Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00407) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Sulfisomidine
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
SULFISOMIDINE; sulfisomidin; Sulfaisodimidine; 515-64-0; Sulphasomidine; Sulfasomidine; 4-amino-N-(2,6-dimethylpyrimidin-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide; Sulfadimetine; Sulfamethin; Sulfaisodimerazine; Elkosin; Domian; Sulfaisodimidinum; Solfisomidina; Aristamid; Aristogyn; Elcosine; Elkosine; Elkosil; Erycon; Mefenal; 4-Sulfa-2,6-dimethylpyrimidine; 2,4-Dimethyl-6-sulfanilamidopyrimidine; 2,6-Dimethyl-4-sulfanilamidopyrimidine; 4-Sulfanilamido-2,6-dimethylpyrimidine; 6-Sulfanilamido-2,4-dimethylpyrimidine; UNII-W03L3ODK6E; 6-(4-Aminobenzenesulfonamido)-2,4-dimethylpyrimidine; 6-(p-Aminobenzenesulfonamido)-2,4-dimethylpyrimidine; 6-(p-Aminobenzenesulfonyl)amino-2,4-dimethylpyrimidine; CHEBI:32166; Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-N-(2,6-dimethyl-4-pyrimidinyl)-; W03L3ODK6E; N(sup 1)-(2,6-Dimethyl-4-pyrimidinyl)sulfanilamide; (p-Aminobenzolsulfonyl)-4-amino-2,6-dimethylpyrimidin; Sulfaisomidine; N(1)-(2,6-Dimethyl-4-pyrimidinyl)sulfanilamide; (p-Aminobenzolsulfonyl)-4-amino-2,6-dimethylpyrimidine; Sulfanilamide, N(sup 1)-(2,6-dimethyl-4-pyrimidinyl)-; NCGC00164492-01; Sulfisomidina; Sulfisomidinum; Isosulf; Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-N-(2,6-dimethyl-4-pyrimidinyl)-(9CI); DSSTox_CID_26390; DSSTox_RID_81570; DSSTox_GSID_46390; Solfisomidina [DCIT]; Sulfisomidinum [INN-Latin]; Sulfisomidina [INN-Spanish]; CAS-515-64-0; EINECS 208-204-3; BRN 0261305; Aristamide; Elcosin; Domain; AI3-50168; Sulfisomidine [INN:BAN:JAN]; N1-(2,6-Dimethyl-4-pyrimidinyl)sulfanilamide; Sulfisomidine (TN); Sulfisomidine (JAN); 4-amino-N-(2,6-dimethylpyrimidin-4-yl)benzene-1-sulfonamide; (p-Aminobenzolsulfonyl)-4-amino-2,6-dimethylpyrimidin [German]; Oprea1_339670; SCHEMBL34791; 5-25-10-00216 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); MLS004773916; CHEMBL485696; DTXSID1046390; YZMCKZRAOLZXAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-; ZINC56658; ALBB-023545; HY-B1784; Tox21_112130; BDBM50548727; MFCD00010567; s5291; STL481971; AKOS000119092; Tox21_112130_1; CCG-267227; CS-7658; DB13283; MCULE-6011761791; SB58524; NCGC00164492-02; NCGC00164492-03; NCGC00186655-01; AS-10637; SMR001346487; AB0126295; DB-051990; FT-0632265; S0362; Sulfisomidine 100 microg/mL in Acetonitrile; A12593; D01526; Sulfisomidin, VETRANAL(TM), analytical standard; SR-01000940235; Q6577315; SR-01000940235-2; F1716-0354; 4-Amino-N-(2,6-dimethylpyrimidin-4-yl) benzenesulfonamide; 4-Amino-N-(2,6-dimethyl-4-pyrimidinyl)benzenesulfonamide (9CI)
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
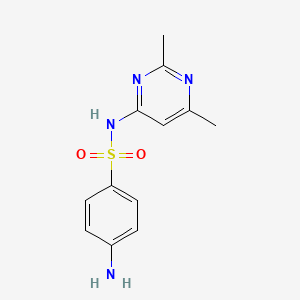
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C12H14N4O2S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC1=CC(=NC(=N1)C)NS(=O)(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C12H14N4O2S/c1-8-7-12(15-9(2)14-8)16-19(17,18)11-5-3-10(13)4-6-11/h3-7H,13H2,1-2H3,(H,14,15,16)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
YZMCKZRAOLZXAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus pyogenes infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E9D+p.A37V+p.D39Q+p.H40Q+p.E42D+p.M44L+p.D47G+p.C63Y+p.T69A+p.D73E+p.V78M+p.E84A+p.N85K+p.I88V+p.W115R+p.Q122E+p.F124L+p.A132V+p.D141K+p.E147D+p.G157S+p.N158A+p.L164I+p.K171D+p.A182P+p.Q187H+p.R197H+p.R213G+p.I246L+p.D257E |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Streptococcus pyogenes strain G1 | 1314 | ||
| Streptococcus pyogenes strain G2 | 1314 | |||
| Streptococcus pyogenes strain G52 | 1314 | |||
| Streptococcus pyogenes strain G56 | 1314 | |||
| Streptococcus pyogenes strain G68 | 1314 | |||
| Streptococcus pyogenes strain G71 | 1314 | |||
| Streptococcus pyogenes strain G72 | 1314 | |||
| Streptococcus pyogenes strain G76 | 1314 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Dideoxy-chain termination method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Sulfonamide resistance in recent isolates of Streptococcus pyogenes was found to be associated with alterations of the chromosomally encoded dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS). There were 111 different nucleotides (13.8%) in the genes found in susceptible and resistant isolates, respectively, resulting in 30 amino acid changes (11.3%). | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptococcus pyogenes infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I8V+p.N11K+p.D39Q+p.H40Q+p.E42D+p.M44L+p.D47G+p.C63Y+p.T69A+p.D73E+p.V78M+p.K80I+p.E84A+p.N85K+p.I88V+p.Q122E+p.F124L+p.A132V+p.D141K+p.E147D+p.G157S+p.N158A+p.L164I+p.K171D+p.Q187H+p.R213G+p.V214I+p.I246L+p.D257E |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Streptococcus pyogenes strain G1 | 1314 | ||
| Streptococcus pyogenes strain G2 | 1314 | |||
| Streptococcus pyogenes strain G52 | 1314 | |||
| Streptococcus pyogenes strain G56 | 1314 | |||
| Streptococcus pyogenes strain G68 | 1314 | |||
| Streptococcus pyogenes strain G71 | 1314 | |||
| Streptococcus pyogenes strain G72 | 1314 | |||
| Streptococcus pyogenes strain G76 | 1314 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Dideoxy-chain termination method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Sulfonamide resistance in recent isolates of Streptococcus pyogenes was found to be associated with alterations of the chromosomally encoded dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS). There were 111 different nucleotides (13.8%) in the genes found in susceptible and resistant isolates, respectively, resulting in 30 amino acid changes (11.3%). | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
