Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00232)
| Name |
Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein (ARC)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
hArc; Activity-regulated gene 3.1 protein homolog; ARC/ARG3.1; Arg3.1; KIAA0278
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
ARC
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr8:142611049-142614479[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MELDHRTSGGLHAYPGPRGGQVAKPNVILQIGKCRAEMLEHVRRTHRHLLAEVSKQVERE
LKGLHRSVGKLESNLDGYVPTSDSQRWKKSIKACLCRCQETIANLERWVKREMHVWREVF YRLERWADRLESTGGKYPVGSESARHTVSVGVGGPESYCHEADGYDYTVSPYAITPPPAA GELPGQEPAEAQQYQPWVPGEDGQPSPGVDTQIFEDPREFLSHLEEYLRQVGGSEEYWLS QIQNHMNGPAKKWWEFKQGSVKNWVEFKKEFLQYSEGTLSREAIQRELDLPQKQGEPLDQ FLWRKRDLYQTLYVDADEEEIIQYVVGTLQPKLKRFLRHPLPKTLEQLIQRGMEVQDDLE QAAEPAGPHLPVEDEAETLTPAPNSESVASDRTQPE Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Master regulator of synaptic plasticity that self-assembles into virion-like capsids that encapsulate RNAs and mediate intercellular RNA transfer in the nervous system. ARC protein is released from neurons in extracellular vesicles that mediate the transfer of ARC mRNA into new target cells, where ARC mRNA can undergo activity-dependent translation. ARC capsids are endocytosed and are able to transfer ARC mRNA into the cytoplasm of neurons. Acts as a key regulator of synaptic plasticity: required for protein synthesis-dependent forms of long-term potentiation (LTP) and depression (LTD) and for the formation of long-term memory. Regulates synaptic plasticity by promoting endocytosis of AMPA receptors (AMPARs) in response to synaptic activity: this endocytic pathway maintains levels of surface AMPARs in response to chronic changes in neuronal activity through synaptic scaling, thereby contributing to neuronal homeostasis. Acts as a postsynaptic mediator of activity-dependent synapse elimination in the developing cerebellum by mediating elimination of surplus climbing fiber synapses. Accumulates at weaker synapses, probably to prevent their undesired enhancement. This suggests that ARC-containing virion-like capsids may be required to eliminate synaptic material. Required to transduce experience into long-lasting changes in visual cortex plasticity and for long-term memory (By similarity). Involved in postsynaptic trafficking and processing of amyloid-beta A4 (APP) via interaction with PSEN1 (By similarity). In addition to its role in synapses, also involved in the regulation of the immune system: specifically expressed in skin-migratory dendritic cells and regulates fast dendritic cell migration, thereby regulating T-cell activation (By similarity).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | BGC-823 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3360 |
| MGC-803 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5334 | |
| AGS cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0139 | |
| GES-1 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_EQ22 | |
| NCI-N87 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1603 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Trypan blue exclusion assay; Tunel assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Restoration of miR-185 alone can inhibit gastric cancer tumor growth. Moreover, combination therapy using enforced miR-185 expression and lower dose chemotherapeutic drugs had an effective therapeutic activity against large established tumors, with decreased host toxicity. miR-185 increases the chemosensitivity of gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. It exerts tumor-suppressing function through negatively regulating ARC. Besides, miR-185 upregulation in response to cisplatin or doxorubicin treatment in gastric cancer cells is dependent on RUNX3 transcriptional activity. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | BGC-823 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3360 |
| MGC-803 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5334 | |
| AGS cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0139 | |
| GES-1 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_EQ22 | |
| NCI-N87 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1603 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Trypan blue exclusion assay; Tunel assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Restoration of miR-185 alone can inhibit gastric cancer tumor growth. Moreover, combination therapy using enforced miR-185 expression and lower dose chemotherapeutic drugs had an effective therapeutic activity against large established tumors, with decreased host toxicity. miR-185 increases the chemosensitivity of gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. It exerts tumor-suppressing function through negatively regulating ARC. Besides, miR-185 upregulation in response to cisplatin or doxorubicin treatment in gastric cancer cells is dependent on RUNX3 transcriptional activity. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.23E-01; Fold-change: 8.08E-02; Z-score: 3.15E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.98E-07; Fold-change: 2.40E-01; Z-score: 1.43E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
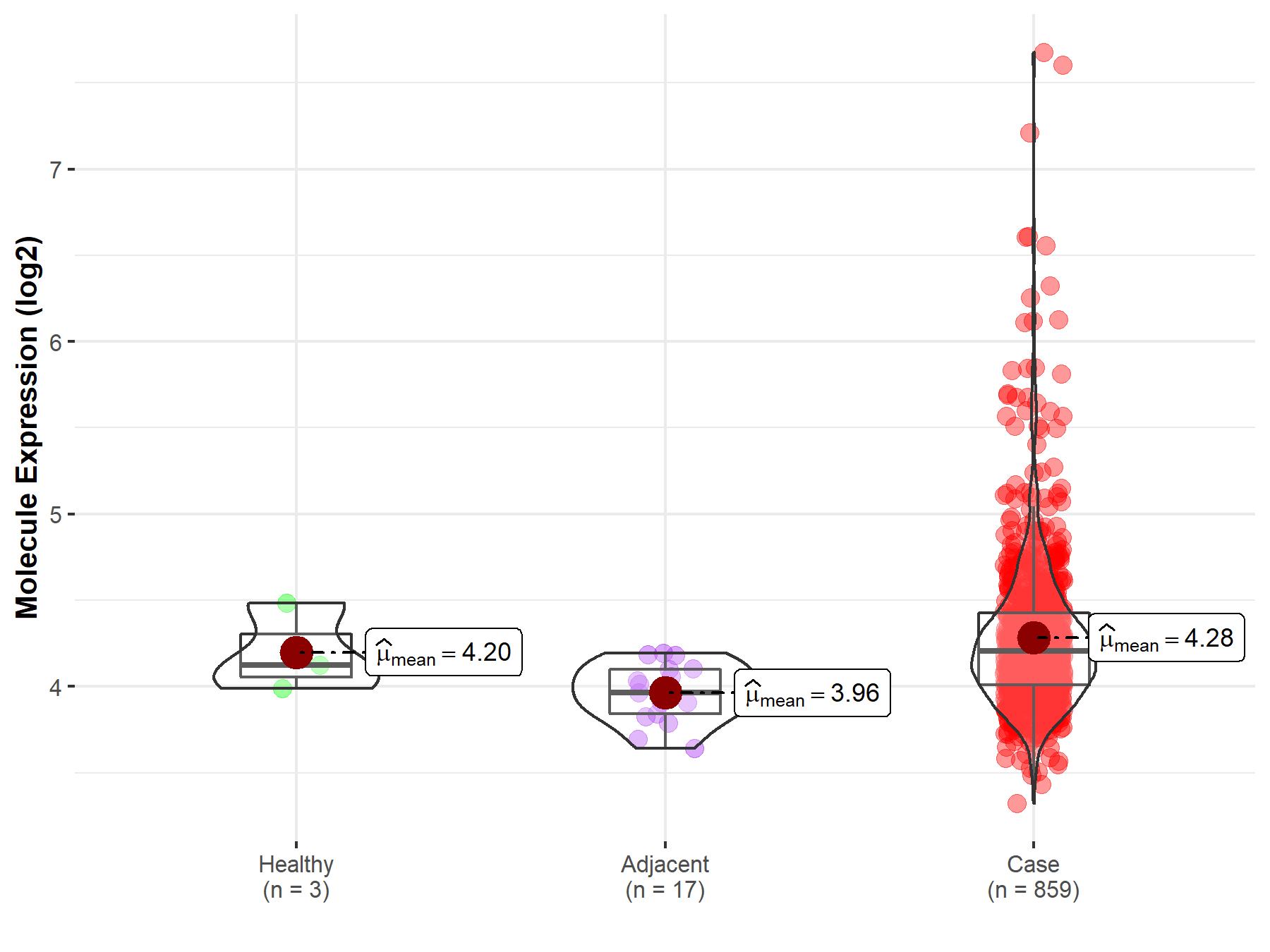
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

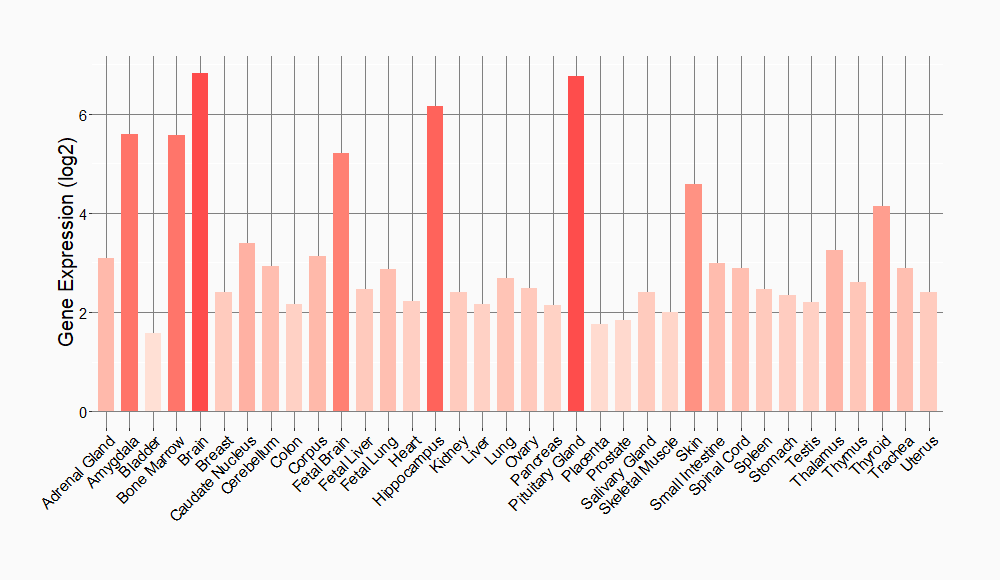
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
