Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01937)
| Name |
Geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase 1 (GGPS1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
GGPS1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
GGPS1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr1:235,327,350-235,344,532[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MEKTQETVQRILLEPYKYLLQLPGKQVRTKLSQAFNHWLKVPEDKLQIIIEVTEMLHNAS
LLIDDIEDNSKLRRGFPVAHSIYGIPSVINSANYVYFLGLEKVLTLDHPDAVKLFTRQLL ELHQGQGLDIYWRDNYTCPTEEEYKAMVLQKTGGLFGLAVGLMQLFSDYKEDLKPLLNTL GLFFQIRDDYANLHSKEYSENKSFCEDLTEGKFSFPTIHAIWSRPESTQVQNILRQRTEN IDIKKYCVHYLEDVGSFEYTRNTLKELEAKAYKQIDARGGNPELVALVKHLSKMFKEENE Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Catalyzes the trans-addition of the three molecules of IPP onto DMAPP to form geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate, an important precursor of carotenoids and geranylated proteins.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Small cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.1] | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Lipid metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Small cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Etoposide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Small cell lung carcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.06E-02 Fold-change: 8.03E-02 Z-score: 2.18E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Biosynthesis of terpenoids and steroids | Activation | hsa01062 | |
| Indole diterpene alkaloid biosynthesis | Activation | hsa00403 | ||
| In Vitro Model | DMS-114 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1174 |
| H146 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1473 | |
| H209 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9V41 | |
| H446 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1562 | |
| H526 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1569 | |
| H82 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1591 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanistically, statins induce oxidative stress accumulation and apoptosis through the GGPP synthase?1 (GGPS1)-RAB7A-autophagy axis. Statin treatment overcomes both intrinsic and acquired SCLC chemoresistance in vivo across different SCLC PDX models bearing high GGPS1 levels. Moreover, we show that GGPS1 expression is negatively associated with survival in patients with SCLC | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Small cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.1] | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Lipid metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Small cell lung carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.06E-20 Fold-change: 4.40E-02 Z-score: 9.57E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Biosynthesis of terpenoids and steroids | Activation | hsa01062 | |
| Indole diterpene alkaloid biosynthesis | Activation | hsa00403 | ||
| In Vitro Model | DMS-114 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1174 |
| H146 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1473 | |
| H209 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9V41 | |
| H446 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1562 | |
| H526 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1569 | |
| H82 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1591 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanistically, statins induce oxidative stress accumulation and apoptosis through the GGPP synthase?1 (GGPS1)-RAB7A-autophagy axis. Statin treatment overcomes both intrinsic and acquired SCLC chemoresistance in vivo across different SCLC PDX models bearing high GGPS1 levels. Moreover, we show that GGPS1 expression is negatively associated with survival in patients with SCLC | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Fluvastatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.77E-55 Fold-change: 1.07E-01 Z-score: 1.81E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Steroid biosynthesis signaling pathway | Activation | hsa00100 | |
| Terpenoid bacKbone biosynthesis signaling pathway | Activation | hsa00900 | ||
| Steroid hormone biosynthesis signaling pathway | Activation | hsa00140 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-10A-neoT cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5554 |
| In Vivo Model | SV40 C3TAg transgenic mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Clariom D RNA profiling assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired resistance to fluvastatin is mediated by restorative upregulation of cholesterol biosynthesis pathway genes. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.77E-55; Fold-change: 5.78E-01; Z-score: 1.12E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 4.14E-12; Fold-change: 6.97E-01; Z-score: 1.36E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
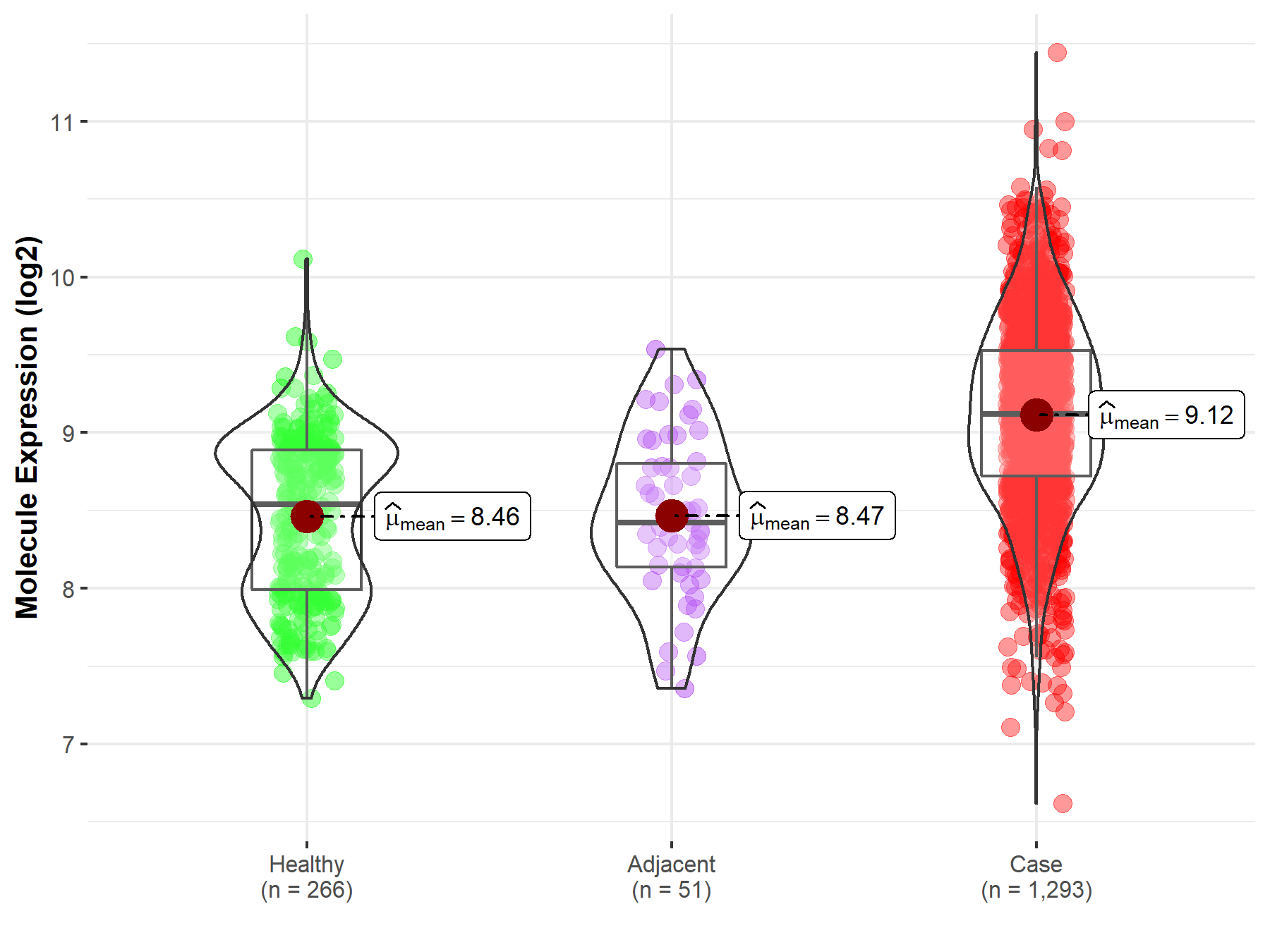
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

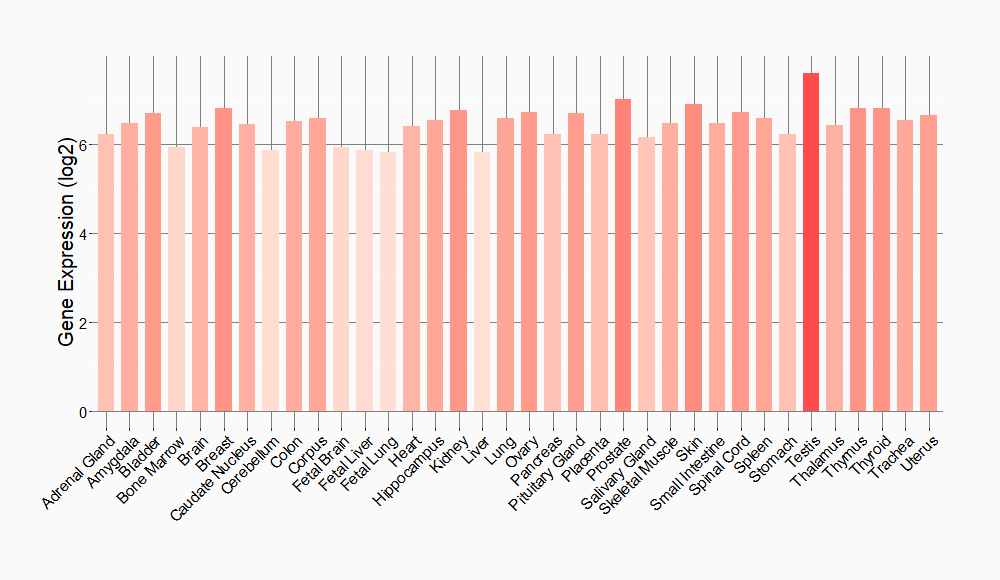
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
