Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01074) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Epalrestat
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Epalrestat; 82159-09-9; Kinedak; Epalrestatum; Ono 2235; Ono-2235; ONO-2; 2-((z)-5-((e)-2-methyl-3-phenylallylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid; UNII-424DV0807X; C15H13NO3S2; 2-[(5Z)-5-[(E)-2-methyl-3-phenylprop-2-enylidene]-4-oxo-2-sulfanylidene-1,3-thiazolidin-3-yl]acetic acid; CHEMBL56337; 5-((1Z,2E)-2-Methyl-3-phenylpropenylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxo-3-thiazolidineacetic acid; CHEBI:31539; ONO2235; 5-((Z,E)-beta-Methylcinnamylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxo-3-thiazolidineacetic acid; MFCD00865484; 424DV0807X; {(5Z)-5-[(2E)-2-methyl-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]-4-oxo-2-thioxo-1,3-thiazolidin-3-yl}acetic acid; Epalrestat [INN]; Epalrestatum [Latin]; {5-[(E)-2-Methyl-3-phenyl-prop-2-en-(Z)-ylidene]-4-oxo-2-thioxo-thiazolidin-3-yl}-acetic acid; 2-[(5Z)-5-[(2E)-2-methyl-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-ylidene]-4-oxo-2-sulfanylidene-1,3-thiazolidin-3-yl]acetic acid; ONO 2; Kinedak (TN); Aldonil; Aldorin; Tanglin; NCGC00164613-01; Epalrestat- Bio-X; 5-[(1Z, 2E)-2-methyl-3-phenylpropenylidene]-4-oxo2-thioxo-3-thiazolidineacetic acid; Epalrestat (JP17/INN); 3-Thiazolidineacetic acid, 5-(2-methyl-3-phenyl-2-propenylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxo-, (E,E)-; SCHEMBL49049; MLS000806985; GTPL11371; REGID_for_CID_1549120; HMS2747M09; HMS3887A17; ZINC1533688; BBL029067; BDBM50049730; s2035; STK337187; AKOS000274207; BCP9000649; CCG-267693; DB15293; NCGC00164613-08; NCGC00164613-12; AS-13345; BE164412; H951; HY-66009; SMR000414799; BCP0726000053; E0906; SW219826-1; D01688; AB00647195_06; 159E099; Q5382029; [5-(2-Methyl-3-phenyl-allylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxo-thiazolidin-3-yl]-acetic acid; 2-(5-(2-methyl-3-phenylallylidene)-4-oxo-2-thioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid; (5-[(e)-2-methyl-3-phenyl-prop-2-en-(z)-ylidene]-4-oxo-2-thioxo-thiazolidin-3-yl)-acetic acid 82159-; {(5Z)-5-[(2E)-2-methyl-3-phenylprop-2-enylidene]-4-oxo-2-thioxo-1,3-thiazolidin-3-yl}acetic acid; 2-[(5Z)-5-[(E)-3-phenil-2-methylprop-2-enylidene]-4-oxo-2-thioxo-3-thiazolidinyl]acetic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 2 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
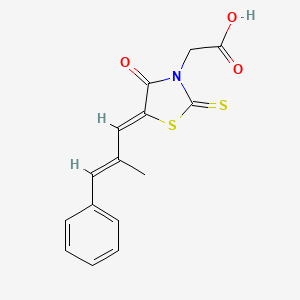
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Aldose reductase (AKR1B1) | ALDR_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Voltage-gated L-type calcium channel (L-CaC) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C15H13NO3S2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C/C(=C\\C1=CC=CC=C1)/C=C\\2/C(=O)N(C(=S)S2)CC(=O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C15H13NO3S2/c1-10(7-11-5-3-2-4-6-11)8-12-14(19)16(9-13(17)18)15(20)21-12/h2-8H,9H2,1H3,(H,17,18)/b10-7+,12-8-
|
||||
| InChIKey |
CHNUOJQWGUIOLD-NFZZJPOKSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B (AKR1B1) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain | 1773 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain | 562 | |||
| In Vivo Model | Xenograft mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Coimmunoprecipitation assay; Immunofluorescence staining assay; High-content imaging analysis; Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Up-regulation of AKR1B1 led to enhanced glutathione synthesis and resistance to EGFR inhibitors in cell lines and xenograft mouse models. In addition, the antidiabetic drug epalrestat inhibited AKR1B1 and restored sensitivity to EGFR TKIs in patient-derived xenograft tumors. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 (AKR1B10) | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vivo Model | MU375/MU383 patient-derived tumor organoids | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR; IHC assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Drug sensitivity testing | |||
| Mechanism Description | Epalrestat can be repurposed to overcome chemoresistance. PDTOs retained histomorphology and pathological biomarker expression, mutational/transcriptomic signatures, and cellular heterogeneity of the matched tumor tissues. Five (50%) PDTOs were chemoresistant toward carboplatin/paclitaxel. Chemoresistant PDTOs and matched tumor tissues demonstrated overexpression of AKR1B10. Epalrestat, an orally available AKR1B10 inhibitor in clinical use for diabetic polyneuropathy, was repurposed to overcome chemoresistance of PDTOs. In vivo efficacy of epalrestat to overcome drug resistance corresponded to intratumoral epalrestat levels. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
