Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol03004)
| Name |
Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B (AKR1B1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
AKR1B1; ALDR1; ALR2
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
AKR1B1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr7:134,442,356-134,459,284[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MASRLLLNNGAKMPILGLGTWKSPPGQVTEAVKVAIDVGYRHIDCAHVYQNENEVGVAIQ
EKLREQVVKREELFIVSKLWCTYHEKGLVKGACQKTLSDLKLDYLDLYLIHWPTGFKPGK EFFPLDESGNVVPSDTNILDTWAAMEELVDEGLVKAIGISNFNHLQVEMILNKPGLKYKP AVNQIECHPYLTQEKLIQYCQSKGIVVTAYSPLGSPDRPWAKPEDPSLLEDPRIKAIAAK HNKTTAQVLIRFPMQRNLVVIPKSVTPERIAENFKVFDFELSSQDMTTLLSYNRNWRVCA LLSCTSHKDYPFHEEF Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of a wide variety of carbonyl-containing compounds to their corresponding alcohols. Displays enzymatic activity towards endogenous metabolites such as aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes, ketones, monosacharides, bile acids and xenobiotics substrates. Key enzyme in the polyol pathway, catalyzes reduction of glucose to sorbitol during hyperglycemia. Reduces steroids and their derivatives and prostaglandins. Displays low enzymatic activity toward all-trans-retinal, 9-cis-retinal, and 13-cis-retinal. Catalyzes the reduction of diverse phospholipid aldehydes such as 1-palmitoyl-2-(5-oxovaleroyl)-sn -glycero-3-phosphoethanolamin (POVPC) and related phospholipid aldehydes that are generated from the oxydation of phosphotidylcholine and phosphatdyleethanolamides. Plays a role in detoxifying dietary and lipid-derived unsaturated carbonyls, such as crotonaldehyde, 4-hydroxynonenal, trans-2-hexenal, trans-2,4-hexadienal and their glutathione-conjugates carbonyls (GS-carbonyls).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Epalrestat | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain | 1773 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain | 562 | |||
| In Vivo Model | Xenograft mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Coimmunoprecipitation assay; Immunofluorescence staining assay; High-content imaging analysis; Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Up-regulation of AKR1B1 led to enhanced glutathione synthesis and resistance to EGFR inhibitors in cell lines and xenograft mouse models. In addition, the antidiabetic drug epalrestat inhibited AKR1B1 and restored sensitivity to EGFR TKIs in patient-derived xenograft tumors. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.33E-06; Fold-change: -1.87E-01; Z-score: -4.93E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.87E-03; Fold-change: -1.12E-01; Z-score: -2.68E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
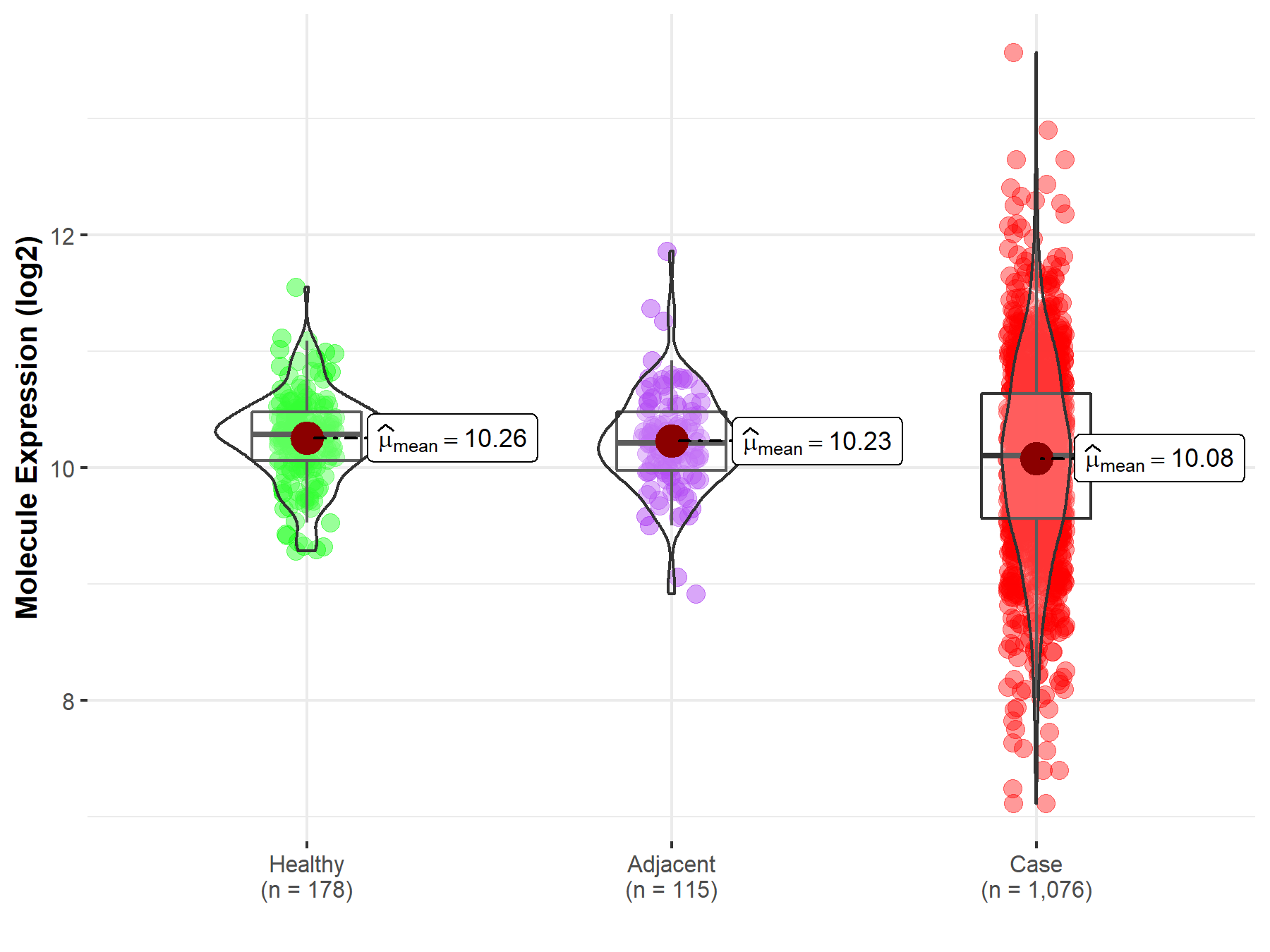
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

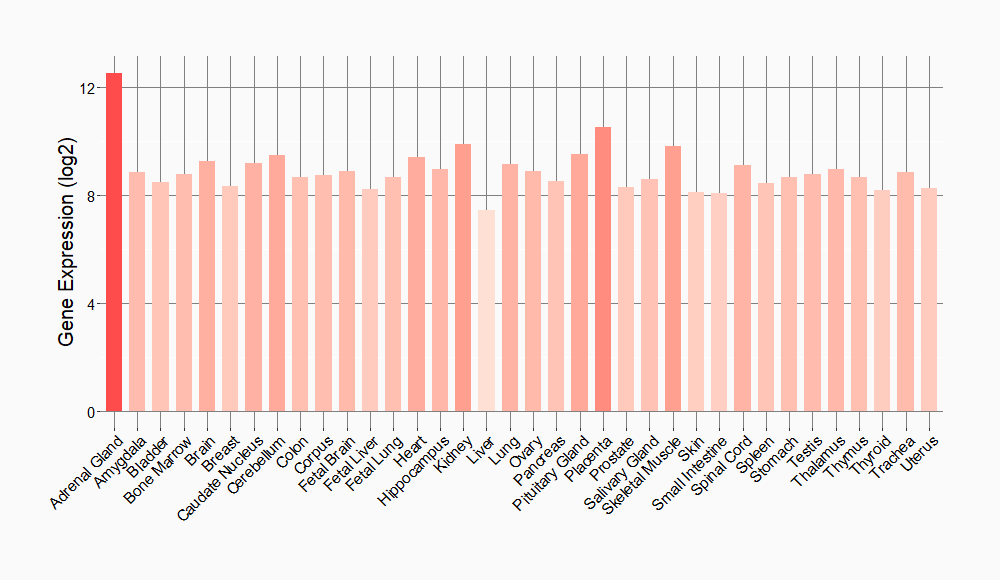
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
