Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00252) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Penicillin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cillin; Pentids; 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(2-phenylacetyl)amino]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; 3,3-Dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(phenylacetyl)amino]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; (Phenylmethyl)penicillin; 7005-30-3; NSC131815; (Phenylmethyl)penicillinic acid; 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-((phenylacetyl)amino)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; AC1L1DHC; AC1Q5UVJ; Penicilline G sodium salt; Oprea1_713794; Oprea1_861345; CHEMBL300052; SCHEMBL2109546; CTK2H5530
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
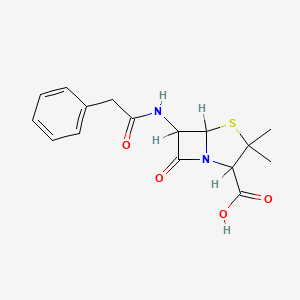
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[1]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[4]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial Penicillin binding protein (Bact PBP) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C16H18N2O4S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC1(C(N2C(S1)C(C2=O)NC(=O)CC3=CC=CC=C3)C(=O)O)C
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C16H18N2O4S/c1-16(2)12(15(21)22)18-13(20)11(14(18)23-16)17-10(19)8-9-6-4-3-5-7-9/h3-7,11-12,14H,8H2,1-2H3,(H,17,19)(H,21,22)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
JGSARLDLIJGVTE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [2], [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Anaerobic bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1A09] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli HB101 | 634468 | ||
| Escherichia coli JM109 | 562 | |||
| Acidaminococcus fermentans RYC-MR95 | 905 | |||
| Acidaminococcus fermentans RYC4093 | 905 | |||
| Acidaminococcus fermentans RYC4356 | 905 | |||
| Escherichia coli RYC1000 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A. intestini is the first Gram-negative coccus with demonstrated resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. The reference genome of the A. intestini strain RyC-MR95, which was isolated from a perianal abscess of a European male diabetic patient, contains the aci1 gene, which encodes the ACI-1 class A beta-lactamase that confers resistance to penicillins and extended-spectrum cephalosporins. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Penicillin-binding protein 2C (PBP2C) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lactobacillus casei infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | jk0412 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion assay; Microdilution assay; E-Test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Six genes encoding putative high molecular weight penicillin-binding proteins (Pbp) are present in the genome of the beta-lactam-resistant strain?Corynebacterium jeikeium?K411. In this study, we show that?pbp2c, one of these six genes, is present in resistant strains of?Corynebacteriaceae?but absent from sensitive strains. The molecular study of the?pbp2c?locus from?C. jeikeium?and its heterologous expression in?Corynebacterium glutamicum?allowed us to show that Pbp2c confers high levels of beta-lactam resistance to the host and is under the control of a beta-lactam-induced regulatory system encoded by two adjacent genes,?jk0410?and?jk0411. The detection of this inducible resistance may require up to 48?h of incubation, particularly in?Corynebacterium amycolatum. Finally, the Pbp2c-expressing strains studied were resistant to all the beta-lactam antibiotics tested, including carbapenems, ceftaroline, and ceftobiprole. | |||
| Key Molecule: Penicillin-binding protein 2C (PBP2C) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lactobacillus casei infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | cu1571 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion assay; Microdilution assay; E-Test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Six genes encoding putative high molecular weight penicillin-binding proteins (Pbp) are present in the genome of the beta-lactam-resistant strain?Corynebacterium jeikeium?K411. In this study, we show that?pbp2c, one of these six genes, is present in resistant strains of?Corynebacteriaceae?but absent from sensitive strains. The molecular study of the?pbp2c?locus from?C. jeikeium?and its heterologous expression in?Corynebacterium glutamicum?allowed us to show that Pbp2c confers high levels of beta-lactam resistance to the host and is under the control of a beta-lactam-induced regulatory system encoded by two adjacent genes,?jk0410?and?jk0411. The detection of this inducible resistance may require up to 48?h of incubation, particularly in?Corynebacterium amycolatum. Finally, the Pbp5c-expressing strains studied were resistant to all the beta-lactam antibiotics tested, including carbapenems, ceftaroline, and ceftobiprole. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Penicillin-binding protein 1A (PBP1A) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gonococcal infection [ICD-11: 1A70.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L421P |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Neisseria gonorrhoeae 0387 | 485 | ||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae 2227 | 485 | |||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae 3391 | 485 | |||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae 5611 | 485 | |||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae 9634 | 485 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The ponA1 gene encodes PBP 1 containing a single amino acid mutation, Leu-421-Pro. This single amino acid mutation was present in all chromosomally mediated resistant N. gonorrhoeae (CMRNG) strains for which MICs of penicillin were >=1 ug/ml. PBP 1 harboring this point mutation (PBP 1*) had a three- to fourfold lower rate of acylation (k2/k') than wild-type PBP 1 with a variety of Beta-lactam antibiotics. | |||
| Key Molecule: Probable peptidoglycan D,D-transpeptidase PenA (PENA) | [5], [6], [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gonococcal infection [ICD-11: 1A70.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G545S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates strain | 485 | ||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain ATCC 49226 | 485 | |||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain ATCC 700825 | 485 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Three mutations (G545S, I312M, and V316T) in mosaic PBP2 were identified as the amino acid substitutions responsible for reduced susceptibility to cefixime in N. gonorrhoeae. | |||
| Key Molecule: Probable peptidoglycan D,D-transpeptidase PenA (PENA) | [5], [6], [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gonococcal infection [ICD-11: 1A70.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G545S+p.I312M |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates strain | 485 | ||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain ATCC 49226 | 485 | |||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain ATCC 700825 | 485 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Three mutations (G545S, I312M, and V316T) in mosaic PBP2 were identified as the amino acid substitutions responsible for reduced susceptibility to cefixime in N. gonorrhoeae. | |||
| Key Molecule: Probable peptidoglycan D,D-transpeptidase PenA (PENA) | [5], [6], [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Gonococcal infection [ICD-11: 1A70.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G545S+p.V316T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates strain | 485 | ||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain ATCC 49226 | 485 | |||
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain ATCC 700825 | 485 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Three mutations (G545S, I312M, and V316T) in mosaic PBP2 were identified as the amino acid substitutions responsible for reduced susceptibility to cefixime in N. gonorrhoeae. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Klebsiella pneumoniae 11978 | 573 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing and protein assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The Beta-lactamase OXA-48 hydrolyzed imipenem at a high level. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
