Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00382) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Kasugamycin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
KASUGAMYCIN; 6980-18-3; Kasumin L; Kasumin 2L; Kasuminl; UNII-O957UYB9DY; alpha-D-lyxo-; O957UYB9DY; CHEBI:81419; 2-amino-2-[(2R,3S,5S,6R)-5-amino-2-methyl-6-[(2R,3S,5S,6S)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxycyclohexyl]oxyoxan-3-yl]iminoacetic acid; Kasu B; (1s,2r,3s,4r,5s,6s)-2,3,4,5,6-Pentahydroxycyclohexyl 2-Amino-4-{[carboxy(Imino)methyl]amino}-2,3,4,6-Tetradeoxy-Alpha-D-Arabino-Hexopyranoside; HSDB 6695; KSM; BRN 1403823; SR-05000001429; C14H25N3O9; EINECS 234-260-3; NSC 100858; SCHEMBL70535; CHEMBL1631109; DTXSID1040374; SCHEMBL12858482; SCHEMBL16011710; HMS2089A11; ZINC4216682; AKOS025310863; ZINC100042889; ZINC100045947; 11030-24-3; 3-O-(2-Amino-4-((carboxyiminomethyl)amino)-2,3,4,6-tetradeoxy-alpha-D-arabino-hexopyranosyl)-D-chiro-inositol sulphate; D-chiro-Inositol, 3-O-(2-amino-4-((carboxyiminomethyl)amino)-2,3,4,6-tetradeoxy-alpha-D-arabino-hexopyranosyl)-; X6751; C17968; Q3193879; SR-05000001429-1; (1S,2R,3S,4R,5S,6S)-2,3,4,5,6-PENTAHYDROXYCYCLOHEXYL; (1S,2R,3S,4R,5S,6S)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxycyclohexyl 2-amino-4-{[(Z)-carboxy(imino)methyl]amino}-2,3,4,6-tetradeoxy-alpha-D-arabino-hexopyranoside; 2-((2R,3S,5S,6R)-5-amino-2-methyl-6-((1S,2R,3S,4R,5S,6S)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxycyclohexyloxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-ylamino)-2-iminoacetic acid; 2-[[(2R,3S,5S,6R)-5-amino-2-methyl-6-[(2R,3S,5S,6S)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxycyclohexoxy]tetrahydropyran-3-yl]amino]-2-imino-acetic acid; 2-AMINO-4-{[CARBOXY(IMINO)METHYL]AMINO}-2,3,4,6-TETRADEOXY-ALPHA-D-ARABINO-HEXOPYRANOSIDE; 3-O-[2-amino-4-[(carboxyiminomethyl)amino]-2,3,4,6-tetradeoxy-alpha-D-arabino-hexopyranosyl]-D-chiro-inositol
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
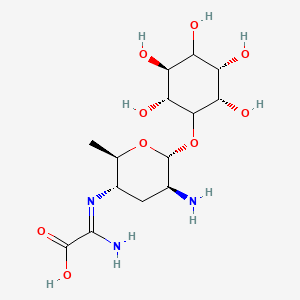
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[2]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C14H25N3O9
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C[C@@H]1[C@H](C[C@@H]([C@H](O1)OC2[C@@H]([C@H](C([C@@H]([C@@H]2O)O)O)O)O)N)N=C(C(=O)O)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C14H25N3O9/c1-3-5(17-12(16)13(23)24)2-4(15)14(25-3)26-11-9(21)7(19)6(18)8(20)10(11)22/h3-11,14,18-22H,2,15H2,1H3,(H2,16,17)(H,23,24)/t3-,4+,5+,6 ,7+,8+,9-,10+,11 ,14-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
PVTHJAPFENJVNC-UQTMRZPGSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: 16S rRNA adenine dimethyltransferase (KsgA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lactobacillus casei infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | A1518/1519 |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain UCBPP-PA14 | 1763 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Primer extension analysis; MS analysis; Western blot assay; Semiquantitative RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Phenotypic microarrays assay; MIC assay; Oxidative stress sensitivity testing; Superoxide dismutase enzyme activity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, we demonstrated the absence of A1518/1519 methylation in the 16S rRNA of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa ksgA mutant. Biolog phenotypic microarrays were used to screen the phenotypes of the ksgA mutant against various antimicrobial agents. The loss of ksgA led to increased sensitivity to menadione, a superoxide generator, which was, at least in part, attributed to decreased in a superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. Interestingly, the decrease in SOD activity in the ksgA mutant was linked to a decrease in the SodM protein levels, but not the sodM mRNA levels. Furthermore, the ksgA mutant strain exhibited sensitivity to hygromycin B and tylosin antibiotics. The tylosin-sensitive phenotype was correlated with decreased transcriptional levels of tufA, tufB, and tsf, which encode elongation factors. Additionally, the ksgA mutant showed resistance to kasugamycin. Collectively, these findings highlight the role of KsgA in oxidative stress responses and antibiotic sensitivity in P. aeruginosa. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Kasugamycin 2' acetyltransferase (KA2A) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Paenibacillus sp. LC231 | 1120679 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aminoglycoside acetyltransferases can often modify a variety of aminoglycosides and we therefore evaluated the ability of AAC(2')-IIb to modify a range of aminoglycosides. AAC(2')-IIb specifically modified kasugamycin and no other aminoglycoside by acetylation. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
