Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00105)
| Name |
Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cytosolic thyroid hormone-binding protein; CTHBP; Opa-interacting protein 3; OIP-3; Pyruvate kinase 2/3; Pyruvate kinase muscle isozyme; Thyroid hormone-binding protein 1; THBP1; Tumor M2-PK; p58; OIP3; PK2; PK3; PKM2
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
PKM
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr15:72199029-72231819[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MSKPHSEAGTAFIQTQQLHAAMADTFLEHMCRLDIDSPPITARNTGIICTIGPASRSVET
LKEMIKSGMNVARLNFSHGTHEYHAETIKNVRTATESFASDPILYRPVAVALDTKGPEIR TGLIKGSGTAEVELKKGATLKITLDNAYMEKCDENILWLDYKNICKVVEVGSKIYVDDGL ISLQVKQKGADFLVTEVENGGSLGSKKGVNLPGAAVDLPAVSEKDIQDLKFGVEQDVDMV FASFIRKASDVHEVRKVLGEKGKNIKIISKIENHEGVRRFDEILEASDGIMVARGDLGIE IPAEKVFLAQKMMIGRCNRAGKPVICATQMLESMIKKPRPTRAEGSDVANAVLDGADCIM LSGETAKGDYPLEAVRMQHLIAREAEAAIYHLQLFEELRRLAPITSDPTEATAVGAVEAS FKCCSGAIIVLTKSGRSAHQVARYRPRAPIIAVTRNPQTARQAHLYRGIFPVLCKDPVQE AWAEDVDLRVNFAMNVGKARGFFKKGDVVIVLTGWRPGSGFTNTMRVVPVP Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
Glycolytic enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphoryl group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to ADP, generating ATP. The ratio between the highly active tetrameric form and nearly inactive dimeric form determines whether glucose carbons are channeled to biosynthetic processes or used for glycolytic ATP production. The transition between the 2 forms contributes to the control of glycolysis and is important for tumor cell proliferation and survival. In addition to its role in glycolysis, also regulates transcription. Stimulates POU5F1-mediated transcriptional activation. Promotes in a STAT1-dependent manner, the expression of the immune checkpoint protein CD274 in ARNTL/BMAL1-deficient macrophages. Also acts as a translation regulator for a subset of mRNAs, independently of its pyruvate kinase activity: associates with subpools of endoplasmic reticulum-associated ribosomes, binds directly to the mRNAs translated at the endoplasmic reticulum and promotes translation of these endoplasmic reticulum-destined mRNAs. Plays a general role in caspase independent cell death of tumor cells.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
6 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Sorafenib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.02E-21 Fold-change: 1.99E-01 Z-score: 1.08E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PKM2 mediated glycolysis signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05230 | |
| In Vitro Model | HCCLM3 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6832 |
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | |
| In Vivo Model | SCID mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-374b/hnRNPA1/PkM2 axis functions as an important mechanism in sorafenib resistance, with sorafenib-induced miR-374b downregulation and subsequently elevated glycolysis. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Tamoxifen | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.62E-40 Fold-change: 1.53E-01 Z-score: 1.50E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Hk2, PFkB3, ENO-1, and PkM-2 are the main enzymes of glycolysis and their expression is upregulated in TAMR cells. Hk2 is also involved in the activation of pro-survival autophagy. ENO-1 plays an important role by inhibiting apoptosis via downregulation of c-Myc. In mitochondria, PDk4 phosphorylation regulate Pyruvate dehydrogenase of PDC. NSD2 activates Hk-2, G6PD, and TIGAR expression and upregulates the PPP pathway. PPP produces NADH and Ribulose 5-Phosphate, a substrate for nucleotide biosynthesis. NADH reduces ROS and inhibits apoptosis. LDHA overexpression helps in aerobic glycolysis and indirectly promotes autophagy. To reduce the concentration of lactate in the cells, MCT expression is increased, which facilitates the efflux of lactate and cell survival. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | COC1 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6891 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Down-regulations of PkM2 and HSPD1 involved in MDR in ovarian cancer. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell growth | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR133b can inhibit the growth and proliferation of lung cancer stem cells by down regulating PkM2, and can enhance the sensitivity of lung cancer stem cells to DDP. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| miR122/PKM2 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | |
| PLC cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0485 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR-122 in Huh7/R cells reversed the doxorubicin-resistance through the inhibition of PkM2, inducing the apoptosis in doxorubicin-resistant cancer cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Castration-resistant prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [6] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glucose metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Castration-resistant prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Enzalutamide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Central carbon metabolism in cancer | Activation | hsa05230 | |
| In Vitro Model | C4-2 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4782 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanistic dissection demonstrated that lncRNA SNHG3 facilitated the advance of CRPC by adjusting the expression of PKM2. Further explorations unraveled the role of lncRNA SNHG3 as a 'sponge' of miR-139-5p and released its binding with PKM2 mRNA, leading to PKM2 up-regulation. Together, Our studies suggest that lncRNA SNHG3 / miR-139-5p / PKM4 pathway promotes the development of CRPC via regulating glycolysis process and provides valuable insight into a novel therapeutic approach for the disordered disease. | |||
| Disease Class: Castration-resistant prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [6] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glucose metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Castration-resistant prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Enzalutamide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Central carbon metabolism in cancer | Activation | hsa05230 | |
| In Vivo Model | 4-weeks-old male nude mice, with empty vector, sh-LncRNA SNHG3, sh-PKM2, sh-LncRNA SNHG3 + sh-PKM4 were separately injected | Mice | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor weight assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanistic dissection demonstrated that lncRNA SNHG3 facilitated the advance of CRPC by adjusting the expression of PKM2. Further explorations unraveled the role of lncRNA SNHG3 as a 'sponge' of miR-139-5p and released its binding with PKM2 mRNA, leading to PKM2 up-regulation. Together, Our studies suggest that lncRNA SNHG3 / miR-139-5p / PKM7 pathway promotes the development of CRPC via regulating glycolysis process and provides valuable insight into a novel therapeutic approach for the disordered disease. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.6] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Methotrexate | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Curcumin mediated the amputation of chemoresistance by repressing the hyperglycolytic behavior of malignant cells via modulated expression of metabolic enzymes (HkII, PFk1, GAPDH, PkM2, LDH, SDH, IDH, and FASN), transporters (GLUT-1, MCT-1, and MCT-4), and their regulators. Along altered constitution of extracellular milieu, these molecular changes culminated into improved drug accumulation, chromatin condensation, and induction of cell death. | |||
Preclinical Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Cutaneous metastatic melanoma [ICD-11: 2E08.0] | [8] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glucose metabolism | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cutaneous metastatic melanoma [ICD-11: 2E08.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | HA344 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 |
| SkMEL28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | the mechanism of action of HA344 provides potential therapeutic avenues for patients with CMM and a broad range of different cancers | |||
| Disease Class: Cutaneous metastatic melanoma [ICD-11: 2E08.0] | [8] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glucose metabolism | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cutaneous metastatic melanoma [ICD-11: 2E08.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | HA344 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | A375 S cells, Five weeks old female athymic nude mice; A375R cells, Five weeks old female athymic nude mice | Mice | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor volume assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | the mechanism of action of HA344 provides potential therapeutic avenues for patients with CMM and a broad range of different cancers | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.02E-21; Fold-change: 5.94E-01; Z-score: 1.76E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.91E-28; Fold-change: 6.67E-01; Z-score: 1.15E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 5.92E-02; Fold-change: 9.88E-01; Z-score: 1.22E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
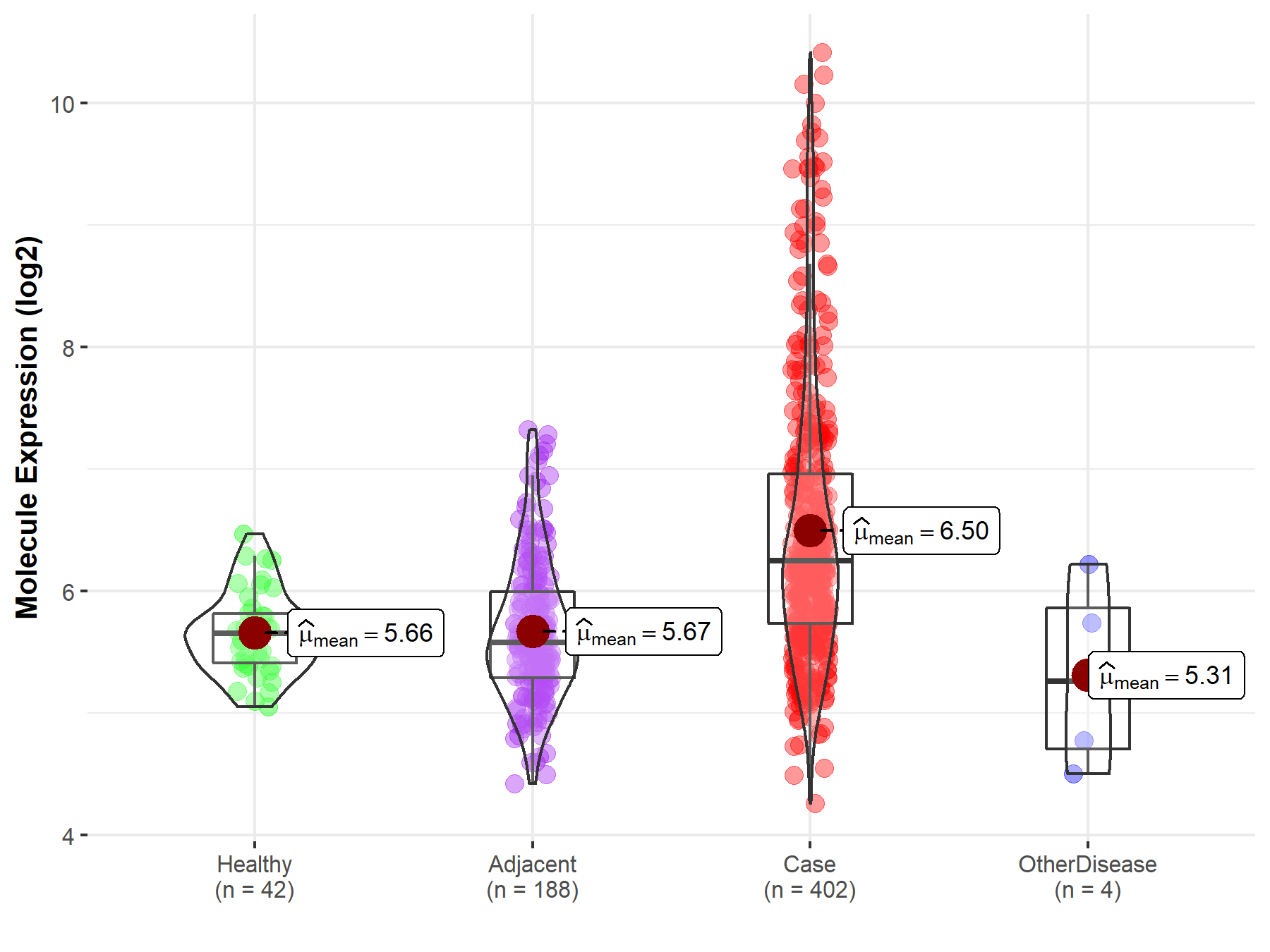
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.61E-14; Fold-change: 4.12E-01; Z-score: 1.03E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.66E-05; Fold-change: 2.69E-01; Z-score: 4.90E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
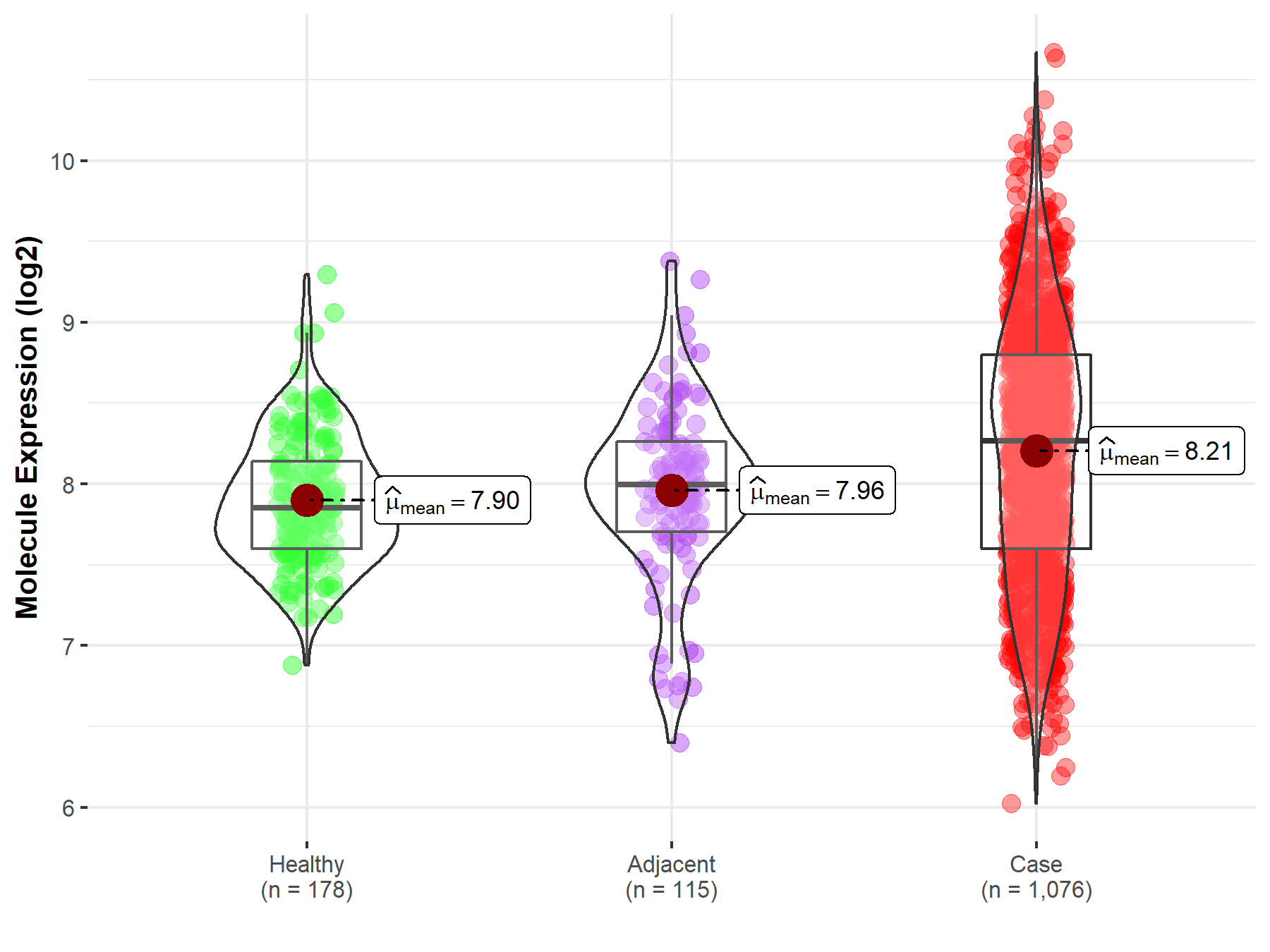
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.62E-40; Fold-change: 8.25E-01; Z-score: 9.43E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 6.74E-06; Fold-change: 5.66E-01; Z-score: 6.07E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.69E-03; Fold-change: 7.25E-01; Z-score: 1.44E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.23E-04; Fold-change: 1.57E+00; Z-score: 1.85E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

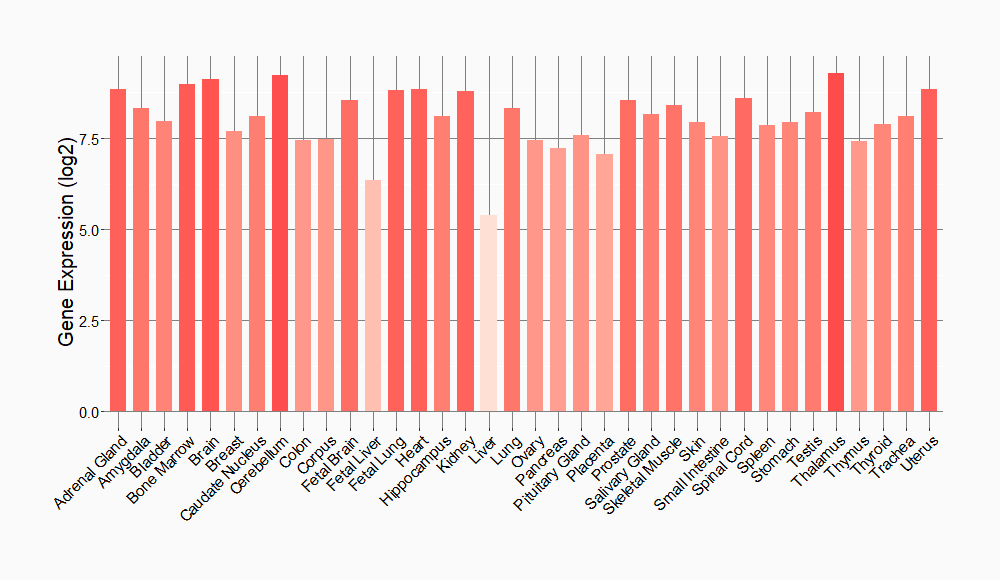
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
