Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00027) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Tretinoin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Retinoic acid; tretinoin; 302-79-4; Vitamin A acid; all-trans-Retinoic acid; trans-Retinoic acid; ATRA; Airol; Retin-A; Vesanoid; Renova; Dermairol; Aknoten; Eudyna; Aberel; all-trans-Vitamin A acid; Aknefug; All-trans Retinoic Acid; Cordes vas; Epi-aberel; Atralin; Vitamin A1 acid, all-trans-; Tretin M; Retin-A Micro; all-trans-Vitamin A1 acid; Vitamin A acid, all-trans-; all-trans-Tretinoin; Effederm; Retionic acid; TRETINON; Retinoic acid, all-trans-; Alltrans-retinoic acid; beta-Ra; all-(E)-Retinoic acid; beta-Retinoic acid; Avitoin; Aberela; Acnavit; Atragen; Betarretin; Lsotretinoin; Nexret; Panretyn; REA; Retacnyl; Retinoate; Retinova; Solage; Tretinoina; Tretinoine; Tretinoino; Tretinoinum; Vesnaroid; Vitinoin; Aberela [Norway]; Accutane Roche; Acnavit [Denmark]; All Trans Retinoic Acid; Avita Gel; Avitoin [Norway]; Beta all trans Retinoic Acid; Cordes VAS [Germany]; Effederm [France]; Panretin Gel; Retin A; Trans Retinoic Acid; Tretinoin Potassium Salt; Tretinoin Sodium Salt; Tretinoin Zinc Salt; Tretinoin liposome; AGN100335; AGN 192013; ALRT 1057; BAL4079; LGD 100057; R 2625; [3H]Retinoic acid; A-Vitaminsyre; A-Vitaminsyre [Denmark]; AT-RA; Aberela (TN); Acid, Retinoic; Acid, Vitamin A; All trans-Retinoic acid; Atra-IV; Avita (TN); B-Retinoic acid; BML2-E05; Beta-Ra; Beta-Retinoic acid; Potassium Salt, Tretinoin; RETINOIC ACID, ALL TRANS; Renova (TN); Retin A (TN); Retisol-A; Ro 1-5488; Salt, Tretinoin Potassium; Salt, Tretinoin Sodium; Salt, Tretinoin Zinc; Sodium Salt, Tretinoin; Stieva-A; Stieva-a Forte; Trans-Retinoicacid; Tretinoin (TN); Tretinoina [INN-Spanish]; Tretinoine [INN-French]; Tretinoino [INN-Spanish]; Tretinoinum [INN-Latin]; Tri-Luma; Vesanoid (TN); Zinc Salt, Tretinoin; A-Acido (Argentina); Acid A Vit (Belgium, Netherlands); Acid, trans-Retinoic; Acide retinoique (French) (DSL); All-trans-Retinoic acid; All-trans-Tretinoin; All-trans-Vitamin A acid; All-trans-Vitamin A1 acid; PDT-002-002; Retin-A (TN); Stieva-A (TN); Tretinoin 01% cream or placebo; Tretinoin [USAN:INN:BAN]; Tretinoin/All-Trans Retinoic Acid; Tretinoine (French) (EINECS); Acid, all-trans-Retinoic; All-(E)-Retinoic acid; All-trans-b-Retinoic acid; All-trans-beta-Retinoic acid; Beta-all-trans-Retinoic acid; Tretinoin (JAN/USP/INN); Acid, beta-all-trans-Retinoic; Retinoic acid, all-trans-(8CI); Vesanoid, Airol, Renova, Atralin, Retin-A, Avita, Tretinoin; 15-Apo-beta-caroten-15-oic acid; 3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid; 9(Z)-Retinoic acid; 9-cis-RA; 9-trans-retinoic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 2 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
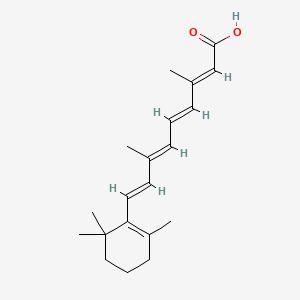
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[3]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[4]
|
||||
| Target | Retinoic acid receptor (RAR) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Retinoic acid receptor gamma (RARG) | RARG_HUMAN | [1] | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C20H28O2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC1=C(C(CCC1)(C)C)/C=C/C(=C/C=C/C(=C/C(=O)O)/C)/C
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C20H28O2/c1-15(8-6-9-16(2)14-19(21)22)11-12-18-17(3)10-7-13-20(18,4)5/h6,8-9,11-12,14H,7,10,13H2,1-5H3,(H,21,22)/b9-6+,12-11+,15-8+,16-14+
|
||||
| InChIKey |
SHGAZHPCJJPHSC-YCNIQYBTSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Neurofibromin (NF1) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Alteration | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK/RAS signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | |
| In Vitro Model | Kelly cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2092 |
| Sk-N-AS cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1700 | |
| IMR-5 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1306 | |
| NBL-S cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2136 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | NF1 i.ctivation has been reported in neuroblastoma and confers activation of RAS-MAPk signalling and resistance to retinoic acid. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ZBTB16-RARA fusion protein (ZBTB16-RARA) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural mutation | Structural variation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT/PI3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | |
| MAPK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | ||
| STAT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04630 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | However, rarer variant translocations such as t(11;17)(q23;q21); ZBTB16-RARA or t(17;17)(q21;q21); STAT5B-RARA may result in resistance to ATRA. | |||
| Key Molecule: STAT5B-RARA fusion protein (STAT5B-RARA) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural mutation | Structural variation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT/PI3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | |
| MAPK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | ||
| STAT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04630 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | However, rarer variant translocations such as t(11;17)(q23;q21); ZBTB16-RARA or t(17;17)(q21;q21); STAT5B-RARA may result in resistance to ATRA. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Methyltransferase like 3 (METTL3) | [4] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glucose metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute promyelocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | NB4 cells transfected with METTL3-OE were transplanted into BALB/C nude mice via subcutaneously inoculation; NB4 cells transfected with METTL3-OE were transplanted into BALB/C nude mice via tail vein injection | Mice | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis, qRT-PCR and CO-IP | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor images assay; Tumor volume assay; Tumor weight assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Histone lactylation and METTL3 expression levels were considerably upregulated in ATRA-resistant APL cells. METTL3 was regulated by histone lactylation and direct lactylation modification. Overexpression of METTL3 promoted ATRA-resistance. GRh2 ameliorated ATRA-resistance by downregulated lactylation level and directly inhibiting METTL3. | |||
| Key Molecule: Transglutaminase 2 (TG2) | [5] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Redox metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute promyelocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| NB4 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0005 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In the present study, we showed that ATO increased ROS production and apoptosis ratios in ATRA-differentiated NB4 leukaemia cells, and that these responses were enhanced when TG2 was deleted. The combined ATRA + ATO treatment also increased the amount of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) transcription factor, an adaptive regulator of the cellular oxidative stress response, and calpain proteolytic activity, resulting in TG2 degradation and the reduced survival of WT leukaemia cells. We further showed that the induced TG2 protein expression was degraded in the MCF-7 epithelial cell line and primary peripheral blood mononuclear cells upon ATO treatment, thereby sensitising these cell types to apoptotic signals. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: t(17;17)(q21;q21) (Unclear) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural mutation | Structural variation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT/PI3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | |
| MAPK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | ||
| STAT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04630 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | However, rarer variant translocations such as t(11;17)(q23;q21); ZBTB16-RARA or t(17;17)(q21;q21); STAT5B-RARA may result in resistance to ATRA. | |||
| Key Molecule: t(11;17)(q23;q21) (Unclear) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Structural mutation | Structural variation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT/PI3 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | |
| MAPK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | ||
| STAT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04630 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | However, rarer variant translocations such as t(11;17)(q23;q21); ZBTB16-RARA or t(17;17)(q21;q21); STAT5B-RARA may result in resistance to ATRA. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
