Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00227)
| Name |
Annexin A1 (ANXA1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Annexin I; Annexin-1; Calpactin II; Calpactin-2; Chromobindin-9; Lipocortin I; Phospholipase A2 inhibitory protein; p35; ANX1; LPC1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
ANXA1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr9:73151865-73170393[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MAMVSEFLKQAWFIENEEQEYVQTVKSSKGGPGSAVSPYPTFNPSSDVAALHKAIMVKGV
DEATIIDILTKRNNAQRQQIKAAYLQETGKPLDETLKKALTGHLEEVVLALLKTPAQFDA DELRAAMKGLGTDEDTLIEILASRTNKEIRDINRVYREELKRDLAKDITSDTSGDFRNAL LSLAKGDRSEDFGVNEDLADSDARALYEAGERRKGTDVNVFNTILTTRSYPQLRRVFQKY TKYSKHDMNKVLDLELKGDIEKCLTAIVKCATSKPAFFAEKLHQAMKGVGTRHKALIRIM VSRSEIDMNDIKAFYQKMYGISLCQAILDETKGDYEKILVALCGGN Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Plays important roles in the innate immune response as effector of glucocorticoid-mediated responses and regulator of the inflammatory process. Has anti-inflammatory activity. Plays a role in glucocorticoid-mediated down-regulation of the early phase of the inflammatory response. Contributes to the adaptive immune response by enhancing signaling cascades that are triggered by T-cell activation, regulates differentiation and proliferation of activated T-cells. Promotes the differentiation of T-cells into Th1 cells and negatively regulates differentiation into Th2 cells. Has no effect on unstimulated T cells. Negatively regulates hormone exocytosis via activation of the formyl peptide receptors and reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. Has high affinity for Ca(2+) and can bind up to eight Ca(2+) ions. Displays Ca(2+)-dependent binding to phospholipid membranes. Plays a role in the formation of phagocytic cups and phagosomes. Plays a role in phagocytosis by mediating the Ca(2+)-dependent interaction between phagosomes and the actin cytoskeleton.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Chronic myelogenous leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic myelogenous leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The downregulated ANXA1,whose new role in apoptosis and cancer revealed recently,expression contributes considerably to the observed drug resistance in k562/ADR cells. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Whole blood | |
| The Specified Disease | Myelofibrosis | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.22E-01; Fold-change: 1.03E-01; Z-score: 2.16E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
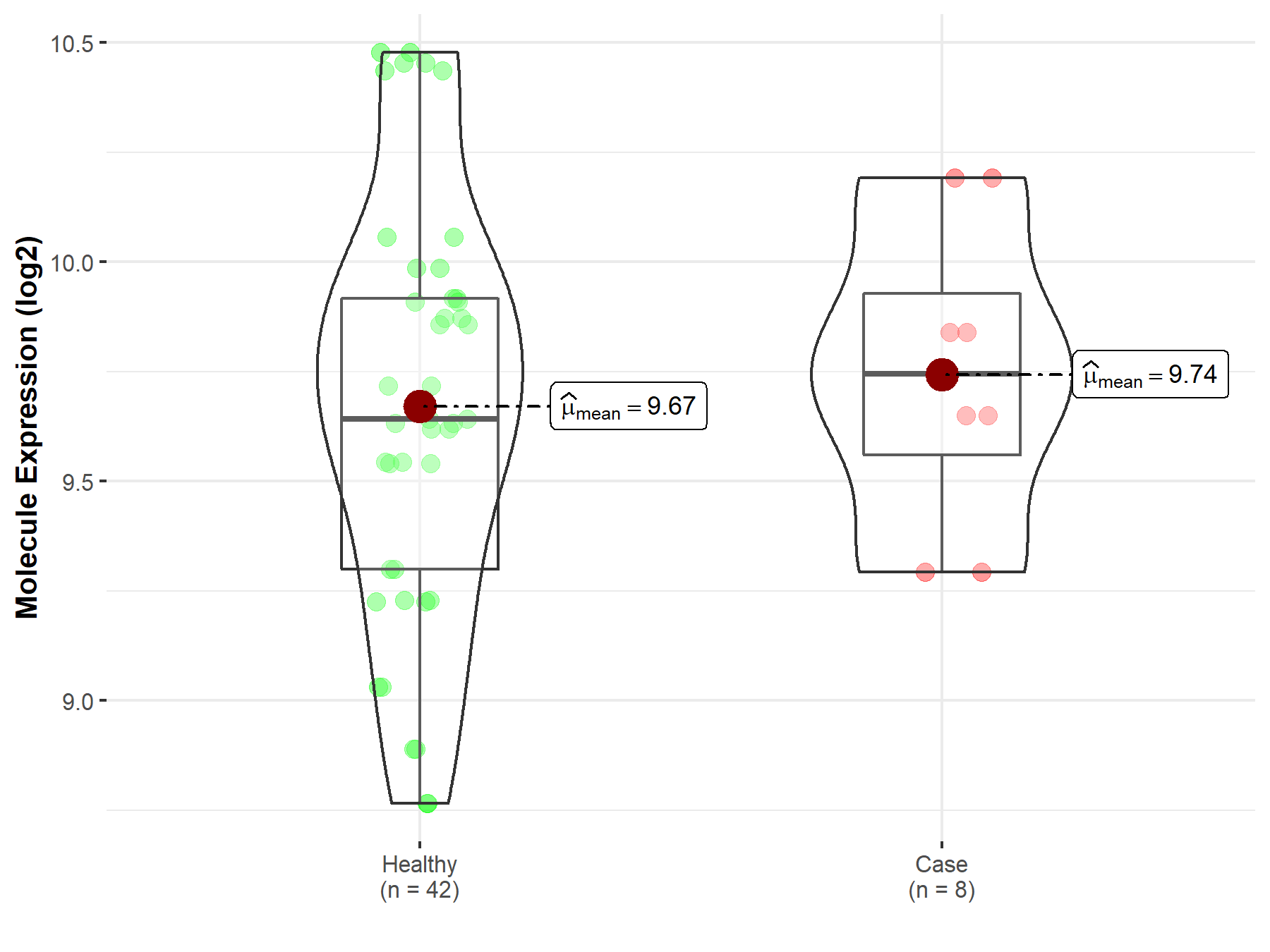
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Whole blood | |
| The Specified Disease | Polycythemia vera | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.25E-04; Fold-change: -3.36E-01; Z-score: -6.91E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
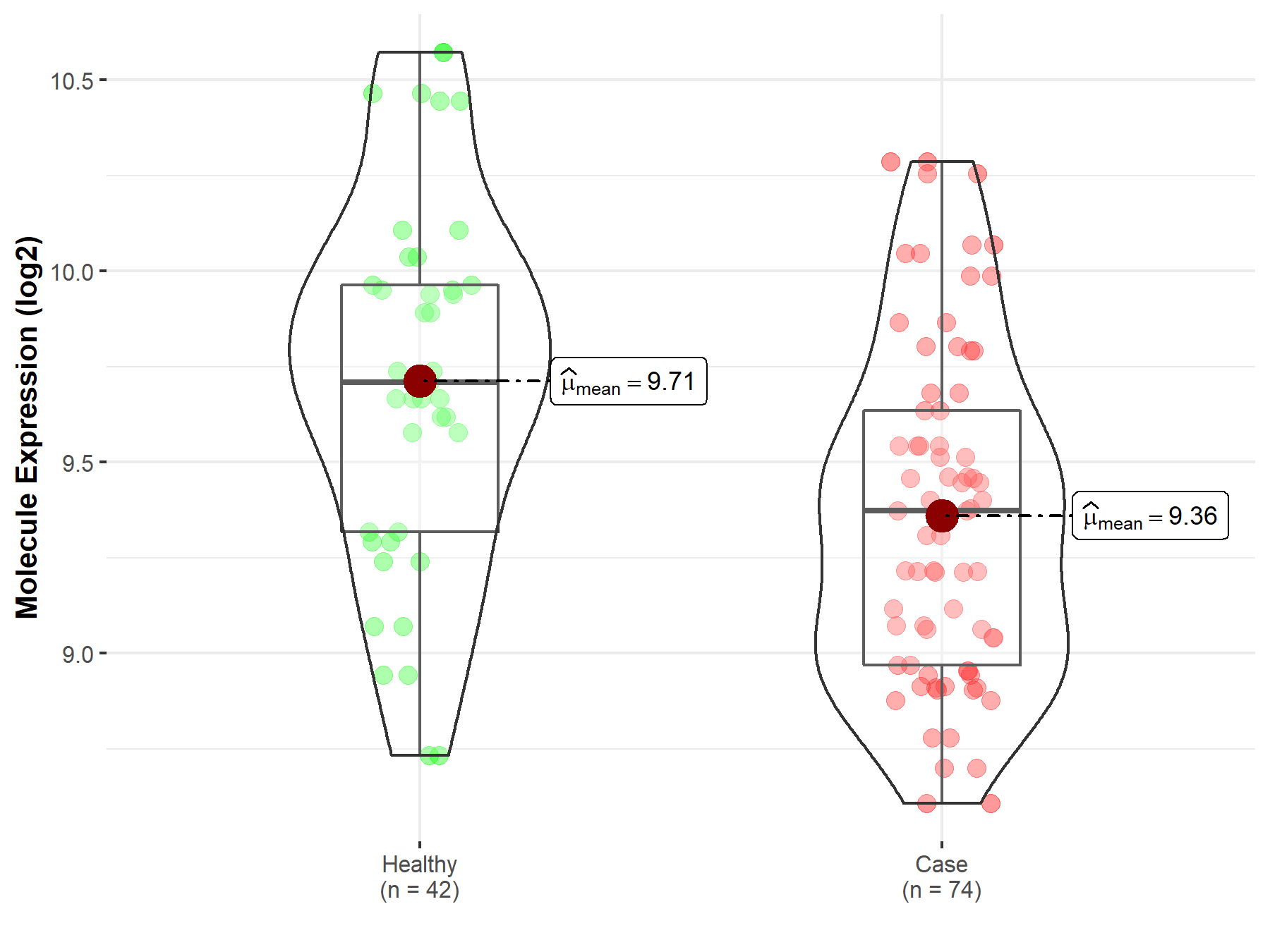
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

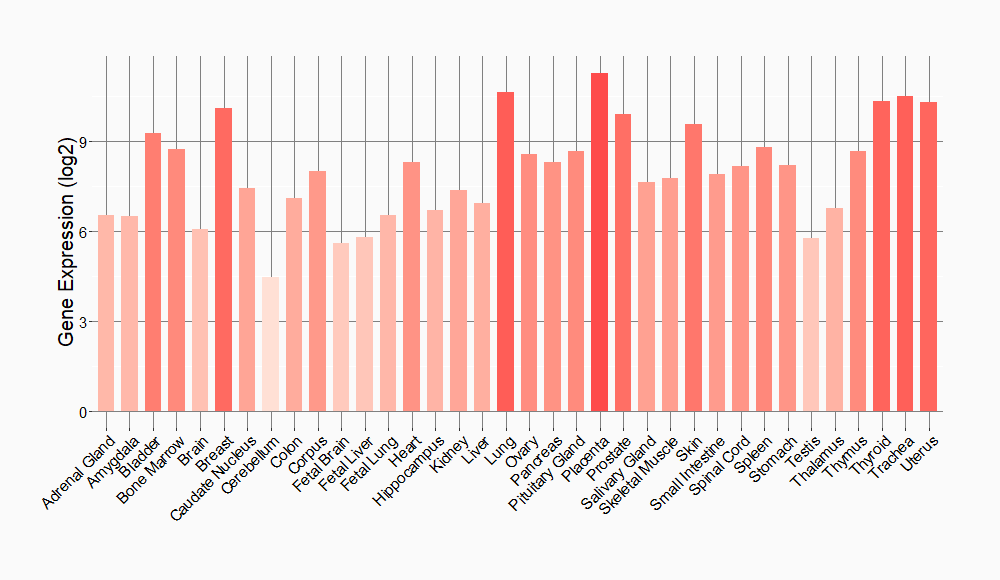
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
