Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00225)
| Name |
Androgen receptor (AR)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Dihydrotestosterone receptor; Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group C member 4; DHTR; NR3C4
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
AR
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chrX:67544021-67730619[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MEVQLGLGRVYPRPPSKTYRGAFQNLFQSVREVIQNPGPRHPEAASAAPPGASLLLLQQQ
QQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQQETSPRQQQQQQGEDGSPQAHRRGPTGYLVLDEEQQPSQPQ SALECHPERGCVPEPGAAVAASKGLPQQLPAPPDEDDSAAPSTLSLLGPTFPGLSSCSAD LKDILSEASTMQLLQQQQQEAVSEGSSSGRAREASGAPTSSKDNYLGGTSTISDNAKELC KAVSVSMGLGVEALEHLSPGEQLRGDCMYAPLLGVPPAVRPTPCAPLAECKGSLLDDSAG KSTEDTAEYSPFKGGYTKGLEGESLGCSGSAAAGSSGTLELPSTLSLYKSGALDEAAAYQ SRDYYNFPLALAGPPPPPPPPHPHARIKLENPLDYGSAWAAAAAQCRYGDLASLHGAGAA GPGSGSPSAAASSSWHTLFTAEEGQLYGPCGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGEAGAVAP YGYTRPPQGLAGQESDFTAPDVWYPGGMVSRVPYPSPTCVKSEMGPWMDSYSGPYGDMRL ETARDHVLPIDYYFPPQKTCLICGDEASGCHYGALTCGSCKVFFKRAAEGKQKYLCASRN DCTIDKFRRKNCPSCRLRKCYEAGMTLGARKLKKLGNLKLQEEGEASSTTSPTEETTQKL TVSHIEGYECQPIFLNVLEAIEPGVVCAGHDNNQPDSFAALLSSLNELGERQLVHVVKWA KALPGFRNLHVDDQMAVIQYSWMGLMVFAMGWRSFTNVNSRMLYFAPDLVFNEYRMHKSR MYSQCVRMRHLSQEFGWLQITPQEFLCMKALLLFSIIPVDGLKNQKFFDELRMNYIKELD RIIACKRKNPTSCSRRFYQLTKLLDSVQPIARELHQFTFDLLIKSHMVSVDFPEMMAEII SVQVPKILSGKVKPIYFHTQ Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Steroid hormone receptors are ligand-activated transcription factors that regulate eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Transcription factor activity is modulated by bound coactivator and corepressor proteins like ZBTB7A that recruits NCOR1 and NCOR2 to the androgen response elements/ARE on target genes, negatively regulating androgen receptor signaling and androgen-induced cell proliferation. Transcription activation is also down-regulated by NR0B2. Activated, but not phosphorylated, by HIPK3 and ZIPK/DAPK3.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
7 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Abiraterone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number gain |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequencing assay; Exome sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Accordingly, AR amplification was detected in circulating cell-free DNA and was shown to be associated with enzalutamide and abiraterone treatment resistance in a cohort of 62 CRPC patients. | |||
| Disease Class: Primary prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.Z] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Primary prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Abiraterone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number gain |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequencing assay; Exome sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Accordingly, AR amplification was detected in circulating cell-free DNA and was shown to be associated with enzalutamide and abiraterone treatment resistance in a cohort of 62 CRPC patients. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Apalutamide | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F877L (c.2629T>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.44 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.69 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
-
H
-
I
-
E
-
G
-
Y
-
E
670
|
-
C
P
Q
I
P
F
I
L
F
N
L
V
N
L
V
E
L
A
E
680
|
I
A
E
I
P
E
G
P
V
G
V
V
C
V
A
C
G
A
H
G
690
|
D
H
N
D
N
N
Q
N
P
Q
D
P
S
D
F
S
A
F
A
A
700
|
L
A
L
L
S
L
S
S
L
S
N
L
E
N
L
E
G
L
E
G
710
|
R
E
Q
R
L
Q
V
L
H
V
V
H
V
V
K
V
W
K
A
W
720
|
K
A
A
K
L
A
P
L
G
P
F
G
R
F
N
R
L
N
H
L
730
|
V
H
D
V
D
D
Q
D
M
Q
A
M
V
A
I
V
Q
I
Y
Q
740
|
S
Y
W
S
M
W
G
M
L
G
M
L
V
M
F
V
A
F
M
A
750
|
G
M
W
G
R
W
S
R
F
S
T
F
N
T
V
N
N
V
S
N
760
|
R
S
M
R
L
M
Y
L
F
Y
A
F
P
A
D
P
L
D
V
L
770
|
F
V
N
F
E
N
Y
E
R
Y
M
R
H
M
K
H
S
K
R
S
780
|
M
R
Y
M
S
Y
Q
S
C
Q
V
C
R
V
M
R
R
M
H
R
790
|
L
H
S
L
Q
S
E
Q
F
E
G
F
W
G
L
W
Q
L
I
Q
800
|
T
I
P
T
Q
P
E
Q
F
E
L
F
C
L
M
C
K
M
A
K
810
|
L
A
L
L
L
L
F
L
S
F
I
S
I
I
P
I
V
P
D
V
820
|
G
D
L
G
K
L
N
K
Q
N
K
Q
F
K
F
F
D
F
E
D
830
|
L
E
R
L
M
R
N
M
Y
N
I
Y
K
I
E
K
L
E
D
L
840
|
R
D
I
R
I
I
A
I
C
A
A
C
R
K
K
R
N
K
P
N
850
|
T
P
S
T
C
S
S
C
R
S
R
R
F
R
Y
F
Q
Y
L
Q
860
|
T
L
K
T
L
K
L
L
D
L
S
D
V
S
Q
V
P
Q
I
P
870
|
A
I
R
A
E
R
L
E
H
L
Q
H
F
Q
T
L
F
A
D
F
880
|
L
D
L
L
I
L
K
I
S
K
H
S
M
H
V
M
S
V
V
S
890
|
D
V
F
D
P
F
E
P
M
E
M
M
A
M
E
A
I
E
I
I
900
|
S
I
V
S
Q
V
V
Q
P
V
K
P
I
K
L
I
S
L
G
S
910
|
K
G
V
K
K
V
P
K
I
P
Y
I
F
Y
H
F
T
H
Q
T
920
|
-
Q
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 | |||||||||
| PC3 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | SHO male mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.F877L (c.2629T>C) in gene AR cause the resistance of Apalutamide by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Apalutamide | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F877L (c.2629T>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.44 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.69 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
S
-
H
-
I
-
E
-
G
-
Y
-
E
670
|
-
C
P
Q
I
P
F
I
L
F
N
L
V
N
L
V
E
L
A
E
680
|
I
A
E
I
P
E
G
P
V
G
V
V
C
V
A
C
G
A
H
G
690
|
D
H
N
D
N
N
Q
N
P
Q
D
P
S
D
F
S
A
F
A
A
700
|
L
A
L
L
S
L
S
S
L
S
N
L
E
N
L
E
G
L
E
G
710
|
R
E
Q
R
L
Q
V
L
H
V
V
H
V
V
K
V
W
K
A
W
720
|
K
A
A
K
L
A
P
L
G
P
F
G
R
F
N
R
L
N
H
L
730
|
V
H
D
V
D
D
Q
D
M
Q
A
M
V
A
I
V
Q
I
Y
Q
740
|
S
Y
W
S
M
W
G
M
L
G
M
L
V
M
F
V
A
F
M
A
750
|
G
M
W
G
R
W
S
R
F
S
T
F
N
T
V
N
N
V
S
N
760
|
R
S
M
R
L
M
Y
L
F
Y
A
F
P
A
D
P
L
D
V
L
770
|
F
V
N
F
E
N
Y
E
R
Y
M
R
H
M
K
H
S
K
R
S
780
|
M
R
Y
M
S
Y
Q
S
C
Q
V
C
R
V
M
R
R
M
H
R
790
|
L
H
S
L
Q
S
E
Q
F
E
G
F
W
G
L
W
Q
L
I
Q
800
|
T
I
P
T
Q
P
E
Q
F
E
L
F
C
L
M
C
K
M
A
K
810
|
L
A
L
L
L
L
F
L
S
F
I
S
I
I
P
I
V
P
D
V
820
|
G
D
L
G
K
L
N
K
Q
N
K
Q
F
K
F
F
D
F
E
D
830
|
L
E
R
L
M
R
N
M
Y
N
I
Y
K
I
E
K
L
E
D
L
840
|
R
D
I
R
I
I
A
I
C
A
A
C
R
K
K
R
N
K
P
N
850
|
T
P
S
T
C
S
S
C
R
S
R
R
F
R
Y
F
Q
Y
L
Q
860
|
T
L
K
T
L
K
L
L
D
L
S
D
V
S
Q
V
P
Q
I
P
870
|
A
I
R
A
E
R
L
E
H
L
Q
H
F
Q
T
L
F
A
D
F
880
|
L
D
L
L
I
L
K
I
S
K
H
S
M
H
V
M
S
V
V
S
890
|
D
V
F
D
P
F
E
P
M
E
M
M
A
M
E
A
I
E
I
I
900
|
S
I
V
S
Q
V
V
Q
P
V
K
P
I
K
L
I
S
L
G
S
910
|
K
G
V
K
K
V
P
K
I
P
Y
I
F
Y
H
F
T
H
Q
T
920
|
-
Q
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 | |||||||||
| PC3 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | SHO male mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.F877L (c.2629T>C) in gene AR cause the resistance of Apalutamide by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Apalutamide | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F877L (. |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 | |||||||||
| PC3 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | SHO male mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.F877L (. in gene AR cause the resistance of Apalutamide by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Bicalutamide | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.W742L (c.2225G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.07 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.70 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
640
|
S
-
L
-
E
-
E
-
G
-
E
-
A
-
S
-
S
-
T
-
650
|
T
-
S
-
P
-
T
-
E
-
E
-
T
-
T
-
Q
-
K
-
660
|
L
-
T
-
V
-
S
-
H
-
I
I
E
E
G
G
Y
Y
E
E
670
|
C
C
Q
Q
P
P
I
I
F
F
L
L
N
N
V
V
L
L
E
E
680
|
A
A
I
I
E
E
P
P
G
G
V
V
V
V
C
C
A
A
G
G
690
|
H
H
D
D
N
N
N
N
Q
Q
P
P
D
D
S
S
F
F
A
A
700
|
A
A
L
L
L
L
S
S
S
S
L
L
N
N
E
E
L
L
G
G
710
|
E
E
R
R
Q
Q
L
L
V
V
H
H
V
V
V
V
K
K
W
W
720
|
A
A
K
K
A
A
L
L
P
P
G
G
F
F
R
R
N
N
L
L
730
|
H
H
V
V
D
D
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
740
|
Y
Y
S
S
W
L
M
M
G
G
L
L
M
M
V
V
F
F
A
A
750
|
M
M
G
G
W
W
R
R
S
S
F
F
T
T
N
N
V
V
N
N
760
|
S
S
R
R
M
M
L
L
Y
Y
F
F
A
A
P
P
D
D
L
L
770
|
V
V
F
F
N
N
E
E
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
H
H
K
K
S
S
780
|
R
R
M
M
Y
Y
S
S
Q
Q
C
C
V
V
R
R
M
M
R
R
790
|
H
H
L
L
S
S
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
W
W
L
L
Q
Q
800
|
I
I
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
L
L
C
C
M
M
K
K
810
|
A
A
L
L
L
L
L
L
F
F
S
S
I
I
I
I
P
P
V
V
820
|
D
D
G
G
L
L
K
K
N
N
Q
Q
K
K
F
F
F
F
D
D
830
|
E
E
L
L
R
R
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
840
|
D
D
R
R
I
I
I
I
A
A
C
C
K
K
R
R
K
K
N
N
850
|
P
P
T
T
S
S
C
C
S
S
R
R
R
R
F
F
Y
Y
Q
Q
860
|
L
L
T
T
K
K
L
L
L
L
D
D
S
S
V
V
Q
Q
P
P
870
|
I
I
A
A
R
R
E
E
L
L
H
H
Q
Q
F
F
T
T
F
F
880
|
D
D
L
L
L
L
I
I
K
K
S
S
H
H
M
M
V
V
S
S
890
|
V
V
D
D
F
F
P
P
E
E
M
M
M
M
A
A
E
E
I
I
900
|
I
I
S
S
V
V
Q
Q
V
V
P
P
K
K
I
I
L
L
S
S
910
|
G
G
K
K
V
V
K
K
P
P
I
I
Y
Y
F
F
H
H
T
T
920
|
Q
Q
E
-
G
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Bicalutamide | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.W742C (c.2226G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Prolactinomas [ICD-11: 2F37.2] | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prolactinomas [ICD-11: 2F37.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Bromocriptine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | GH3 cells | Pituitary gland | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | CVCL_0273 |
| MMQ cells | Pituitary gland | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | CVCL_2117 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | AR plays a crucial role in mediating DA resistance in PRL adenoma. Mechanistically, AR promotes cell proliferation and PRL secretion and confers drug resistance by transcriptionally regulating NRF2 expression to maintain redox homeostasis in PA cells. Finally, combining AR targeting agents with BRC shows promise as a therapeutic strategy for treating PRL adenomas.?Antioxid. Redox Signal. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Enzalutamide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number gain |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequencing assay; Exome sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Accordingly, AR amplification was detected in circulating cell-free DNA and was shown to be associated with enzalutamide and abiraterone treatment resistance in a cohort of 62 CRPC patients. | |||
| Disease Class: Primary prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.Z] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Primary prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Enzalutamide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural variation | Copy number gain |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequencing assay; Exome sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Accordingly, AR amplification was detected in circulating cell-free DNA and was shown to be associated with enzalutamide and abiraterone treatment resistance in a cohort of 62 CRPC patients. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Flutamide | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T878A (c.2632A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.44 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
G
-
S
-
S
-
H
-
H
650
|
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
L
-
V
-
P
660
|
-
R
-
G
-
S
-
H
-
M
-
I
-
E
-
G
-
Y
-
E
670
|
-
C
-
Q
P
P
I
I
F
F
L
L
N
N
V
V
L
L
E
E
680
|
A
A
I
I
E
E
P
P
G
G
V
V
V
V
C
C
A
A
G
G
690
|
H
H
D
D
N
N
N
N
Q
Q
P
P
D
D
S
S
F
F
A
A
700
|
A
A
L
L
L
L
S
S
S
S
L
L
N
N
E
E
L
L
G
G
710
|
E
E
R
R
Q
Q
L
L
V
V
H
H
V
V
V
V
K
K
W
W
720
|
A
A
K
K
A
A
L
L
P
P
G
G
F
F
R
R
N
N
L
L
730
|
H
H
V
V
D
D
D
D
Q
Q
M
M
A
A
V
V
I
I
Q
Q
740
|
Y
Y
S
S
W
W
M
M
G
G
L
L
M
M
V
V
F
F
A
A
750
|
M
M
G
G
W
W
R
R
S
S
F
F
T
T
N
N
V
V
N
N
760
|
S
S
R
R
M
M
L
L
Y
Y
F
F
A
A
P
P
D
D
L
L
770
|
V
V
F
F
N
N
E
E
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
H
H
K
K
S
S
780
|
R
R
M
M
Y
Y
S
S
Q
Q
C
C
V
V
R
R
M
M
R
R
790
|
H
H
L
L
S
S
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
G
G
W
W
L
L
Q
Q
800
|
I
I
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
E
E
F
F
L
L
C
C
M
M
K
K
810
|
A
A
L
L
L
L
L
L
F
F
S
S
I
I
I
I
P
P
V
V
820
|
D
D
G
G
L
L
K
K
N
N
Q
Q
K
K
F
F
F
F
D
D
830
|
E
E
L
L
R
R
M
M
N
N
Y
Y
I
I
K
K
E
E
L
L
840
|
D
D
R
R
I
I
I
I
A
A
C
C
A
K
R
R
K
K
N
N
850
|
P
P
T
T
S
S
C
C
S
S
R
R
R
R
F
F
Y
Y
Q
Q
860
|
L
L
T
T
K
K
L
L
L
L
D
D
S
S
V
V
Q
Q
P
P
870
|
I
I
A
A
R
R
E
E
L
L
H
H
Q
Q
F
F
T
A
F
F
880
|
D
D
L
L
L
L
I
I
K
K
S
S
H
H
M
M
V
V
S
S
890
|
V
V
D
D
F
F
P
P
E
E
M
M
M
M
A
A
E
E
I
I
900
|
I
I
S
S
V
V
Q
Q
V
V
P
P
K
K
I
I
L
L
S
S
910
|
G
G
K
K
V
V
K
K
P
P
I
I
Y
Y
F
F
H
H
T
T
920
|
Q
Q
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Flutamide | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T877A |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Flutamide | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | LN-FLU cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | To obtain molecular evidence of the acquired resistance of the LN-FLU cells, we checked the expressions of significant proteins involved in prostate cell growth. As shown in, the LN-FLU cells showed less expression of the androgen receptor (AR) compared with the parental LNCaP cells, further confirming the androgen refractory state of the cells. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Hydroxyflutamide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T877A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Energy decomposition assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | However, a drug resistance problem appears after about one year's treatment. AR T877A is the first mutation that was found to cause a resistance problem. Then W741C_T877A and F876L_T877A mutations were also reported to cause resistance to HF, while W741C and F876L single mutations cannot. | |||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Hydroxyflutamide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation+Missense mutation | p.W741C+T877 |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Energy decomposition assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | However, a drug resistance problem appears after about one year's treatment. AR T877A is the first mutation that was found to cause a resistance problem. Then W741C_T877A and F876L_T877A mutations were also reported to cause resistance to HF, while W741C and F876L single mutations cannot. | |||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Hydroxyflutamide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation+Missense mutation | p.F876L+T877A |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Energy decomposition assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | However, a drug resistance problem appears after about one year's treatment. AR T877A is the first mutation that was found to cause a resistance problem. Then W741C_T877A and F876L_T877A mutations were also reported to cause resistance to HF, while W741C and F876L single mutations cannot. | |||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Activation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |
| In Vitro Model | LNCaP clone FGC cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1379 |
| 22Rv-1 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1045 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Cell protein extraction assay; Western blot assay; qRT-PCR; Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | This study revealed the role of p35-CDK5 in between PI3K/Akt and AR by utilizing LNCaP and 22Rv1 cells. Through the TCGA database analysis, we observed a positive correlation between PTEN and p35 expression, implying a potential negative correlation between PI3K/Akt activation and p35-CDK5. Inhibiting PI3K/Akt with LY294002, Capivasertib (AZD5363), or using an inactive Akt mutant significantly increased p35 expression and subsequently enhanced AR stability and activation in PCa cells. On the other hand, CDK5-knockdown reversed these effects. The involvement of the beta-catenin/Egr1-axis was observed in regulating PI3K/Akt inhibition and p35-CDK5 activation, implying a possible mechanistic connection. Importantly, CDK5 knockdown further reduced PI3K/Akt-inhibition-induced AR and cell viability maintenance, suggesting a compensatory role for CDK5-AR in maintaining cell viability under Akt inhibition. In conclusion, PI3K/Akt inhibition could trigger p35-CDK5-dependent AR activation and cell viability, highlighting p35-CDK5 as a critical link connecting PI3K/Akt inhibition to AR activation and pivotal in PCa cell resistance to PI3K/Akt blockade. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | LY-294002 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Activation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |
| In Vitro Model | LNCaP clone FGC cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1379 |
| 22Rv-1 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1045 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Cell protein extraction assay; Western blot assay; qRT-PCR; Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | This study revealed the role of p35-CDK5 in between PI3K/Akt and AR by utilizing LNCaP and 22Rv1 cells. Through the TCGA database analysis, we observed a positive correlation between PTEN and p35 expression, implying a potential negative correlation between PI3K/Akt activation and p35-CDK5. Inhibiting PI3K/Akt with LY294002, Capivasertib (AZD5363), or using an inactive Akt mutant significantly increased p35 expression and subsequently enhanced AR stability and activation in PCa cells. On the other hand, CDK5-knockdown reversed these effects. The involvement of the beta-catenin/Egr1-axis was observed in regulating PI3K/Akt inhibition and p35-CDK5 activation, implying a possible mechanistic connection. Importantly, CDK5 knockdown further reduced PI3K/Akt-inhibition-induced AR and cell viability maintenance, suggesting a compensatory role for CDK5-AR in maintaining cell viability under Akt inhibition. In conclusion, PI3K/Akt inhibition could trigger p35-CDK5-dependent AR activation and cell viability, highlighting p35-CDK5 as a critical link connecting PI3K/Akt inhibition to AR activation and pivotal in PCa cell resistance to PI3K/Akt blockade. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Prostate | |
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.81E-01; Fold-change: -2.29E-01; Z-score: -2.85E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
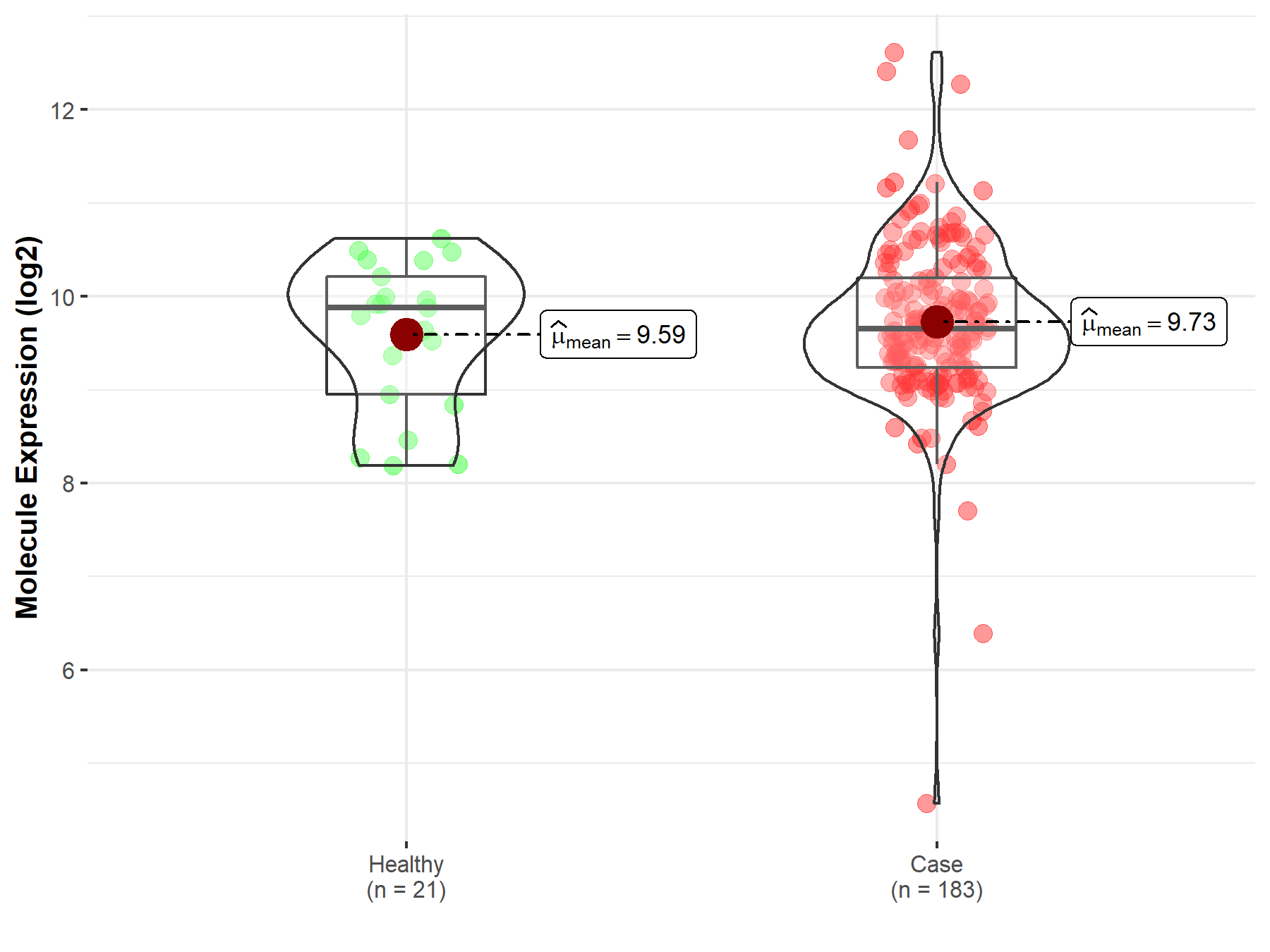
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

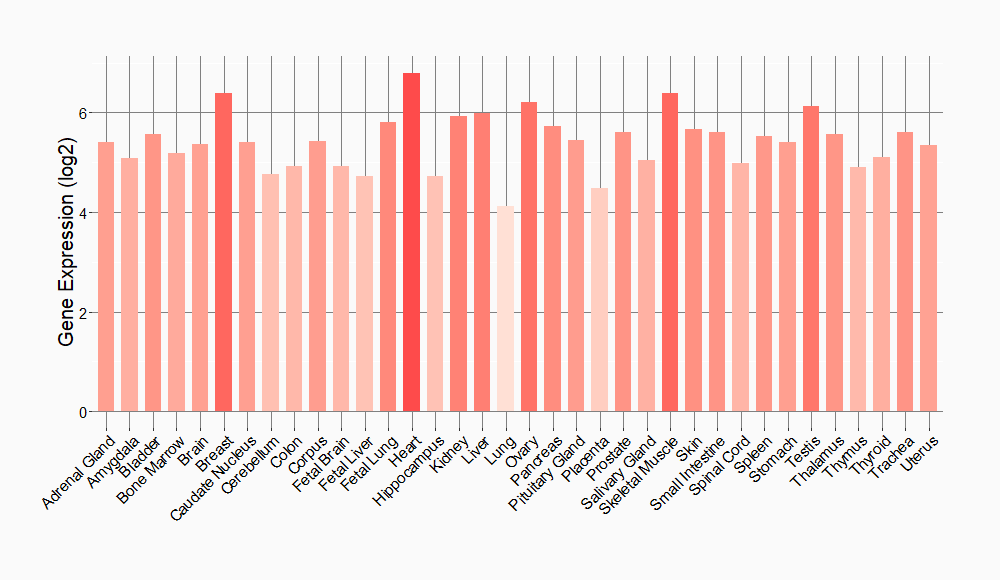
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
