Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00648)
| Name |
Spindlin-1 (SFPQ)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ovarian cancer-related protein; Spindlin1; OCR; SPIN
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
SPIN1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr9:88388430-88478694[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MKTPFGKTPGQRSRADAGHAGVSANMMKKRTSHKKHRSSVGPSKPVSQPRRNIVGCRIQH
GWKEGNGPVTQWKGTVLDQVPVNPSLYLIKYDGFDCVYGLELNKDERVSALEVLPDRVAT SRISDAHLADTMIGKAVEHMFETEDGSKDEWRGMVLARAPVMNTWFYITYEKDPVLYMYQ LLDDYKEGDLRIMPDSNDSPPAEREPGEVVDSLVGKQVEYAKEDGSKRTGMVIHQVEAKP SVYFIKFDDDFHIYVYDLVKTS Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Chromatin reader that specifically recognizes and binds histone H3 both trimethylated at 'Lys-4' and asymmetrically dimethylated at 'Arg-8' (H3K4me3 and H3R8me2a) and acts as an activator of Wnt signaling pathway downstream of PRMT2. In case of cancer, promotes cell cancer proliferation via activation of the Wnt signaling pathway. Overexpression induces metaphase arrest and chromosomal instability. Localizes to active rDNA loci and promotes the expression of rRNA genes. May play a role in cell-cycle regulation during the transition from gamete to embryo. Involved in oocyte meiotic resumption, a process that takes place before ovulation to resume meiosis of oocytes blocked in prophase I: may act by regulating maternal transcripts to control meiotic resumption.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.38E-01 Fold-change: -6.79E-03 Z-score: -1.49E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| MDA-MB-468 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0419 | |
| MCF-7/ADM cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-489 inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells. miR-489 suppressed cell migration and invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro. miR-489 increased the chemosensitivity of breast cancer and impaired tumour growth and invasion capabilities in vivo. PIk3CA, AkT, CREB1 and BCL2 act downstream of SPIN1 and were found to be decreased by miR-489. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.38E-01; Fold-change: -4.00E-02; Z-score: -1.00E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.49E-01; Fold-change: -1.26E-01; Z-score: -1.65E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
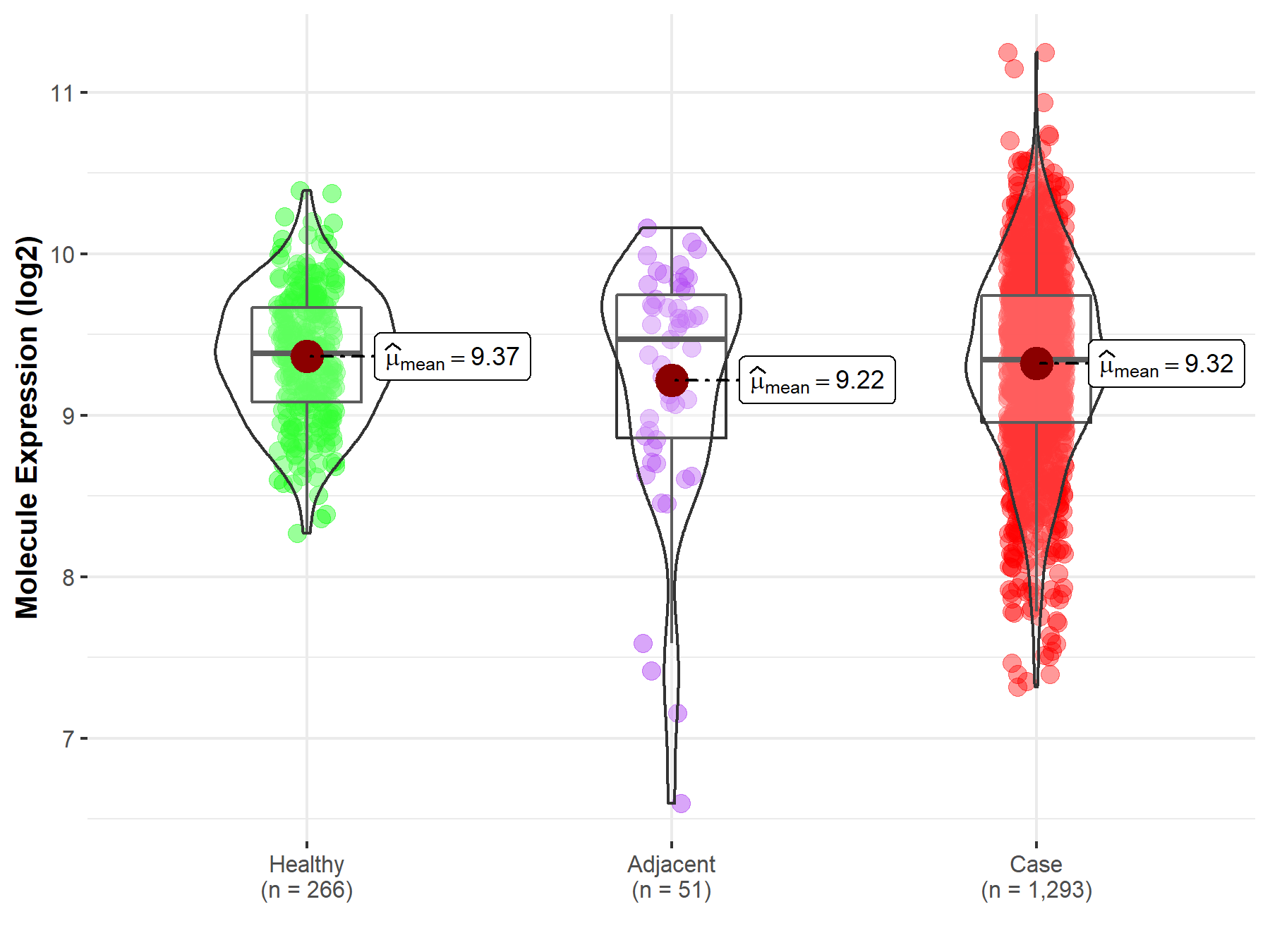
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

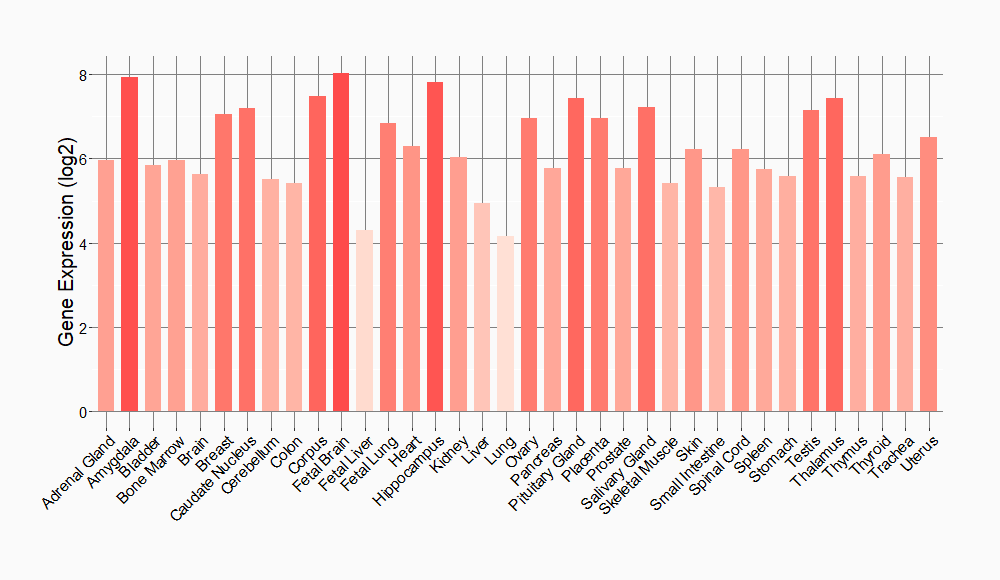
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
