Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00384) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Gentamicin A
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Gentamicin A; C01917; 13291-74-2; C18H36N4O10; ZINC56870883; Y1680; (2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-5-amino-6-[(1R,2S,3S,4R,6S)-4,6-diamino-3-[(2R,3R,4S,5S)-3,5-dihydroxy-4-(methylamino)tetrahydropyran-2-yl]oxy-2-hydroxy-cyclohexoxy]-2-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydropyran-3,4-diol
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
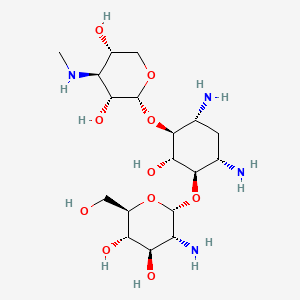
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(6 diseases)
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C18H36N4O10
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CN[C@H]1[C@@H](CO[C@@H]([C@@H]1O)O[C@H]2[C@@H](C[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]2O)O[C@@H]3[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O3)CO)O)O)N)N)N)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C18H36N4O10/c1-22-10-7(24)4-29-18(13(10)27)32-16-6(20)2-5(19)15(14(16)28)31-17-9(21)12(26)11(25)8(3-23)30-17/h5-18,22-28H,2-4,19-21H2,1H3/t5-,6+,7+,8+,9+,10-,11+,12+,13+,14-,15+,16-,17+,18+/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
LKKVGKXCMYHKSL-QVNYEEQUSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gram-negative pathogens infection [ICD-11: 1B74-1G40] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Sepsis [ICD-11: 1G40.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
ICD-11: Circulatory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Infective endocarditis [ICD-11: BB40.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Respiratory trac infection [ICD-11: CA45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
ICD-13: Digestive system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gram-negative pathogens infection [ICD-11: 1B74-1G40] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
ICD-16: Genitourinary system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC/APH) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gram-negative pathogens infection [ICD-11: 1B74-1G40] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM83 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-PAGE assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside 2"-phosphotransferases are the major aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes in clinical isolates of enterococci and staphylococci.APH(2")-If. This enzyme confers resistance to the 4,6-disubstituted aminoglycosides kanamycin, tobramycin, dibekacin, gentamicin, and sisomicin, but not to arbekacin, amikacin, isepamicin, or netilmicin. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
