Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG02007) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Alisertib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Alisertib|1028486-01-2|MLN8237|MLN-8237|MLN 8237|4-((9-Chloro-7-(2-fluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)-5H-benzo[c]pyrimido[4,5-e]azepin-2-yl)amino)-2-methoxybenzoic acid|MLN8237 (Alisertib)|Alisertib [USAN]|4-[[9-Chloro-7-(2-fluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)-5H-pyrimido[5,4-d][2]benzazepin-2-yl]amino]-2-methoxybenzoic acid|Alisertib [USAN:INN]|Alisertib (USAN)|T66ES73M18|ALISERTIB [INN]|ALISERTIB [WHO-DD]|CHEMBL483158|DTXSID30145539|MLN 8237 (Contain 10% DMSO)|4-((9-Chloro-7-(2-fluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)-5H-benzo[c]pyrimido-[4,5-e]azepin-2-yl)amino)-2-methoxybenzoic acid|Benzoic acid, 4-((9-chloro-7-(2-fluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)-5H-pyrimido(5,4-d)(2)benzazepin-2-yl)amino)-2-methoxy-|4-{[9-chloro-7-(2-fluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)-5H-pyrimido[5,4-d][2]benzazepin-2-yl]amino}-2-methoxybenzoic acid|alisertibum|UNII-T66ES73M18|4-((13-chloro-10-(2-fluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)-3,5,9-triazatricyclo(9.4.0.0^(2,7))pentadeca-1(15),2,4,6,9,11,13-heptaen-4-yl)amino)-2-methoxybenzoic acid|4-((9-CHLORO-7-(2-FLUORO-6-METHOXYPHENYL)-5H-PYRIMIDO(5,4-D)(2)BENZAZEPIN-2-YL)AMINO)-2-METHOXY-BENZOIC ACID|4-((9-chloro-7-(2-fluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)-5H-pyrimido(5,4-d)(2)benzazepin-2-yl)amino)-2-methoxybenzoic acid|4-{[13-chloro-10-(2-fluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)-3,5,9-triazatricyclo[9.4.0.0^{2,7}]pentadeca-1(15),2,4,6,9,11,13-heptaen-4-yl]amino}-2-methoxybenzoic acid|4-{[9-Chloro-7-(2-fluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)-5H-pyrimido[5,4-d][2]benzazepin-2-yl]amino}-2-methoxy-benzoic acid|Benzoic acid, 4-[[9-chloro-7-(2-fluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)-5H-pyrimido[5,4-d][2]benzazepin-2-yl]amino]-2-methoxy-; 4-[[9-Chloro-7-(2-fluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)-5H-pyrimido[5,4-d][2]benzazepin-2-yl]amino]-2-methoxybenzoic acid; MLN 8237|MFCD16621243|MLN8237,Alisertib|Kinome_3770|Alisertib; MLN8237|Alisertib (MLN8237)|MLN8237 (Alisertib)?|MLS006011041|SCHEMBL855823|GTPL7790|DTXCID4068030|EX-A024|CHEBI:125628|ZLHFILGSQDJULK-UHFFFAOYSA-N|HMS3654E08|HMS3673I07|HMS3743E17|BCP01823|Aurora A Kinase Inhibitor MLN8237|BDBM50277545|NSC759677|NSC799329|s1133|AKOS015924647|BCP9000956|CCG-264832|CS-0106|DB05220|FM16476|NSC-759677|NSC-799329|SB16658|SDCCGSBI-0646927.P001|NCGC00263271-01|NCGC00263271-02|NCGC00263271-10|4-(9-chloro-7-(2-fluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)-5H-benzo[c]pyrimido[4,5-e]azepin-2-ylamino)-2-methoxybenzoic acid|AC-25236|AS-17005|HY-10971|SMR004702834|NS00072479|SW219771-1|D10085|EN300-6482023|BRD-K75295174-001-03-5|BRD-K75295174-001-05-0|Q15633917|Z2037281068|4-(9-chloro-7-(2-fluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)-5H-benzo[e]pyrimido[5,4-c]azepin-2-ylamino)-2-methoxybenzoic acid|4-[[9-Chloro-7-(2-fluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)-5H-pyrimido[5,4-d][2]benzazepin-2-yl]amino]-2-methoxy-benzoic acid;Alisertib|4-{[13-chloro-10-(2-fluoro-6-methoxyphenyl)-3,5,9-triazatricyclo[9.4.0.0,2,7]pentadeca-1(11),2(7),3,5,9,12,14-heptaen-4-yl]amino}-2-methoxybenzoic acid|4-{[9-chloro-7-(2-fluoro-6-methoxyphenyl) -5H-pyrimido[5,4-d][2]benzazepin-2-yl]amino}-2-methoxybenzoic acid|A5B
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
Phase 2
|
||||
| Structure |
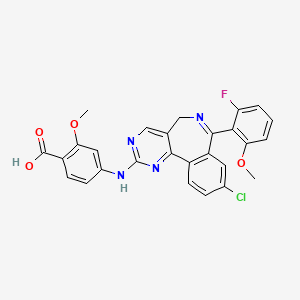
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[1]
[2]
|
||||
| Target | Aurora kinase A (AURKA) | AURKA_HUMAN | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C27H20ClFN4O4
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
COC1=C(C(=CC=C1)F)C2=NCC3=CN=C(N=C3C4=C2C=C(C=C4)Cl)NC5=CC(=C(C=C5)C(=O)O)OC
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C27H20ClFN4O4/c1-36-21-5-3-4-20(29)23(21)25-19-10-15(28)6-8-17(19)24-14(12-30-25)13-31-27(33-24)32-16-7-9-18(26(34)35)22(11-16)37-2/h3-11,13H,12H2,1-2H3,(H,34,35)(H,31,32,33)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
ZLHFILGSQDJULK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aurora kinase A (AURKA) | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glucose metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Autophosphorylation | Thr288 |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | GBM22 PDX cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| SF188 PDX cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6948 | |
| Silenced PGC1alpha in GBM22 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Silenced PGC1alpha in SF188 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6948 | |
| Transfect T58A mutant c-Myc in GBM22 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Transfected c-Myc in GBM22 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The response to Aurora kinase A inhibitors depends on glycolysis and that tumor cells with an oxidative metabolic phenotype will be more resistant to Aurora kinase A inhibitor treatment. Moreover, in a manner dependent on the transcription factors c-MYC and PGC1alpha treatment with Aurora kinase A inhibitors renders GBM cells highly oxidative and dependent on fatty acid oxidation that in turn mediates them to be susceptible to inhibitors of FAO in vitro and in vivo. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aurora kinase A (AURKA) | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glucose metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Autophosphorylation | Thr288 |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | GBM22 orthotopic PDX model; orthotopic murine GBM model; subcutis of immunocompromised Nu/Nu mice, GBM12 cells; subcutis of immunocompromised Nu/Nu mice, GBM43 cells | Mice | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor volume assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The response to Aurora kinase A inhibitors depends on glycolysis and that tumor cells with an oxidative metabolic phenotype will be more resistant to Aurora kinase A inhibitor treatment. Moreover, in a manner dependent on the transcription factors c-MYC and PGC1alpha treatment with Aurora kinase A inhibitors renders GBM cells highly oxidative and dependent on fatty acid oxidation that in turn mediates them to be susceptible to inhibitors of FAO in vitro and in vivo. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: microRNA-125b (miR-125b) | [2] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glucose metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HCT8 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2478 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Similarly, miR-125b mimic decreased the glycolysis [(25.28±9.51) mpH/min] in HCT-8-7T cells as compared with that [(54.38±12.70)mpH/min,P=0.003] in HCT-8-7T cells transfected with control. Meanwhile, in comparison with control transfected HCT-8-7T cells, miR-125b mimic also significantly led to an increase in the levels of p53 and beta-catenin, in parallel with a decrease in the levels of PFK1 and HK1 in HCT-8-7T cells | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
