Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol02117)
| Name |
Amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP) (ABPP) (APPI) (Alzheimer disease amyloid A4 protein homolog) (Alzheimer disease amyloid protein) (Amyloid precursor protein) (Amyloid-beta (A4) precursor protein) (Amyloid-beta A4 protein) (Cerebral vascular amyloid peptide) (CVAP) (PreA4) (Protease nexin-II) (PN-II) [Cleaved into: N-APP; Soluble APP-alpha (S-APP-alpha); Soluble APP-beta (S-APP-beta); C99 (Beta-secretase C-terminal fragment) (Beta-CTF); Amyloid-beta protein 42 (Abeta42) (Beta-APP42); Amyloid-beta protein 40 (Abeta40) (Beta-APP40); C83 (Alpha-secretase C-terminal fragment) (Alpha-CTF); P3(42); P3(40); C80; Gamma-secretase C-terminal fragment 59 (Amyloid intracellular domain 59) (AICD-59) (AID(59)) (Gamma-CTF(59)); Gamma-secretase C-terminal fragment 57 (Amyloid intracellular domain 57) (AICD-57) (AID(57)) (Gamma-CTF(57)); Gamma-secretase C-terminal fragment 50 (Amyloid intracellular domain 50) (AICD-50) (AID(50)) (Gamma-CTF(50)); C31]; APP; A4; AD1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
APP
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
Chromosome 21: 25,880,550-26,171,128 reverse strand
|
||||
| Sequence |
MLPGLALLLLAAWTARALEVPTDGNAGLLAEPQIAMFCGRLNMHMNVQNGKWDSDPSGTK
TCIDTKEGILQYCQEVYPELQITNVVEANQPVTIQNWCKRGRKQCKTHPHFVIPYRCLVG EFVSDALLVPDKCKFLHQERMDVCETHLHWHTVAKETCSEKSTNLHDYGMLLPCGIDKFR GVEFVCCPLAEESDNVDSADAEEDDSDVWWGGADTDYADGSEDKVVEVAEEEEVAEVEEE EADDDEDDEDGDEVEEEAEEPYEEATERTTSIATTTTTTTESVEEVVREVCSEQAETGPC RAMISRWYFDVTEGKCAPFFYGGCGGNRNNFDTEEYCMAVCGSAMSQSLLKTTQEPLARD PVKLPTTAASTPDAVDKYLETPGDENEHAHFQKAKERLEAKHRERMSQVMREWEEAERQA KNLPKADKKAVIQHFQEKVESLEQEAANERQQLVETHMARVEAMLNDRRRLALENYITAL QAVPPRPRHVFNMLKKYVRAEQKDRQHTLKHFEHVRMVDPKKAAQIRSQVMTHLRVIYER MNQSLSLLYNVPAVAEEIQDEVDELLQKEQNYSDDVLANMISEPRISYGNDALMPSLTET KTTVELLPVNGEFSLDDLQPWHSFGADSVPANTENEVEPVDARPAADRGLTTRPGSGLTN IKTEEISEVKMDAEFRHDSGYEVHHQKLVFFAEDVGSNKGAIIGLMVGGVVIATVIVITL VMLKKKQYTSIHHGVVEVDAAVTPEERHLSKMQQNGYENPTYKFFEQMQN Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Functions as a cell surface receptor and performs physiological functions on the surface of neurons relevant to neurite growth, neuronal adhesion and axonogenesis. Interaction between APP molecules on neighboring cells promotes synaptogenesis. Involved in cell mobility and transcription regulation through protein-protein interactions. Can promote transcription activation through binding to APBB1-KAT5 and inhibits Notch signaling through interaction with Numb. Couples to apoptosis-inducing pathways such as those mediated by G(o) and JIP. Inhibits G(o) alpha ATPase activity. Acts as a kinesin I membrane receptor, mediating the axonal transport of beta-secretase and presenilin 1. By acting as a kinesin I membrane receptor, plays a role in axonal anterograde transport of cargo towards synapes in axons. Involved in copper homeostasis/oxidative stress through copper ion reduction. In vitro, copper-metallated APP induces neuronal death directly or is potentiated through Cu(2+)-mediated low-density lipoprotein oxidation. Can regulate neurite outgrowth through binding to components of the extracellular matrix such as heparin and collagen I and IV. The splice isoforms that contain the BPTI domain possess protease inhibitor activity. Induces a AGER-dependent pathway that involves activation of p38 MAPK, resulting in internalization of amyloid-beta peptide and leading to mitochondrial dysfunction in cultured cortical neurons. Provides Cu(2+) ions for GPC1 which are required for release of nitric oxide (NO) and subsequent degradation of the heparan sulfate chains on GPC1.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Alzheimer's disease [ICD-11: 8A20.0] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Alzheimer's disease [ICD-11: 8A20.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Tacrine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | By using tacrine to target the active catalytic site (CAS), the tacrine-based MTDLs can act on both CAS and peripheral anion site (PAS) of AChE to serve as a dual-site AChE inhibitor. Additionally, the tacrine-based MTDLs can also be designed on the basis of other theories of AD, for example, introducing functional moieties to modulate the formation of beta-amyloid (Abeta), oxidation resistance, or metal chelation. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 08

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Entorhinal cortex | |
| The Specified Disease | Alzheimer's disease | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.60E-02; Fold-change: -7.24E-02; Z-score: -3.10E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
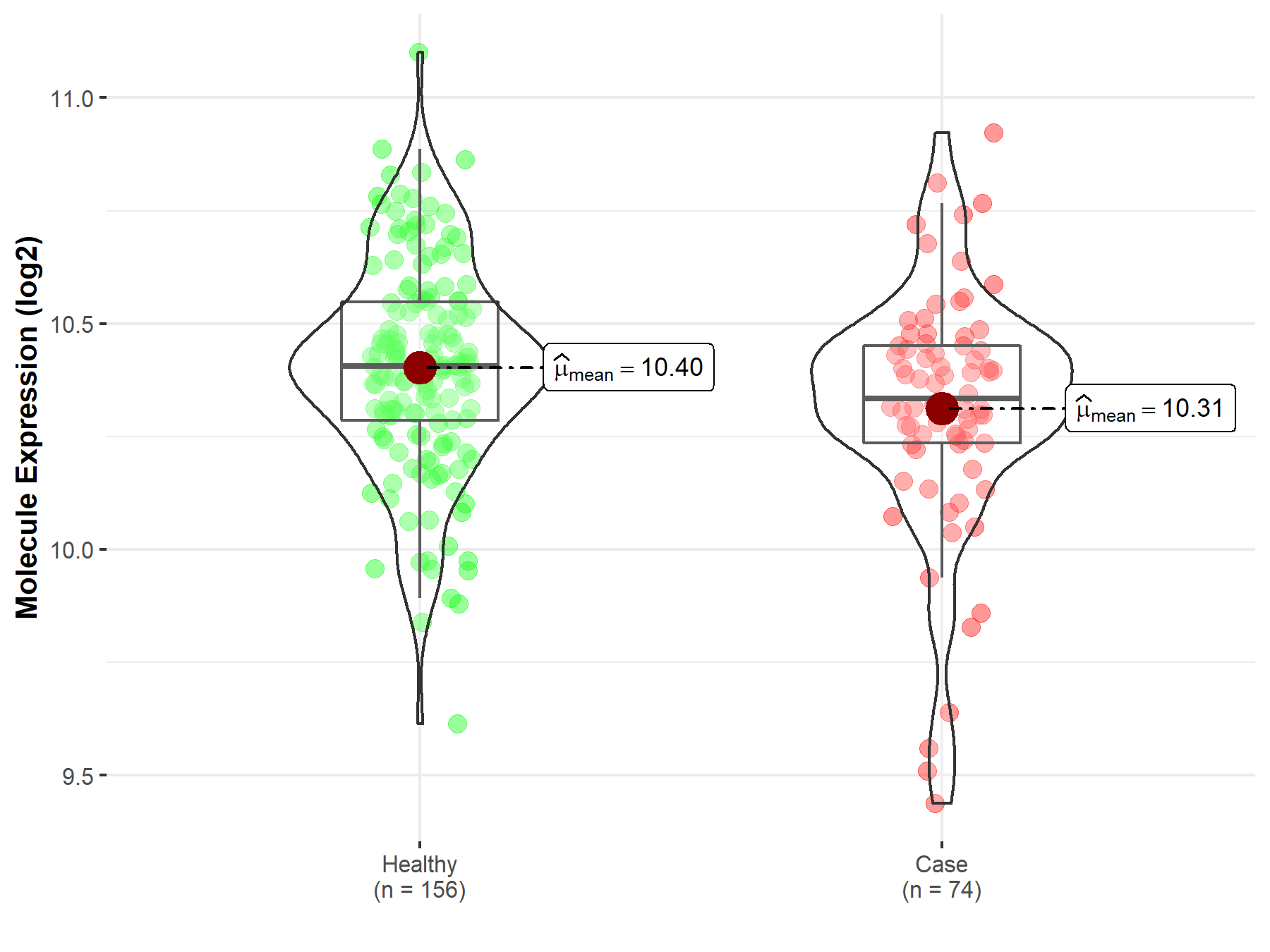
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

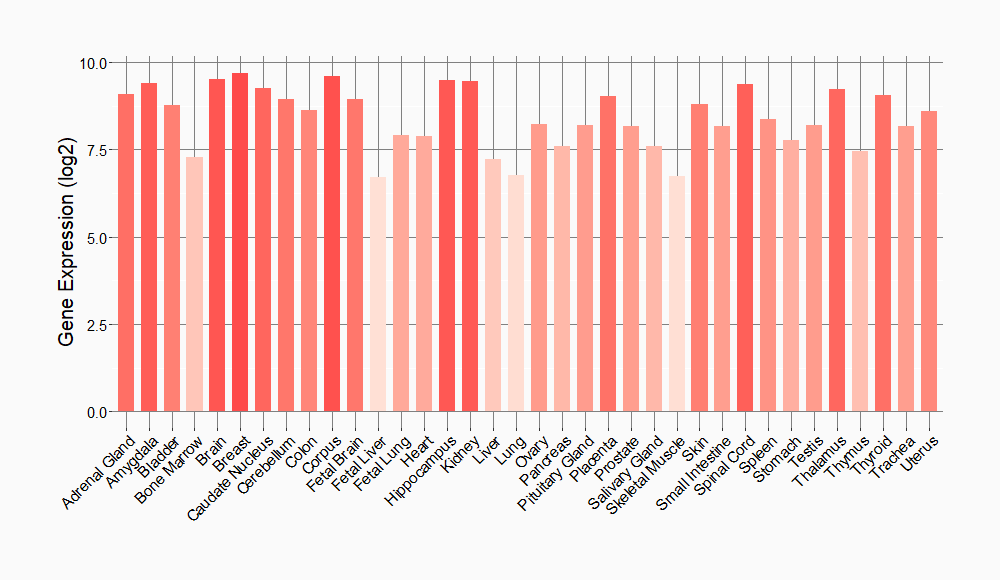
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
