Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00398)
| Name |
Glutathione synthetase (GSH)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
GSH synthetase; GSH-S; Glutathione synthase
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
GSS
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr20:34928432-34956027[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MATNWGSLLQDKQQLEELARQAVDRALAEGVLLRTSQEPTSSEVVSYAPFTLFPSLVPSA
LLEQAYAVQMDFNLLVDAVSQNAAFLEQTLSSTIKQDDFTARLFDIHKQVLKEGIAQTVF LGLNRSDYMFQRSADGSPALKQIEINTISASFGGLASRTPAVHRHVLSVLSKTKEAGKIL SNNPSKGLALGIAKAWELYGSPNALVLLIAQEKERNIFDQRAIENELLARNIHVIRRTFE DISEKGSLDQDRRLFVDGQEIAVVYFRDGYMPRQYSLQNWEARLLLERSHAAKCPDIATQ LAGTKKVQQELSRPGMLEMLLPGQPEAVARLRATFAGLYSLDVGEEGDQAIAEALAAPSR FVLKPQREGGGNNLYGEEMVQALKQLKDSEERASYILMEKIEPEPFENCLLRPGSPARVV QCISELGIFGVYVRQEKTLVMNKHVGHLLRTKAIEHADGGVAAGVAVLDNPYPV Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Catalyzes the production of glutathione from gamma-glutamylcysteine and glycine in an ATP-dependent manner. Glutathione (gamma-glutamylcysteinylglycine, GSH) is the most abundant intracellular thiol in living aerobic cells and is required for numerous processes including the protection of cells against oxidative damage, amino acid transport, the detoxification of foreign compounds, the maintenance of protein sulfhydryl groups in a reduced state and acts as a cofactor for a number of enzymes.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
7 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.67E-68 Fold-change: 8.32E-02 Z-score: 2.09E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |
| Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Vi-cell cell viability analyzer assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-21 achieves the drug resistance effect through three mechanisms: Increasing MDR1 and MPR1 expression levels, and enhancing drug efflux from the cells; increasing GSH, superoxide dismutase and GST-Pi expression levels and promoting drug inactivation; and inhibiting the PI3k signaling pathway and in turn inhibiting apoptotic signaling. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Idebenone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vivo Model | Swiss albino mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Ellman assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Pre-treatment resistance testing; Post-treatment resistance testing | |||
| Mechanism Description | IDB had successful control over drug resistance in the rotenone corneal kindled model by bypassing blocked complex I. IDB has a good safety profile and can be considered an adjuvant along with standard antiseizure drugs in drug-resistant patients. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lamotrigine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vivo Model | Swiss albino mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Ellman assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Pre-treatment resistance testing; Post-treatment resistance testing | |||
| Mechanism Description | The involvement of complex I in drug resistance is well established in epilepsy; therefore, the model chosen for this study was rotenone corneal kindled model of drug resistance using rotenone as a selective irreversible inhibitor of complex I, which have shown resistance to drugs such as valproate, levetiracetam, lamotrigine, pregabalin, carbamazepine, zonisamide, topiramate, gabapentin and their combinations | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Levetiracetam | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vivo Model | Swiss albino mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Ellman assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Pre-treatment resistance testing; Post-treatment resistance testing | |||
| Mechanism Description | The involvement of complex I in drug resistance is well established in epilepsy; therefore, the model chosen for this study was rotenone corneal kindled model of drug resistance using rotenone as a selective irreversible inhibitor of complex I, which have shown resistance to drugs such as valproate, levetiracetam, lamotrigine, pregabalin, carbamazepine, zonisamide, topiramate, gabapentin and their combinations | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Phenytoin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vivo Model | Swiss albino mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Ellman assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Pre-treatment resistance testing; Post-treatment resistance testing | |||
| Mechanism Description | The involvement of complex I in drug resistance is well established in epilepsy; therefore, the model chosen for this study was rotenone corneal kindled model of drug resistance using rotenone as a selective irreversible inhibitor of complex I, which have shown resistance to drugs such as valproate, levetiracetam, lamotrigine, pregabalin, carbamazepine, zonisamide, topiramate, gabapentin and their combinations | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pregabalin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vivo Model | Swiss albino mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Ellman assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Pre-treatment resistance testing; Post-treatment resistance testing | |||
| Mechanism Description | The involvement of complex I in drug resistance is well established in epilepsy; therefore, the model chosen for this study was rotenone corneal kindled model of drug resistance using rotenone as a selective irreversible inhibitor of complex I, which have shown resistance to drugs such as valproate, levetiracetam, lamotrigine, pregabalin, carbamazepine, zonisamide, topiramate, gabapentin and their combinations | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Valproic acid | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vivo Model | Swiss albino mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Ellman assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Pre-treatment resistance testing; Post-treatment resistance testing | |||
| Mechanism Description | The involvement of complex I in drug resistance is well established in epilepsy; therefore, the model chosen for this study was rotenone corneal kindled model of drug resistance using rotenone as a selective irreversible inhibitor of complex I, which have shown resistance to drugs such as valproate, levetiracetam, lamotrigine, pregabalin, carbamazepine, zonisamide, topiramate, gabapentin and their combinations | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.67E-68; Fold-change: 4.98E-01; Z-score: 2.03E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 5.04E-48; Fold-change: 4.94E-01; Z-score: 2.13E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
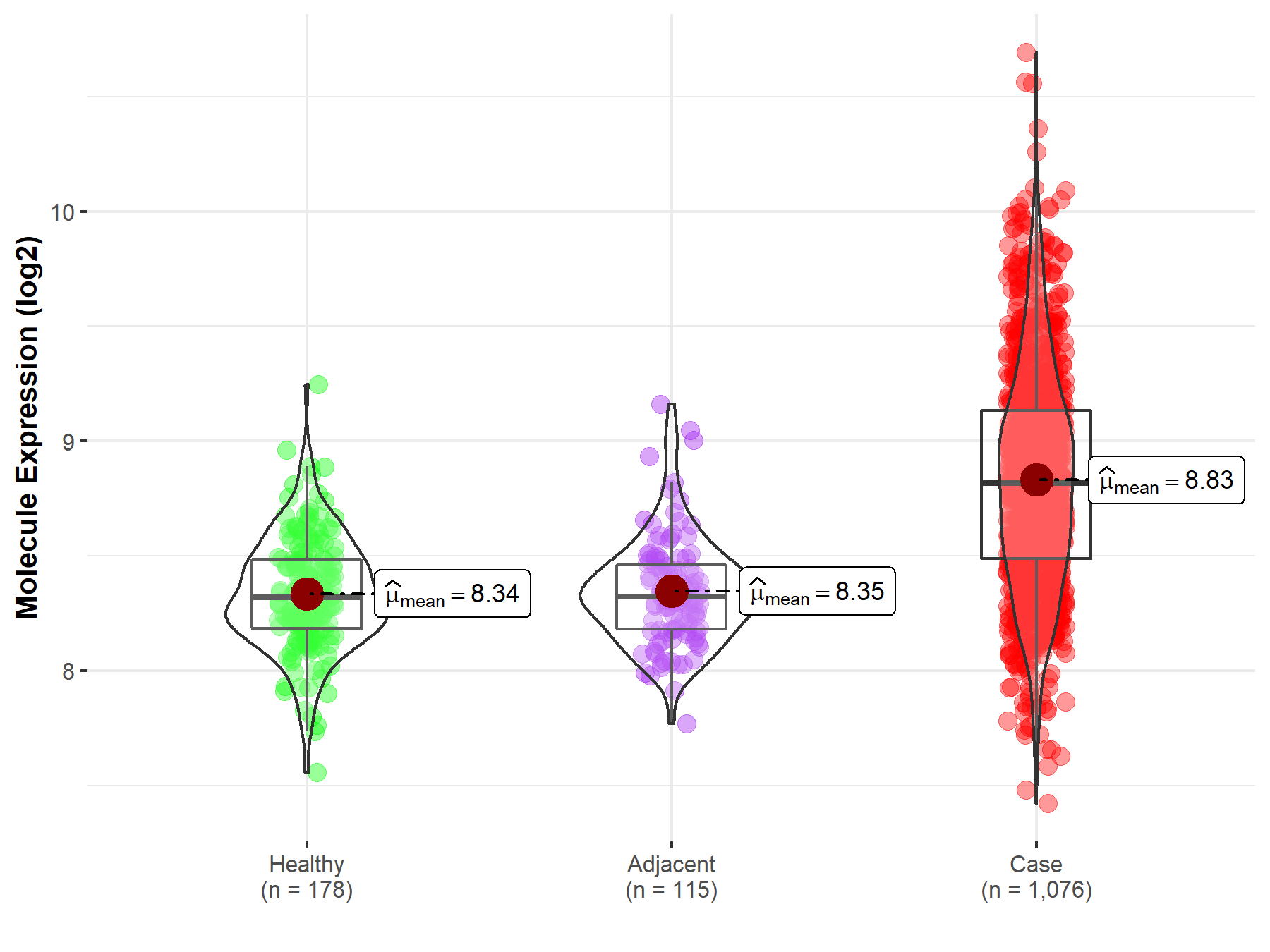
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

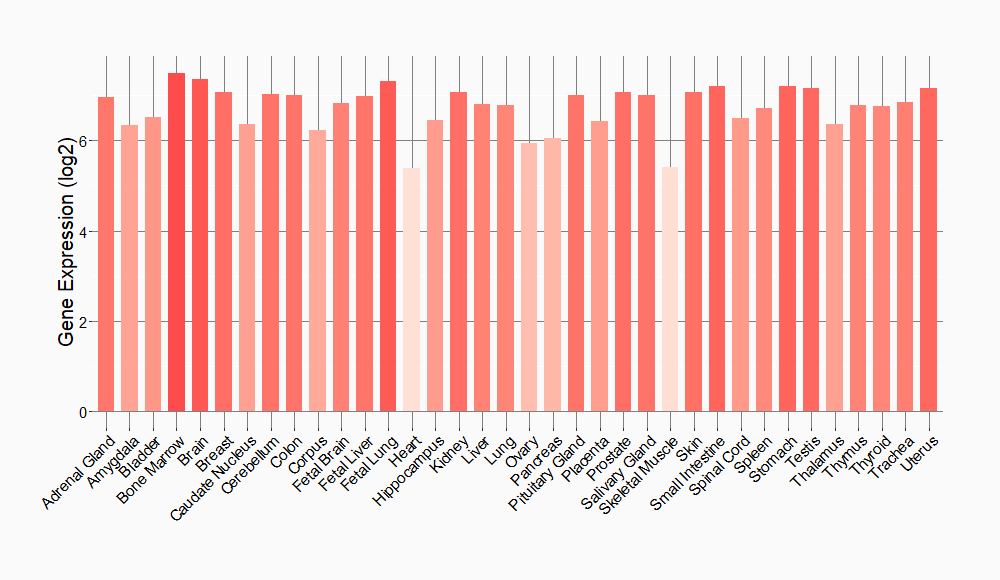
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
