Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01014) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Arzoxifene
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Arzoxifene; 182133-25-1; LY 353381; UNII-E569WG6E60; 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-[4-(2-piperidin-1-ylethoxy)phenoxy]-1-benzothiophen-6-ol; LY353381; E569WG6E60; Benzo[b]thiophene-6-ol, 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-[4-[2-(1-piperidinyl)ethoxy]phenoxy]-; Arzoxifene [INN]; Benzo(b)thiophene-6-ol, 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-(4-(2-(1-piperidinyl)ethoxy)phenoxy)-; LY-353381; SCHEMBL285277; CHEMBL226267; BDBM19442; DTXSID10171255; ZINC1544683; DB06249; SB19713; 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-(4-(2-(piperidin-1-yl)ethoxy)phenoxy)benzo[b]thiophen-6-ol; DA-09024; HY-13556; CS-0007165; FT-0751607; Q4802769; 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-{4-[2-(piperidin-1-yl)ethoxy]phenoxy}-1-benzothiophen-6-ol; 2-(p-Methoxyphenyl)-3-(p-(2-piperidinoethoxy)phenoxy)benzo(b)thiophene-6-ol
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
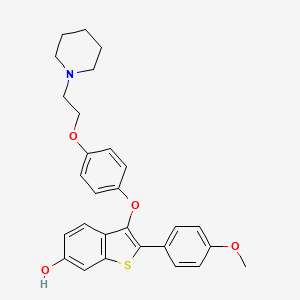
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Estrogen receptor (ESR) | ESR1_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Estrogen receptor beta (ESR2) | ESR2_HUMAN | [1] | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C28H29NO4S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
COC1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=C(C3=C(S2)C=C(C=C3)O)OC4=CC=C(C=C4)OCCN5CCCCC5
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C28H29NO4S/c1-31-22-8-5-20(6-9-22)28-27(25-14-7-21(30)19-26(25)34-28)33-24-12-10-23(11-13-24)32-18-17-29-15-3-2-4-16-29/h5-14,19,30H,2-4,15-18H2,1H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
MCGDSOGUHLTADD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 (CCND1) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | ER positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.07E-09 Fold-change: 5.12E-02 Z-score: 6.18E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SW620 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0547 |
| MDA PCa 2b cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4748 | |
| Prolactinoma samples | N.A. | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Casy model TT cell counter | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of a regular component of the ERalpha transcription factor complex, cyclin D1, which occurs in approximately 40% of breast cancer patients, renders cells resistant to the new promising antiestrogen, arzoxifene. Overexpression of cyclin D1 alters the conformation of ERalpha in the presence of arzoxifene. In this altered conformation, ERalpha still recruits RNA polymerase II to an estrogen response element-containing promoter, inducing transcription of an ERalpha-dependent reporter gene and of endogenous pS2, and promoting arzoxifene-stimulated growth of MCF-7 cells. Arzoxifene is then converted from an ERalpha antagonist into an agonist. This can be explained by a stabilization of the ERalpha/steroid receptor coactivator-1 complex in the presence of arzoxifene, only when cyclin D1 is overexpressed. These results indicate that subtle changes in the conformation of ERalpha upon binding to antiestrogen are at the basis of resistance to antiestrogens. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
