth of MCF-7 cells. Arzoxifene is then converted from an ERalpha antagonist into an agonist. This can be explained by a stabilization of the ERalpha/steroid receptor coactivator-1 complex in the presence of arzoxifene, only when cyclin D1 is overexpressed. These results indicate that subtle changes in the conformation of ERalpha upon binding to antiestrogen are at the basis of resistance to antiestrogens. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovarian tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.12E-03 Fold-change: 3.37E-01 Z-score: 3.94E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 | |
| OVCAR3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0465 | |
| OVCAR8 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1629 | |
| OVCAR4 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1627 | |
| CH1 cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D177 | |
| 41M cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4993 | |
| PXN94 cells | Pelvis | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4994 | |
| HX62 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4995 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ATP cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | CCND1 may induce cisplatin resistance both through cell cycle control and inhibition of cellular apoptosis pathways, which have been previously observed37 and supported by our CCND1 knockdown study. The role of CCND1 in cell cycle control is well documented. CCND1 accumulates in cells at middle and late G1 phase and stimulate G1 progression to S phase. The proportion of parental cells in G1/0 correlated with the cisplatin sensitivity, with 833K cells having the highest G1/0 population cells and lowest EC50 value and GCT27 the lowest G1/0 population but highest EC50 score. | |||
| Disease Class: Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.22E-91 Fold-change: 2.53E-01 Z-score: 2.19E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | U251 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0021 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Cisplatin treatment leads to Let-7b suppression, which in turn up-regulates cyclin D1 expression, resulting in resistance to cisplatin. | |||
| Disease Class: Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | BCL2/cyclin D1 signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MG63 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0426 |
| SAOS-2 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0548 | |
| HOS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0312 | |
| 143B cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2270 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The miR-34c inhibitor restored the BCL-2 and cyclin D1 levels in MG63 and HOS cell line, which implicated that NEAT1 inhibited the tumor suppressor miR-34c and up-regulated cell survival signals for the development of OS. | |||
| Disease Class: Epithelial ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Epithelial ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2B5D.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| Spheroid formation | Activation | hsa04140 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 | |
| ES2 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_AX39 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of let-7e by transfection of agomir could resensitize A2780/CP and reduce the expression of cisplatin-resistant-related proteins enhancer of zeste 2 (EZH2) and cyclin D1 (CCND1), whereas let-7e inhibitors increased resistance to cisplatin in parental A2780 cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | DU-145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 |
| LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 | |
| PC3 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 | |
| 22RV1 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1045 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ATP cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | CCND1 may induce cisplatin resistance both through cell cycle control and inhibition of cellular apoptosis pathways, which have been previously observed37 and supported by our CCND1 knockdown study. The role of CCND1 in cell cycle control is well documented. CCND1 accumulates in cells at middle and late G1 phase and stimulate G1 progression to S phase. The proportion of parental cells in G1/0 correlated with the cisplatin sensitivity, with 833K cells having the highest G1/0 population cells and lowest EC50 value and GCT27 the lowest G1/0 population but highest EC50 score. | |||
| Disease Class: Testicular germ cell tumor [ICD-11: 2C80.2] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Testicular germ cell tumor [ICD-11: 2C80.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Susa cells | Thyroid gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_L280 |
| GCT27 cells | Thyroid gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A344 | |
| 833K cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2292 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ATP cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | CCND1 may induce cisplatin resistance both through cell cycle control and inhibition of cellular apoptosis pathways, which have been previously observed37 and supported by our CCND1 knockdown study. The role of CCND1 in cell cycle control is well documented. CCND1 accumulates in cells at middle and late G1 phase and stimulate G1 progression to S phase. The proportion of parental cells in G1/0 correlated with the cisplatin sensitivity, with 833K cells having the highest G1/0 population cells and lowest EC50 value and GCT27 the lowest G1/0 population but highest EC50 score. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Urothelial carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C92.0] | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Urothelial carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C92.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NTUB1 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_RW29 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometer | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR193b Mediates CEBPD-Induced Cisplatin Sensitization Through Targeting ETS1 and Cyclin D1 in Human Urothelial Carcinoma Cells. miR193b-3p, a known tumor suppressor, down-regulated proto-oncogenes Cyclin D1, and ETS1 expression and led to cell cycle arrest, cell invasion, and migration inhibition. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| MAPK/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| T24 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0554 | |
| HCT8 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2478 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-634 is an important player in cisplatin-resistance. First of all, miR-634 was the only miR miR-634 overexpression in ovarian cancer cell lines and patient samples negatively regulates important cell-cycle genes (CCND1) and Ras-MAPk pathway components (GRB2, ERk2, RSk1 and RSk2). Inhibition of the Ras-MAPk pathway resulted in increased sensitivity to cisplatin, suggesting that the miR-634-mediated repression of this pathway is responsible for the effect of miR-634 on cisplatin resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77.0] | [9] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | Caski cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1100 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR155 reversed EGF-induced EMT by downregulating SMAD2 expression levels, and restraining cell growth by inhibiting CCND1 expression, increased the Chemo-sensitivity of Caski Cells to DDP. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.49E-14 Fold-change: -8.39E-02 Z-score: -7.82E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| NCl-H596 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1571 | |
| NCI-H1734 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1491 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-16 was also significantly downregulated in paclitaxel resistant lung cancer cells. anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 was directly targeted miR-16 in paclitaxel resistant lung cancer cells. the combined overexpression of miR-16 and miR-17 and subsequent paclitaxel treatment greatly sensitized paclitaxel resistant lung cancer cells to paclitaxel by inducing apoptosis via caspase-3 mediated pathway. Combined overexpression of miR-16 and miR-17 greatly reduced Beclin-1 and Bcl-2 expressions respectively. though miR-17 and miR-16 had no common target, both miR-16 and miR-17 jointly played roles in the development of paclitaxel resistance in lung cancer. miR-17 overexpression reduced cytoprotective autophagy by targeting Beclin-1, whereas overexpression of miR-16 potentiated paclitaxel induced apoptotic cell death by inhibiting anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Carboplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| MAPK/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| T24 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0554 | |
| HCT8 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2478 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-634 is an important player in cisplatin-resistance. First of all, miR-634 was the only miR miR-634 overexpression in ovarian cancer cell lines and patient samples negatively regulates important cell-cycle genes (CCND1) and Ras-MAPk pathway components (GRB2, ERk2, RSk1 and RSk2). Inhibition of the Ras-MAPk pathway resulted in increased sensitivity to cisplatin, suggesting that the miR-634-mediated repression of this pathway is responsible for the effect of miR-634 on cisplatin resistance. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| MAPK/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| T24 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0554 | |
| HCT8 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2478 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-634 is an important player in cisplatin-resistance. First of all, miR-634 was the only miR miR-634 overexpression in ovarian cancer cell lines and patient samples negatively regulates important cell-cycle genes (CCND1) and Ras-MAPk pathway components (GRB2, ERk2, RSk1 and RSk2). Inhibition of the Ras-MAPk pathway resulted in increased sensitivity to cisplatin, suggesting that the miR-634-mediated repression of this pathway is responsible for the effect of miR-634 on cisplatin resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [10] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Tumorigenesis | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MkN-45 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0434 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Down-regulation of miR-27a could also confer sensitivity of drugs on gastric cancer cells, and might increase accumulation and decrease releasing amount of adriamycin in gastric cancer cells. Down-regulation of miR-27a could significantly decrease the expression of P-glycoprotein and the transcriptional activity of cyclin D1, and up-regulate the expression of p21. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [11] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | BGC-823 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3360 |
| MGC-803 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5334 | |
| SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 | |
| MkN-45 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0434 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The restored miR-623 expression could inhibit the proliferation of GC cells and enhance their chemosensitivity to 5-FU via the cell apoptosis pathway and the recovered CCND1 expression counteracted the effects of miR-623 on GC cell proliferation, chemosensitivity, and 5-FU-induced apoptosis. | |||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [10] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Tumorigenesis | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MkN-45 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0434 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Down-regulation of miR-27a could also confer sensitivity of drugs on gastric cancer cells, and might increase accumulation and decrease releasing amount of adriamycin in gastric cancer cells. Down-regulation of miR-27a could significantly decrease the expression of P-glycoprotein and the transcriptional activity of cyclin D1, and up-regulate the expression of p21. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Malignant pleural mesothelioma [ICD-11: 2C26.0] | [12] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Malignant pleural mesothelioma [ICD-11: 2C26.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MET-5A cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3749 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Growth inhibition caused by miR-16 correlated with downregulation of target genes including Bcl-2 and CCND1, and miR-16 re-expression sensitised MPM cells to pemetrexed and gemcitabine. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [13] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Palbociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Copy number gain | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Malignant pleural mesothelioma [ICD-11: 2C26.0] | [12] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Malignant pleural mesothelioma [ICD-11: 2C26.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Pemetrexed | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MET-5A cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3749 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Growth inhibition caused by miR-16 correlated with downregulation of target genes including Bcl-2 and CCND1, and miR-16 re-expression sensitised MPM cells to pemetrexed and gemcitabine. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [10] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Vincristine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MkN-45 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0434 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Down-regulation of miR-27a could also confer sensitivity of drugs on gastric cancer cells, and might increase accumulation and decrease releasing amount of adriamycin in gastric cancer cells. Down-regulation of miR-27a could significantly decrease the expression of P-glycoprotein and the transcriptional activity of cyclin D1, and up-regulate the expression of p21. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.22E-91; Fold-change: 1.34E+00; Z-score: 1.94E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.38E-01; Fold-change: 1.77E+00; Z-score: 1.18E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
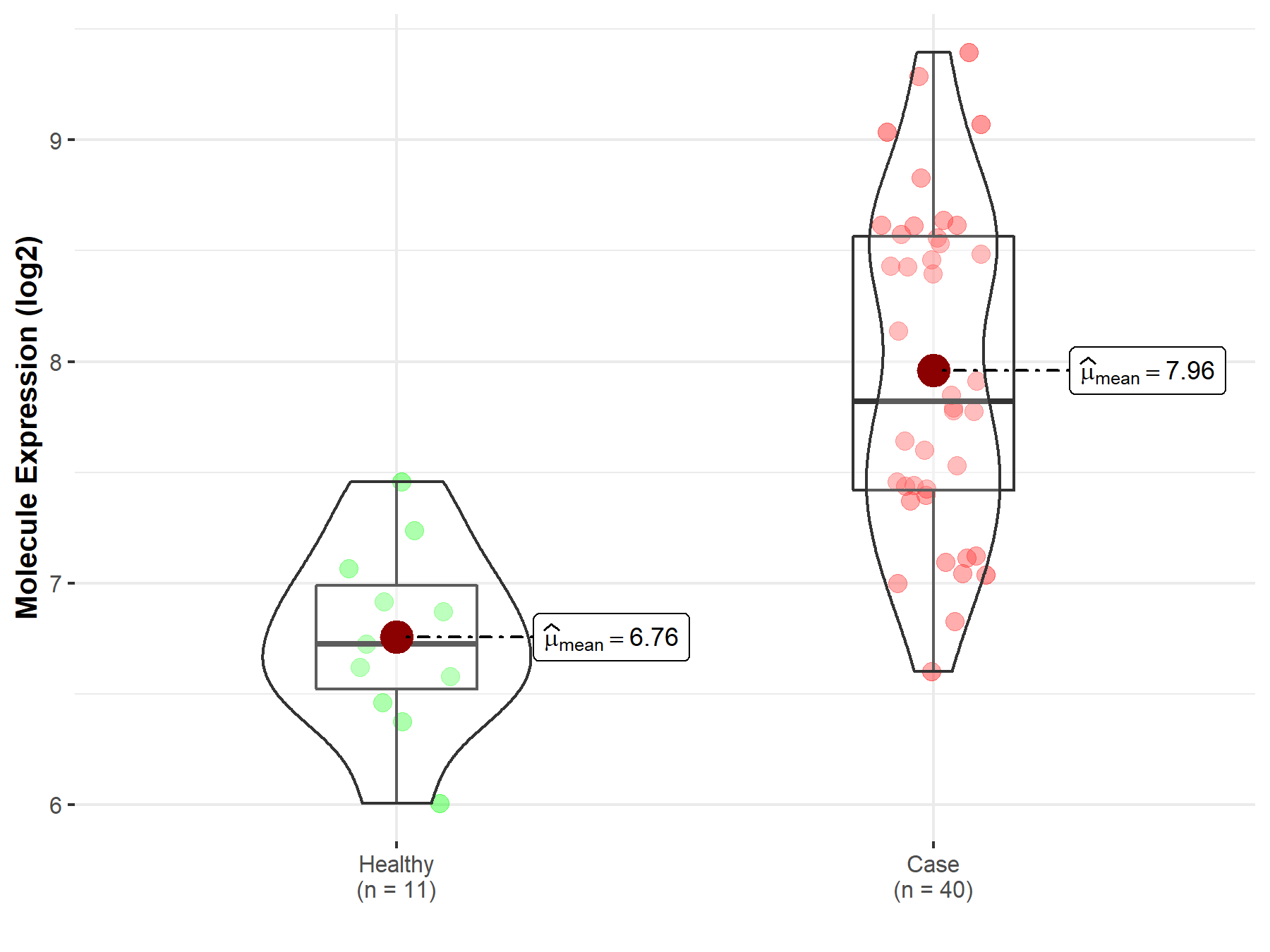
| The Studied Tissue | White matter | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.59E-08; Fold-change: 1.09E+00; Z-score: 2.65E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Neuroectodermal tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.71E-09; Fold-change: 1.79E+00; Z-score: 4.48E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.22E-01; Fold-change: 6.53E-01; Z-score: 7.64E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.89E-01; Fold-change: 2.29E-02; Z-score: 2.81E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
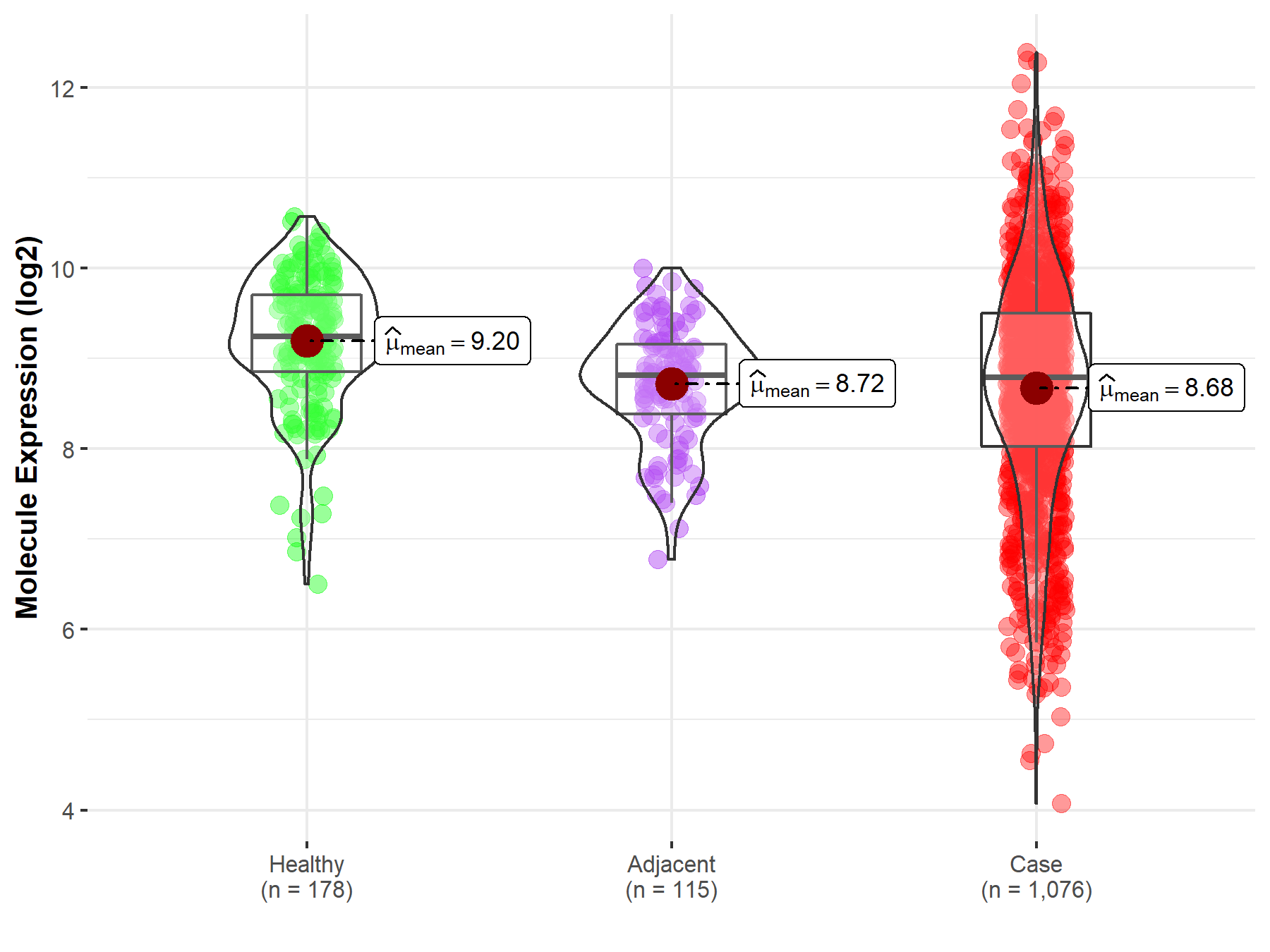
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.49E-14; Fold-change: -4.50E-01; Z-score: -6.17E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 4.98E-01; Fold-change: -1.86E-02; Z-score: -2.89E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.07E-09; Fold-change: 3.31E-01; Z-score: 5.07E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 9.27E-08; Fold-change: 6.53E-01; Z-score: 9.02E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.12E-03; Fold-change: 2.41E+00; Z-score: 1.85E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 8.57E-01; Fold-change: 3.80E-01; Z-score: 2.06E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
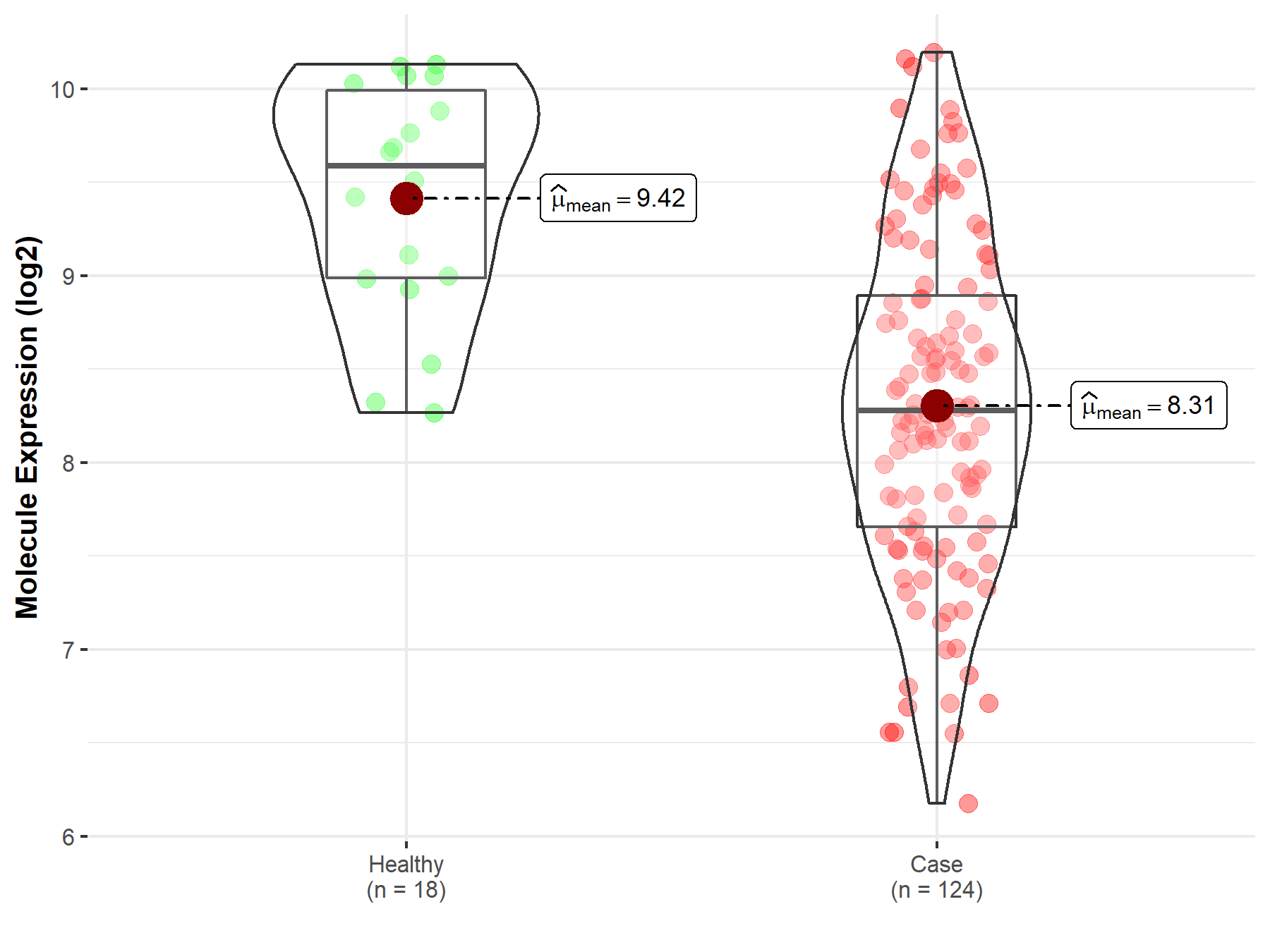
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Cervix uteri | |
| The Specified Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.80E-07; Fold-change: -1.31E+00; Z-score: -2.08E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
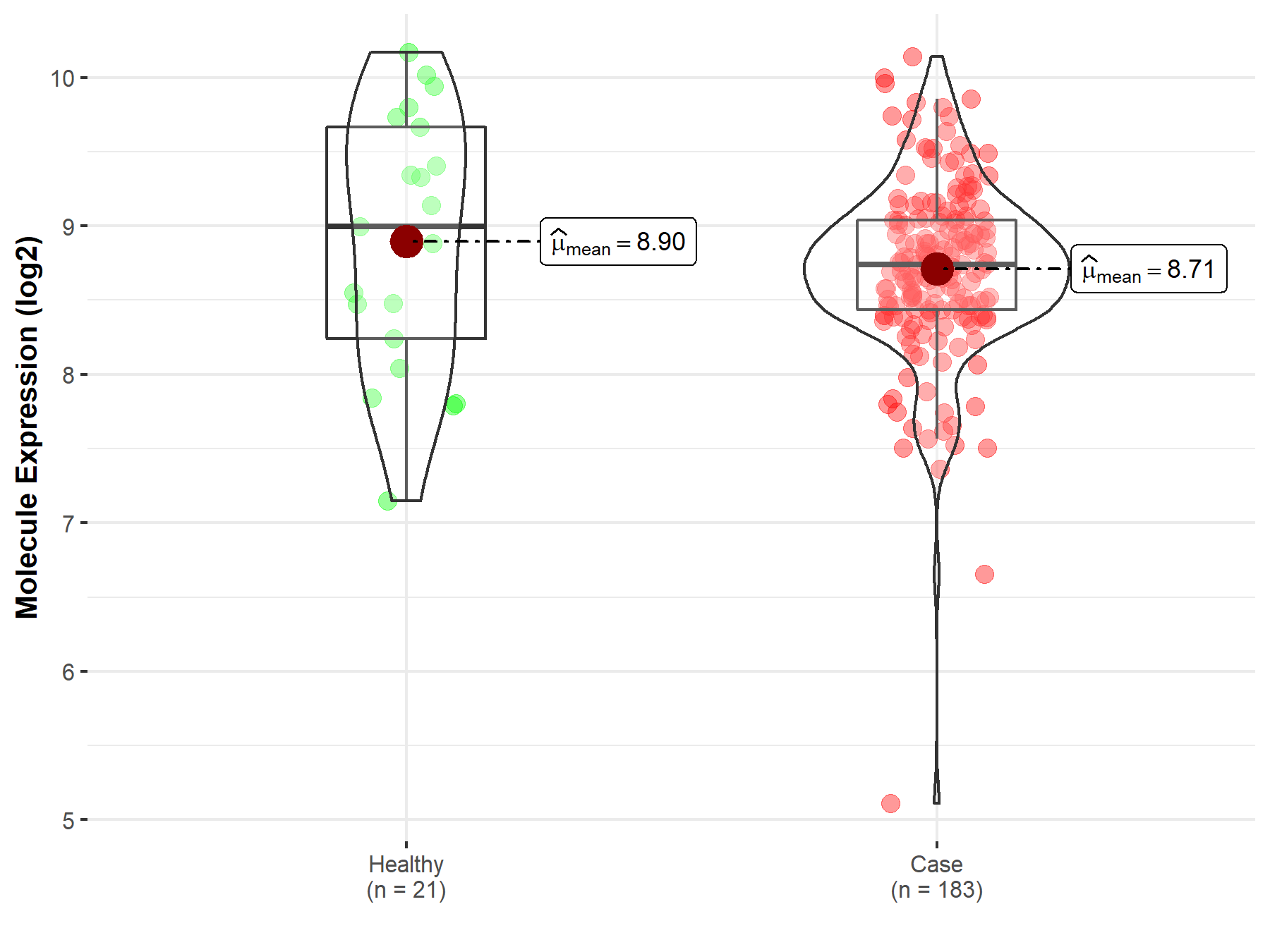
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.57E-01; Fold-change: -2.58E-01; Z-score: -2.98E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Urothelium | |
| The Specified Disease | Ureteral cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.22E-01; Fold-change: -1.29E-01; Z-score: -2.68E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
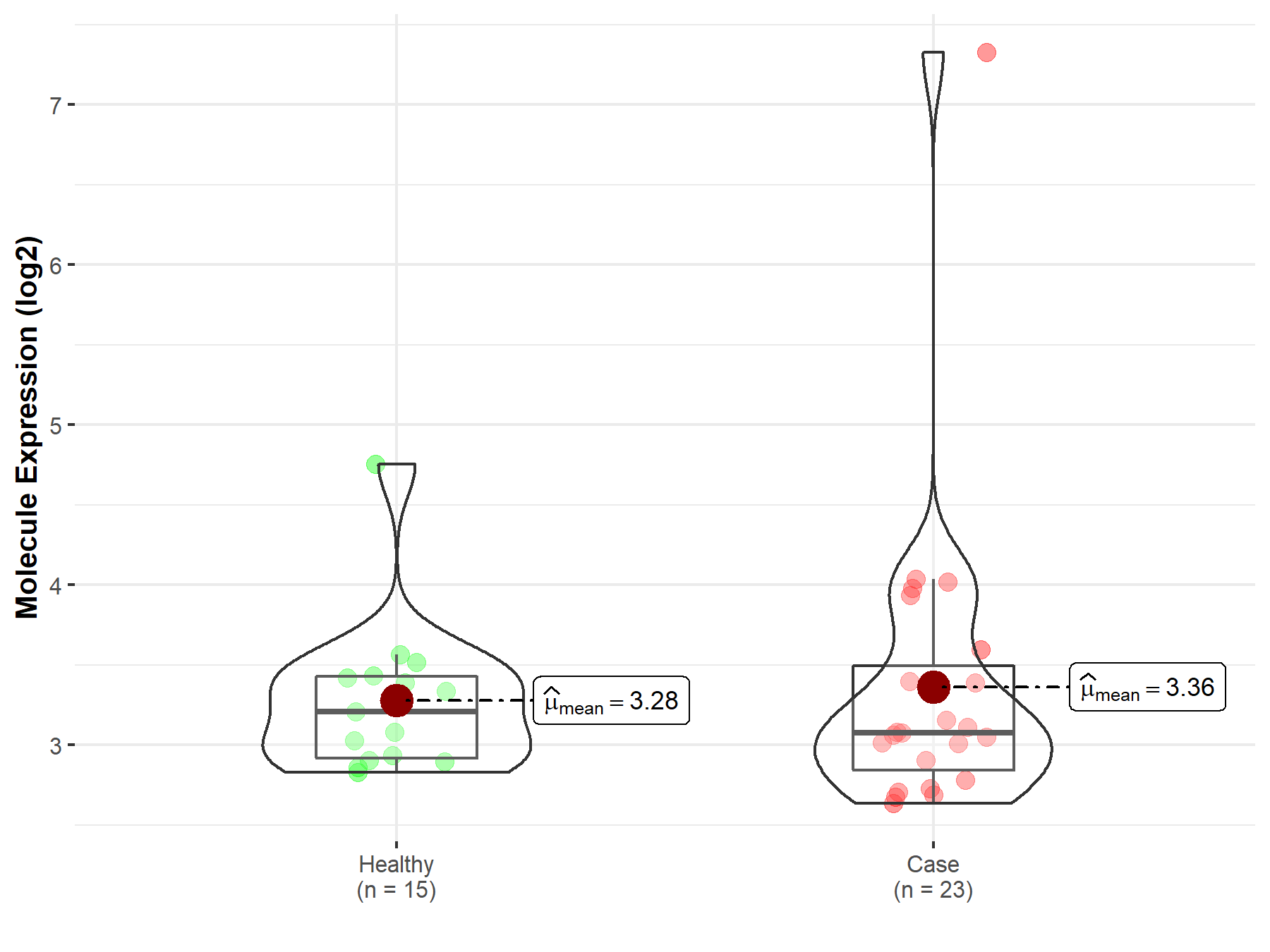
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals


|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
