Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00180) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Aztreonam
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Azactam; Primbactam; Azactam (TN); SQ-26776; Monobactam, SQ 26776, Squibb 26776, Aztreonam; [2S-[2alpha,3beta(Z)]]-2-[[[1-(2-Amino-4-thiazolyl)-2-[(2-methyl-4-oxo-1-sulfo-3-azetidinyl)amino]-2-oxoethylidene]amino]oxy]-2-methylpropanoic acid; 2-({[(1Z)-1-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-{[(2S,3S)-2-methyl-4-oxo-1-sulfoazetidin-3-yl]amino}-2-oxoethylidene]amino}oxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid; 2-[(Z)-[1-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-[[(2S,3S)-2-methyl-4-oxo-1-sulfoazetidin-3-yl]amino]-2-oxoethylidene]amino]oxy-2-methylpropanoic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
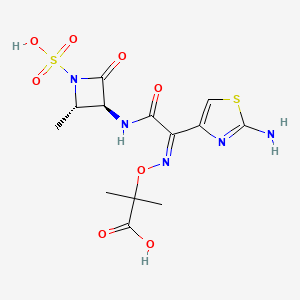
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[2]
[2]
[3]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial Penicillin binding protein 3 (Bact mrcA) | FTSI_ECOLI | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C13H17N5O8S2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C[C@H]1[C@@H](C(=O)N1S(=O)(=O)O)NC(=O)/C(=N\\OC(C)(C)C(=O)O)/C2=CSC(=N2)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C13H17N5O8S2/c1-5-7(10(20)18(5)28(23,24)25)16-9(19)8(6-4-27-12(14)15-6)17-26-13(2,3)11(21)22/h4-5,7H,1-3H3,(H2,14,15)(H,16,19)(H,21,22)(H,23,24,25)/b17-8-/t5-,7-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
WZPBZJONDBGPKJ-VEHQQRBSSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y104A+p.N110D+p.E175Q+p.S179A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Acinetobacter baumannii CIP70.10 | 470 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae kP3 | 1290996 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa PU21 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | K. pneumoniae kP3 was resistant to all Beta-lactams, including carbapenems, and expressed the carbapenem-hydrolyzing Beta-lactamase OXA-181, which differs from OXA-48 by four amino acid substitutions. Compared to OXA-48, OXA-181 possessed a very similar hydrolytic profile. | |||
| Key Molecule: Metallo-beta-lactamase (VIM1) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Achromobacter xylosoxydans infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Achromobacter xylosoxydans subsp. denitrificans AX-22 | 85698 | |||
| Escherichia coli MkD-135 | 562 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 10145/3 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA extraction and Sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | A. xylosoxydans AX22 exhibited broad-spectrum resistance to Beta-lactams and aminoglycosides. The Beta-lactam resistance pattern (including piperacillin, ceftazidime, and carbapenem resistance) was unusual for this species, and the high-level carbapenem resistance suggested the production of an acquired carbapenemase. In fact, carbapenemase activity was detected in a crude extract of AX22 (specific activity, 184 +/- 12 U/mg of protein), and this activity was reduced (>80%) after incubation of the crude extract with 2 mM EDTA, suggesting the presence of a metallo-Beta-lactamase determinant. | |||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [4], [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V77A+p.D114N+p.S140A+p.N288D |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Citrobacter freundii strain 2524/96 | 546 | ||
| Citrobacter freundii strain 2525/96 | 546 | |||
| Citrobacter freundii strain 2526/96 | 546 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 2527/96 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Sequencing has revealed that C. freundii isolates produced a new CTX-M-3 enzyme which is very closely related to the CTX-M-1/MEN-1 Beta-lactamase. | |||
| Key Molecule: Beta-lactamase (BLA) | [4], [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain DH5a | 668369 | ||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strain HEL-1 | 573 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The phenotype of Klebsiella pneumoniae HEL-1 indicates a plasmidic cephamycinase gene (blaCMY-2),which is responsible for cephamycin resistance. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Pyruvate decarboxylase 5 (PDC5) | [4], [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R79Q+p.T105A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 | 208964 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 12B | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa kG2505 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; Etest method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Reduced susceptibility to imipenem, ceftazidime, and cefepime was observed only with recombinant P. aeruginosa strains expressing an AmpC Beta-lactamase that had an alanine residue at position 105.Recently, several ESACs have been described from Escherichia coli contributing to reduced susceptibility to imipenem. | |||
| Key Molecule: Pyruvate decarboxylase 3 (PDC3) | [4], [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T97A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 | 208964 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 12B | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa kG2505 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; Etest method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Reduced susceptibility to imipenem, ceftazidime, and cefepime was observed only with recombinant P. aeruginosa strains expressing an AmpC Beta-lactamase that had an alanine residue at position 105.Recently, several ESACs have been described from Escherichia coli contributing to reduced susceptibility to imipenem. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Metallo-beta-lactamase (VIM1) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Achromobacter xylosoxydans subsp. denitrificans AX-22 | 85698 | |||
| Escherichia coli MkD-135 | 562 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 10145/3 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA extraction and Sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Electroporation of Escherichia coli DH5alpha with the purified plasmid preparation yielded ampicillin-resistant transformants which contained a plasmid apparently identical to pAX22 (data not shown). DH5alpha(pAX22) produced carbapenemase activity (specific activity of crude extract, 202 +/- 14 U/mg of protein) and, compared to DH5alpha, exhibited a decreased susceptibility to several Beta-lactams. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
