Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01956)
| Name |
Decaprenyl diphosphate synthase subunit 1 (PDSS1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
PDSS1; DPS1; TPRT
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
PDSS1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr10:26,697,701-26,746,798[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MASRWWRWRRGCSWKPAARSPGPGSPGRAGPLGPSAAAEVRAQVHRRKGLDLSQIPYINL
VKHLTSACPNVCRISRFHHTTPDSKTHSGEKYTDPFKLGWRDLKGLYEDIRKELLISTSE LKEMSEYYFDGKGKAFRPIIVALMARACNIHHNNSRHVQASQRAIALIAEMIHTASLVHD DVIDDASSRRGKHTVNKIWGEKKAVLAGDLILSAASIALARIGNTTVISILTQVIEDLVR GEFLQLGSKENENERFAHYLEKTFKKTASLIANSCKAVSVLGCPDPVVHEIAYQYGKNVG IAFQLIDDVLDFTSCSDQMGKPTSADLKLGLATGPVLFACQQFPEMNAMIMRRFSLPGDV DRARQYVLQSDGVQQTTYLAQQYCHEAIREISKLRPSPERDALIQLSEIVLTRDK Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
Heterotetrameric enzyme that catalyzes the condensation of farnesyl diphosphate (FPP), which acts as a primer, and isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) to produce prenyl diphosphates of varying chain lengths and participates in the determination of the side chain of ubiquinone. Supplies nona and decaprenyl diphosphate, the precursors for the side chain of the isoprenoid quinones ubiquinone-9 (Q9)and ubiquinone-10 (Q10) respectively. The enzyme adds isopentenyl diphosphate molecules sequentially to farnesyl diphosphate with trans stereochemistry.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Fluvastatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.15E-36 Fold-change: 9.52E-02 Z-score: 1.37E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Steroid biosynthesis signaling pathway | Activation | hsa00100 | |
| Terpenoid bacKbone biosynthesis signaling pathway | Activation | hsa00900 | ||
| Steroid hormone biosynthesis signaling pathway | Activation | hsa00140 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-10A-neoT cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5554 |
| In Vivo Model | SV40 C3TAg transgenic mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Clariom D RNA profiling assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired resistance to fluvastatin is mediated by restorative upregulation of cholesterol biosynthesis pathway genes. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.15E-36; Fold-change: 4.15E-01; Z-score: 1.02E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.62E-05; Fold-change: 1.56E-01; Z-score: 4.62E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
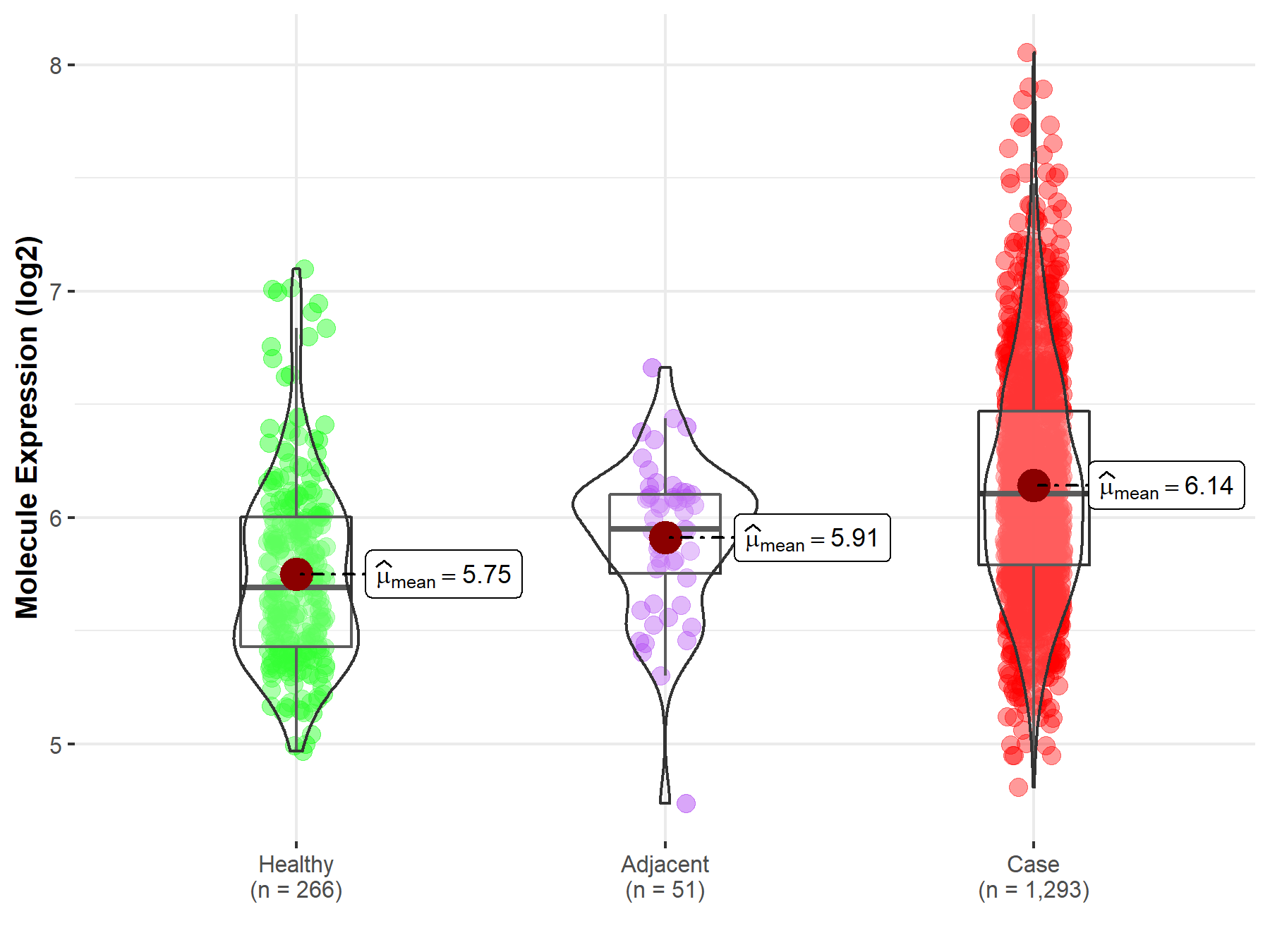
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

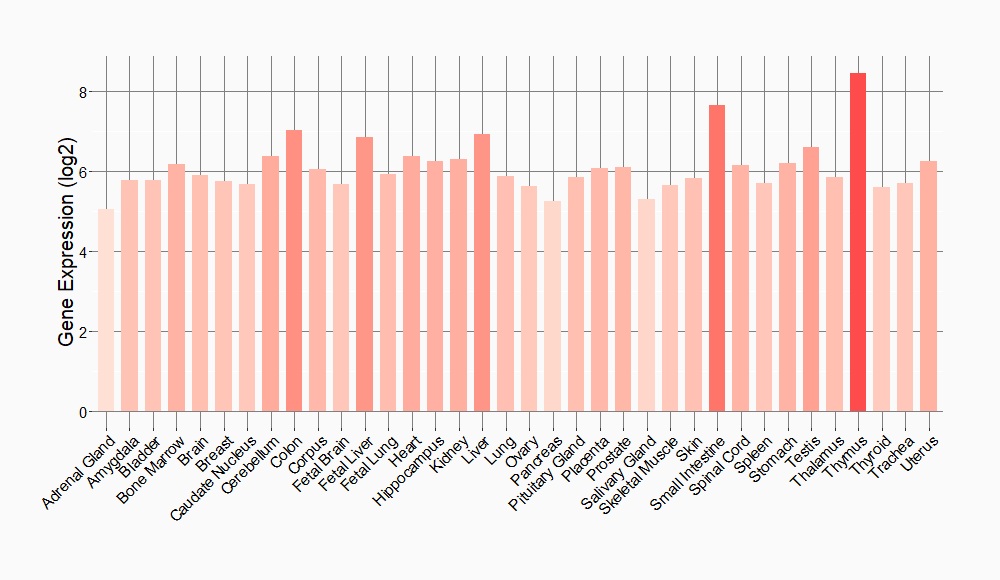
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
