Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01536) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Pictilisib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
957054-30-7; GDC-0941; PICTILISIB; Pictrelisib; GDC0941; GDC 0941; 4-(2-(1H-Indazol-4-yl)-6-((4-(methylsulfonyl)piperazin-1-yl)methyl)thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)morpholine; 2-(1H-Indazol-4-yl)-6-(4-methanesulfonylpiperazin-1-ylmethyl)-4-morpholin-4-yl-thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine; UNII-ICY00EMP8P; GDC-0941 (Pictilisib); Pictilisib (GDC-0941); ICY00EMP8P; 4-[2-(1H-indazol-4-yl)-6-[(4-methylsulfonylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]morpholine; CHEBI:65326; 957054-30-7 (free base); RG7321; 2-(1H-Indazol-4-yl)-6-(4-methanesulfonyl-piperazin-1-ylmethyl)-4-morpholin-4-yl-thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine; C23H27N7O3S2; 2-(1H-indazol-4-yl)-6-{[4-(methylsulfonyl)piperazin-1-yl]methyl}-4-(morpholin-4-yl)thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine; 2-(1h-Indazol-4-Yl)-6-{[4-(Methylsulfonyl)piperazin-1-Yl]methyl}-4-Morpholin-4-Yl-Thieno[3,2-D]pyrimidine; 4-(2-(1H-indazol-4-yl)-6-((4-(methylsulfonyl)piperazin-1-yl)methyl)thieno(3,2-d)pyrimidin-4-yl)morpholine; GD9; Pictilisib [USAN:INN]; Pictilisib (USAN); Kinome_3719; GDC0941(Pictilisib); 957054-50-1; Pictilisib; GDC-0941; 2-(1H-Indazol-4-yl)-6-[[4-(methylsulfonyl)-1-piperazinyl]methyl]-4-(4-morpholinyl)thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine; MLS006010057; SCHEMBL190812; CHEMBL521851; GTPL5682; BDBM25028; DTXSID40241930; EX-A167; SYN1041; HMS2043A16; HMS3244H06; HMS3244H10; HMS3244H14; HMS3265I05; HMS3265I06; HMS3265J05; HMS3265J06; HMS3654K13; HMS3744A19; AOB87310; BCP01714; CDC-0941; EX-A1536; GNE 0941; MFCD11616196; NSC755385; NSC800852; s1065; ZINC16052714; AKOS015966503; BCP9000715; CCG-264801; CS-0081; DB11663; NSC-755385; NSC-800852; QC-4780; RG-7321; SB19941; NCGC00187482-01; NCGC00187482-03; NCGC00187482-10; 2-(1H-indazol-4-yl)-6-((4-(methanesulfonyl)piperazin-1-yl)methyl)-4-(morpholin-4-yl)thieno(3,2-d)pyrimidine; AC-32623; AS-19377; HY-50094; SMR004701219; Thieno(3,2-d)pyrimidine, 2-(1H-indazol-4-yl)-6-((4-(methylsulfonyl)-1-piperazinyl]methyl)-4-(4-morpholinyl)-; FT-0696889; SW202556-4; X7409; EC-000.2335; D10189; 054G307; A845396; J-513238; BRD-K52911425-001-02-3; Q27088388; C532162000; 2-(1H-indazol-4-yl)-6-{[4-(methylsulfonyl)piperazin-1-yl]methyl}-4-morpholin-4-ylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine; 4-[2-(1H-indazol-4-yl)-6-[(4-methanesulfonylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]morpholine; 4-[2-(1H-indazol-4-yl)-6-[(4-methylsulfonyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-4-thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidinyl]morpholine; Thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine,2-(1H-indazol-4-yl)-6-[[4-(methylsulfonyl)-1-piperazinyl]methyl]-4-(4-morpholinyl)-
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
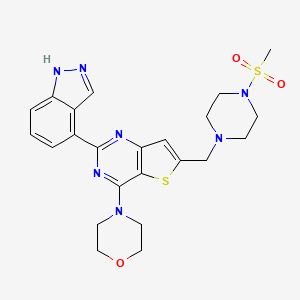
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Janus kinase 2 (JAK-2) | JAK2_HUMAN | [2] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
5
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CS(=O)(=O)N1CCN(CC1)CC2=CC3=C(S2)C(=NC(=N3)C4=C5C=NNC5=CC=C4)N6CCOCC6
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C23H27N7O3S2/c1-35(31,32)30-7-5-28(6-8-30)15-16-13-20-21(34-16)23(29-9-11-33-12-10-29)26-22(25-20)17-3-2-4-19-18(17)14-24-27-19/h2-4,13-14H,5-12,15H2,1H3,(H,24,27)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
LHNIIDJUOCFXAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf (BRAF) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V600E (c.1799T>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.55 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
420
|
M
M
D
D
R
R
G
G
S
S
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
430
|
H
H
G
G
S
S
E
E
D
D
R
R
N
N
R
R
M
M
K
K
440
|
T
T
L
L
G
G
R
R
R
R
D
D
S
S
S
S
D
D
D
D
450
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
P
P
D
D
G
G
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
V
V
460
|
G
G
Q
Q
R
R
I
I
G
G
S
S
G
G
S
S
F
F
G
G
470
|
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
K
K
W
W
H
H
G
G
D
D
480
|
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
L
L
N
N
V
V
T
T
A
A
490
|
P
P
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
Q
Q
L
L
Q
Q
A
A
F
F
K
K
500
|
N
N
E
E
V
V
G
G
V
V
L
L
R
R
K
K
T
T
R
R
510
|
H
H
V
V
N
N
I
I
L
L
L
L
F
F
M
M
G
G
Y
Y
520
|
S
S
T
T
K
K
P
P
Q
Q
L
L
A
A
I
I
V
V
T
T
530
|
Q
Q
W
W
C
C
E
E
G
G
S
S
S
S
L
L
Y
Y
H
H
540
|
H
H
L
L
H
H
I
I
I
I
E
E
T
T
K
K
F
F
E
E
550
|
M
M
I
I
K
K
L
L
I
I
D
D
I
I
A
A
R
R
Q
Q
560
|
T
T
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
M
M
D
D
Y
Y
L
L
H
H
A
A
570
|
K
K
S
S
I
I
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
580
|
N
N
N
N
I
I
F
F
L
L
H
H
E
E
D
D
L
L
T
T
590
|
V
V
K
K
I
I
G
G
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
T
T
600
|
V
E
K
K
S
S
R
R
W
W
S
S
G
G
S
S
H
H
Q
Q
610
|
F
F
E
E
Q
Q
L
L
S
S
G
G
S
S
I
I
L
L
W
W
620
|
M
M
A
A
P
P
E
E
V
V
I
I
R
R
M
M
Q
Q
D
D
630
|
K
K
N
N
P
P
Y
Y
S
S
F
F
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
640
|
Y
Y
A
A
F
F
G
G
I
I
V
V
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
L
L
650
|
M
M
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
S
S
N
N
I
I
660
|
N
N
N
N
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
I
I
I
I
F
F
M
M
V
V
670
|
G
G
R
R
G
G
Y
Y
L
L
S
S
P
P
D
D
L
L
S
S
680
|
K
K
V
V
R
R
S
S
N
N
C
C
P
P
K
K
A
A
M
M
690
|
K
K
R
R
L
L
M
M
A
A
E
E
C
C
L
L
K
K
K
K
700
|
K
K
R
R
D
D
E
E
R
R
P
P
L
L
F
F
P
P
Q
Q
710
|
I
I
L
L
A
A
S
S
I
I
E
E
L
L
L
L
A
A
R
R
720
|
S
S
L
L
P
P
K
K
I
I
H
H
R
R
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ICH assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Plasma level assay; Electrochemiluminescense assay | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: PI3-kinase alpha (PIK3CA) | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E545K (c.1633G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| In Vivo Model | Female NCR nu/nu mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay; IC50 assay | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: PI3-kinase alpha (PIK3CA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D549Y (c.1645G>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MEK/ERK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04011 | |
| In Vitro Model | 5637 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0126 |
| J82 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0359 | |
| RT4 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0036 | |
| T24 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0554 | |
| TCCSuP cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1738 | |
| In Vivo Model | NSG mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; FACS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Pictilisib activated the compensatory MEK/ERK pathways that likely contributed to pictilisib resistance, which was reversed by co-treatment with the RAF inhibitor sorafenib. RNA-sequencing of tumors resistant to treatment suggested that LSP1 down-regulation correlated with drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N48I (c.143A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MEK/ERK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04011 | |
| In Vitro Model | 5637 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0126 |
| J82 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0359 | |
| RT4 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0036 | |
| T24 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0554 | |
| TCCSuP cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1738 | |
| In Vivo Model | NSG mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; FACS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Pictilisib activated the compensatory MEK/ERK pathways that likely contributed to pictilisib resistance, which was reversed by co-treatment with the RAF inhibitor sorafenib. RNA-sequencing of tumors resistant to treatment suggested that LSP1 down-regulation correlated with drug resistance. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
