Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00823) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Thiethylperazine
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Thiethylperazine; Torecan; ETHYLTHIOPERAZINE; 1420-55-9; Tietilperazina; Thiethylperazinum; Norzine; Thiethylperazine maleate; UNII-8ETK1WAF6R; 2-(ethylthio)-10-[3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]-10H-phenothiazine; 8ETK1WAF6R; 3-Ethylmercapto-10-(1'-methylpiperazinyl-4'-propyl)phenothiazine; 10H-Phenothiazine, 2-(ethylthio)-10-(3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl)-; 2-(ethylsulfanyl)-10-[3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]-10H-phenothiazine; CHEBI:9544; 1179-69-7; 2-(Ethylthio)-10-(3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl)phenothiazine; 2-ethylsulfanyl-10-[3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]phenothiazine; Thiethylpipezazine; GS-95; Theithylperazine; 2-(Ethylthio)-10-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl]phenothiazine; Tietilperazina [DCIT]; Phenothiazine, 2-(ethylthio)-10-(3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl)-; 10H-Phenothiazine, 2-(ethylthio)-10-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl]-; Thiethylperazinum [INN-Latin]; 2-Ethylthio-10-(3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl)phenothiazine; Thioethylperazine; MLS002154140; Phenothiazine, 2-(ethylthio)-10-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl]-; Thiethylperazine [USAN:INN:BAN]; 2-(ethylthio)-10-(3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl)-10H-phenothiazine; NSC130044; HSDB 3400; Norzine (*Dimaleate*); SMR001233447; EINECS 215-819-0; GS-95 (*Dimaleate*); Thiethylperazine (USAN/INN); Norzine (Salt/Mix); Torecan (Salt/Mix); Tresten (Salt/Mix); CHEMBL1378; SCHEMBL49124; GTPL7306; DTXSID1023651; BDBM78436; cid_3085006; BCP09601; Thiethylperazine maleate (Salt/Mix); ZINC22446674; DB00372; NCGC00262537-04; AB00514742; C07132; D02354; L000871; Q372725; 2-(Ethylthio)-10-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl]phenthiazine; 2-(ethylthio)-10-[3-(4-methylpiperazino)propyl]phenothiazine;malic acid; 2-(Ethylsulfanyl)-10-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl]-10H-phenothiazine #; 2-(ethylthio)-10-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl]phenothiazine;2-hydroxybutanedioic acid; 2-ethylsulfanyl-10-[3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl]phenothiazine;2-oxidanylbutanedioic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
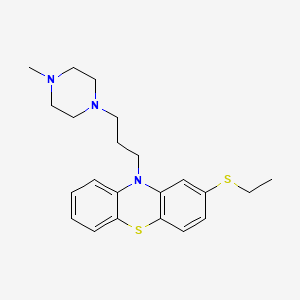
|
||||
| Target | Dopamine D2 receptor (D2R) | DRD2_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C22H29N3S2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CCSC1=CC2=C(C=C1)SC3=CC=CC=C3N2CCCN4CCN(CC4)C
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C22H29N3S2/c1-3-26-18-9-10-22-20(17-18)25(19-7-4-5-8-21(19)27-22)12-6-11-24-15-13-23(2)14-16-24/h4-5,7-10,17H,3,6,11-16H2,1-2H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
XCTYLCDETUVOIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Vancomycin/teicoplanin A-type resistance protein VanA (VANA) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lactobacillus casei infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Enterococcus faecium strain | 1352 | ||
| Streptococcus faecium strain | 1352 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
agar dilution method | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance to vancomycin in enterococci is mainly caused by expression of enzymes such as ligase, dehydrogenase, carboxypeptidase and carboxypeptidase which are encoded by genes such as vanA and vanB. Phenothiazines such as chlorpromazine are well known to deactivate a large number of enzymes. The reversal of vancomycin resistance may be due to enzyme inactivation. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: D-alanine--D-alanine ligase (Q5MPQ2) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lactobacillus casei infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Enterococcus faecium strain | 1352 | ||
| Streptococcus faecium strain | 1352 | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
agar dilution method | |||
| Mechanism Description | Resistance to vancomycin in enterococci is mainly caused by expression of enzymes such as ligase, dehydrogenase, carboxypeptidase and carboxypeptidase which are encoded by genes such as vanA and vanB. Phenothiazines such as chlorpromazine are well known to deactivate a large number of enzymes. The reversal of vancomycin resistance may be due to enzyme inactivation. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
