Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00536)
| Name |
Quinone reductase 1 (NQO1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Azoreductase; DT-diaphorase; DTD; Menadione reductase; NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1; Phylloquinone reductase; Quinone reductase 1; QR1; DIA4; NMOR1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
NQO1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr16:69706996-69726668[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MVGRRALIVLAHSERTSFNYAMKEAAAAALKKKGWEVVESDLYAMNFNPIISRKDITGKL
KDPANFQYPAESVLAYKEGHLSPDIVAEQKKLEAADLVIFQFPLQWFGVPAILKGWFERV FIGEFAYTYAAMYDKGPFRSKKAVLSITTGGSGSMYSLQGIHGDMNVILWPIQSGILHFC GFQVLEPQLTYSIGHTPADARIQILEGWKKRLENIWDETPLYFAPSSLFDLNFQAGFLMK KEVQDEEKNKKFGLSVGHHLGKSIPTDNQIKARK Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
The enzyme apparently serves as a quinone reductase in connection with conjugation reactions of hydroquinons involved in detoxification pathways as well as in biosynthetic processes such as the vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylation of glutamate residues in prothrombin synthesis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
8 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovarian tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.99E-05 Fold-change: 3.77E-01 Z-score: 7.06E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | A2780-DR cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_EG64 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Clonogenic assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The Essential Role of H19 Contributing to Cisplatin Resistance by Regulating Glutathione Metabolism in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer.Additionally, we verified that different H19 expression levels in HGSC tissues showed strong correlation with cancer recurrence. H19 knockdown in A2780-DR cells resulted in recovery of cisplatin sensitivity in vitro and in vivo. Quantitative proteomics analysis indicated that six NRF2-targeted proteins, including NQO1, GSR, G6PD, GCLC, GCLM and GSTP1 involved in the glutathione metabolism pathway, were reduced in H19-knockdown cells. Furthermore, H19-knockdown cells were markedly more sensitive to hydrogen-peroxide treatment and exhibited lower glutathione levels. Our results reveal a previously unknown link between H19 and glutathione metabolism in the regulation of cancer-drug resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Arsenic trioxide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.02E-66 Fold-change: 2.58E-01 Z-score: 2.01E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Nrf2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05208 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT Assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR155 mediates arsenic trioxide resistance by activating Nrf2 and suppressing apoptosis in lung cancer cells. miR155 mediated ATO resistance by upregulating the Nrf2 signaling pathway, but downregulating cellular apoptosis in lung cancer cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Idebenone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Nrf2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05208 | |
| In Vivo Model | Swiss albino mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ELISA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Pre-treatment resistance testing; Post-treatment resistance testing | |||
| Mechanism Description | IDB had successful control over drug resistance in the rotenone corneal kindled model by bypassing blocked complex I. IDB has a good safety profile and can be considered an adjuvant along with standard antiseizure drugs in drug-resistant patients. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lamotrigine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Nrf2 signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05208 | |
| In Vivo Model | Swiss albino mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ELISA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Pre-treatment resistance testing; Post-treatment resistance testing | |||
| Mechanism Description | The involvement of complex I in drug resistance is well established in epilepsy; therefore, the model chosen for this study was rotenone corneal kindled model of drug resistance using rotenone as a selective irreversible inhibitor of complex I, which have shown resistance to drugs such as valproate, levetiracetam, lamotrigine, pregabalin, carbamazepine, zonisamide, topiramate, gabapentin and their combinations | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Levetiracetam | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Nrf2 signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05208 | |
| In Vivo Model | Swiss albino mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ELISA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Pre-treatment resistance testing; Post-treatment resistance testing | |||
| Mechanism Description | The involvement of complex I in drug resistance is well established in epilepsy; therefore, the model chosen for this study was rotenone corneal kindled model of drug resistance using rotenone as a selective irreversible inhibitor of complex I, which have shown resistance to drugs such as valproate, levetiracetam, lamotrigine, pregabalin, carbamazepine, zonisamide, topiramate, gabapentin and their combinations | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Phenytoin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Nrf2 signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05208 | |
| In Vivo Model | Swiss albino mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ELISA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Pre-treatment resistance testing; Post-treatment resistance testing | |||
| Mechanism Description | The involvement of complex I in drug resistance is well established in epilepsy; therefore, the model chosen for this study was rotenone corneal kindled model of drug resistance using rotenone as a selective irreversible inhibitor of complex I, which have shown resistance to drugs such as valproate, levetiracetam, lamotrigine, pregabalin, carbamazepine, zonisamide, topiramate, gabapentin and their combinations | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pregabalin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Nrf2 signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05208 | |
| In Vivo Model | Swiss albino mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ELISA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Pre-treatment resistance testing; Post-treatment resistance testing | |||
| Mechanism Description | The involvement of complex I in drug resistance is well established in epilepsy; therefore, the model chosen for this study was rotenone corneal kindled model of drug resistance using rotenone as a selective irreversible inhibitor of complex I, which have shown resistance to drugs such as valproate, levetiracetam, lamotrigine, pregabalin, carbamazepine, zonisamide, topiramate, gabapentin and their combinations | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | mitochondrial refractory epilepsy [ICD-11: 8A60.A] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Valproic acid | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Nrf2 signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05208 | |
| In Vivo Model | Swiss albino mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ELISA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Pre-treatment resistance testing; Post-treatment resistance testing | |||
| Mechanism Description | The involvement of complex I in drug resistance is well established in epilepsy; therefore, the model chosen for this study was rotenone corneal kindled model of drug resistance using rotenone as a selective irreversible inhibitor of complex I, which have shown resistance to drugs such as valproate, levetiracetam, lamotrigine, pregabalin, carbamazepine, zonisamide, topiramate, gabapentin and their combinations | |||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Amrubicin | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.P187S (c.559C>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.30 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
G
-
S
-
S
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-10
|
-
H
-
H
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
L
-
V
-
P
-
R
-
G
0
|
-
S
-
H
-
M
V
V
R
G
R
R
A
R
L
A
I
L
V
I
10
|
L
V
A
L
H
A
S
H
E
S
R
E
T
R
S
T
F
S
N
F
20
|
Y
N
A
Y
M
A
K
M
E
K
A
E
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
30
|
L
A
K
L
K
K
K
K
G
K
W
G
E
W
V
E
V
V
E
V
40
|
S
E
D
S
L
D
Y
L
A
Y
M
A
N
M
F
N
N
F
P
N
50
|
I
P
I
I
S
I
R
S
K
R
D
K
I
D
T
I
G
T
K
G
60
|
L
K
K
L
D
K
P
D
A
P
N
A
F
N
Q
F
Y
Q
P
Y
70
|
A
P
E
A
S
E
V
S
L
V
A
L
Y
A
K
Y
E
K
G
E
80
|
H
G
L
H
S
L
P
S
D
P
I
D
V
I
A
V
E
A
Q
E
90
|
K
Q
K
K
L
K
E
L
A
E
A
A
D
A
L
D
V
L
I
V
100
|
F
I
Q
F
F
Q
P
F
L
P
Q
L
W
Q
F
W
G
F
V
G
110
|
P
V
A
P
I
A
L
I
K
L
G
K
W
G
F
W
E
F
R
E
120
|
V
R
F
V
I
F
G
I
E
G
F
E
A
F
Y
A
T
Y
Y
T
130
|
A
Y
A
A
M
A
Y
M
D
Y
K
D
G
K
P
G
F
P
R
F
140
|
S
R
K
S
K
K
A
K
V
A
L
V
S
L
I
S
T
I
T
T
150
|
G
T
G
G
S
G
G
S
S
G
M
S
Y
M
S
Y
L
S
Q
L
160
|
G
Q
I
G
H
I
G
H
D
G
M
D
N
M
V
N
I
V
L
I
170
|
W
L
P
W
I
P
Q
I
S
Q
G
S
I
G
L
I
H
L
F
H
180
|
C
F
G
C
F
G
Q
F
V
Q
L
V
E
L
P
E
Q
S
L
Q
190
|
T
L
Y
T
S
Y
I
S
G
I
H
G
T
H
P
T
A
P
D
A
200
|
A
D
R
A
I
R
Q
I
I
Q
L
I
E
L
G
E
W
G
K
W
210
|
K
K
R
K
L
R
E
L
N
E
I
N
W
I
D
W
E
D
T
E
220
|
P
T
L
P
Y
L
F
Y
A
F
P
A
S
P
S
S
L
S
F
L
230
|
D
F
L
D
N
L
F
N
Q
F
A
Q
G
A
F
G
L
F
M
L
240
|
K
M
K
K
E
K
V
E
Q
V
D
Q
E
D
E
E
K
E
N
K
250
|
K
N
K
K
F
K
G
F
L
G
S
L
V
S
G
V
H
G
H
H
260
|
L
H
G
L
K
G
S
K
I
S
P
I
T
P
D
T
N
D
Q
N
270
|
I
Q
K
I
A
K
R
A
K
R
-
K
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |||||||||
| NCI-H69 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1579 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H23 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1547 | ||||||||||
| PC-1 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_S978 | ||||||||||
| PC-10 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7088 | ||||||||||
| QG56 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6943 | ||||||||||
| RERF-LC-MT cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A473 | ||||||||||
| Sk-LC-6 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5474 | ||||||||||
| PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | ||||||||||
| SK-LC-2 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5468 | ||||||||||
| SK-LC-17 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5466 | ||||||||||
| SK-LC-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5458 | ||||||||||
| SBC3 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1678 | ||||||||||
| RERF-LC-OK cells | Central nervous system | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3154 | ||||||||||
| RERF-LC-MS cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1655 | ||||||||||
| PC6 cells | Adrenal gland | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | CVCL_7091 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H417 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1602 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H1688 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1487 | ||||||||||
| DMS53 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1177 | ||||||||||
| ACC-LC-94 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7032 | ||||||||||
| ACC-LC-80 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7028 | ||||||||||
| ACC-LC-73 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7026 | ||||||||||
| ACC-LC-67 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7024 | ||||||||||
| ACC-LC-5 cells | Cervical lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7020 | ||||||||||
| ACC-LC-48 cells | Pericardial effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7018 | ||||||||||
| ACC-LC-314 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7011 | ||||||||||
| ACC-LC-174 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7007 | ||||||||||
| ACC-LC-172 cells | Pericardial effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7005 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter 96 AQueous One assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.P187S (c.559C>T) in gene NQO1 cause the sensitivity of Amrubicin by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.02E-66; Fold-change: 1.67E+00; Z-score: 2.21E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 4.56E-52; Fold-change: 1.85E+00; Z-score: 2.42E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
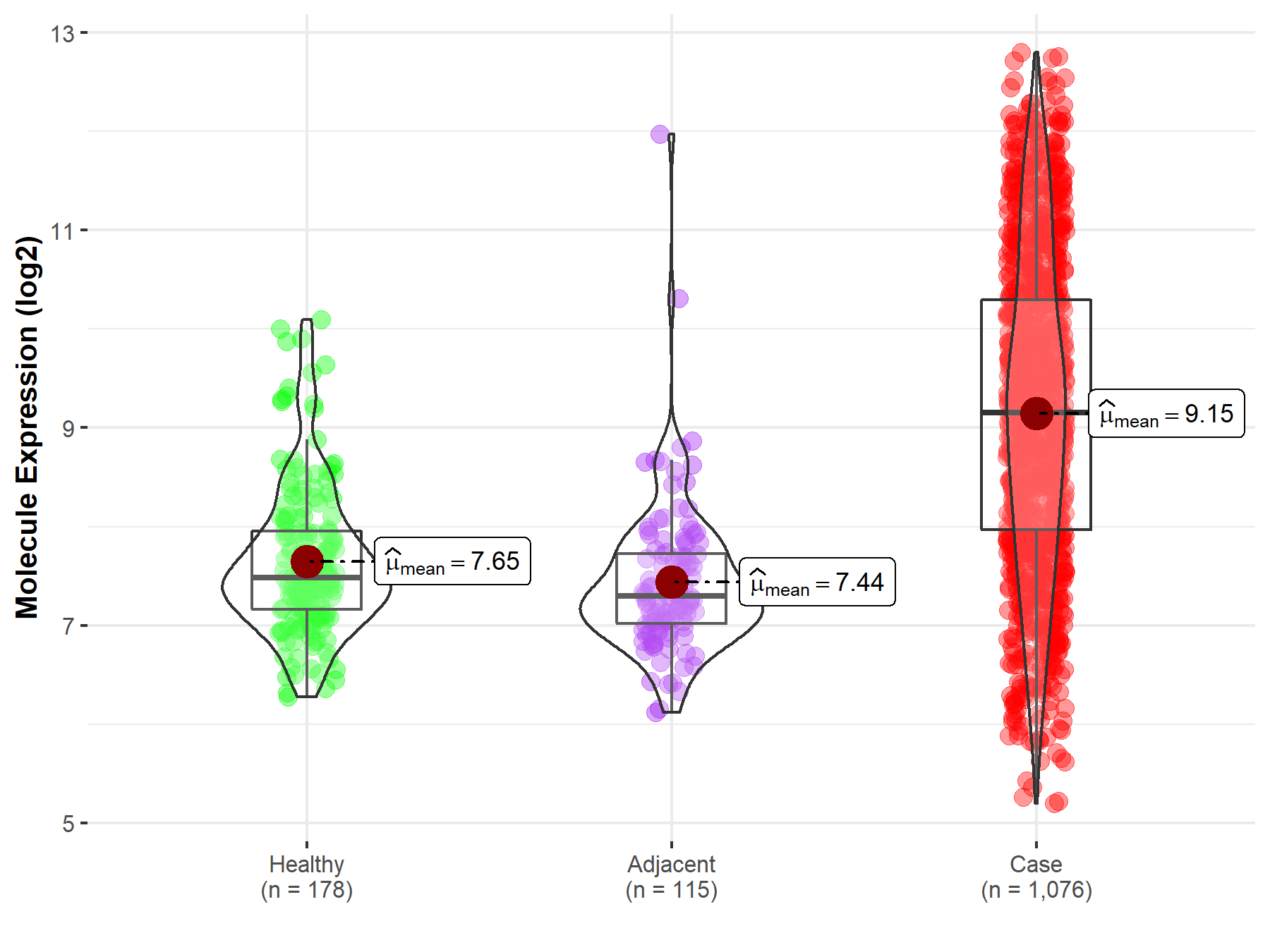
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.99E-05; Fold-change: 1.85E+00; Z-score: 2.27E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.53E-02; Fold-change: -6.59E-03; Z-score: -4.71E-03 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
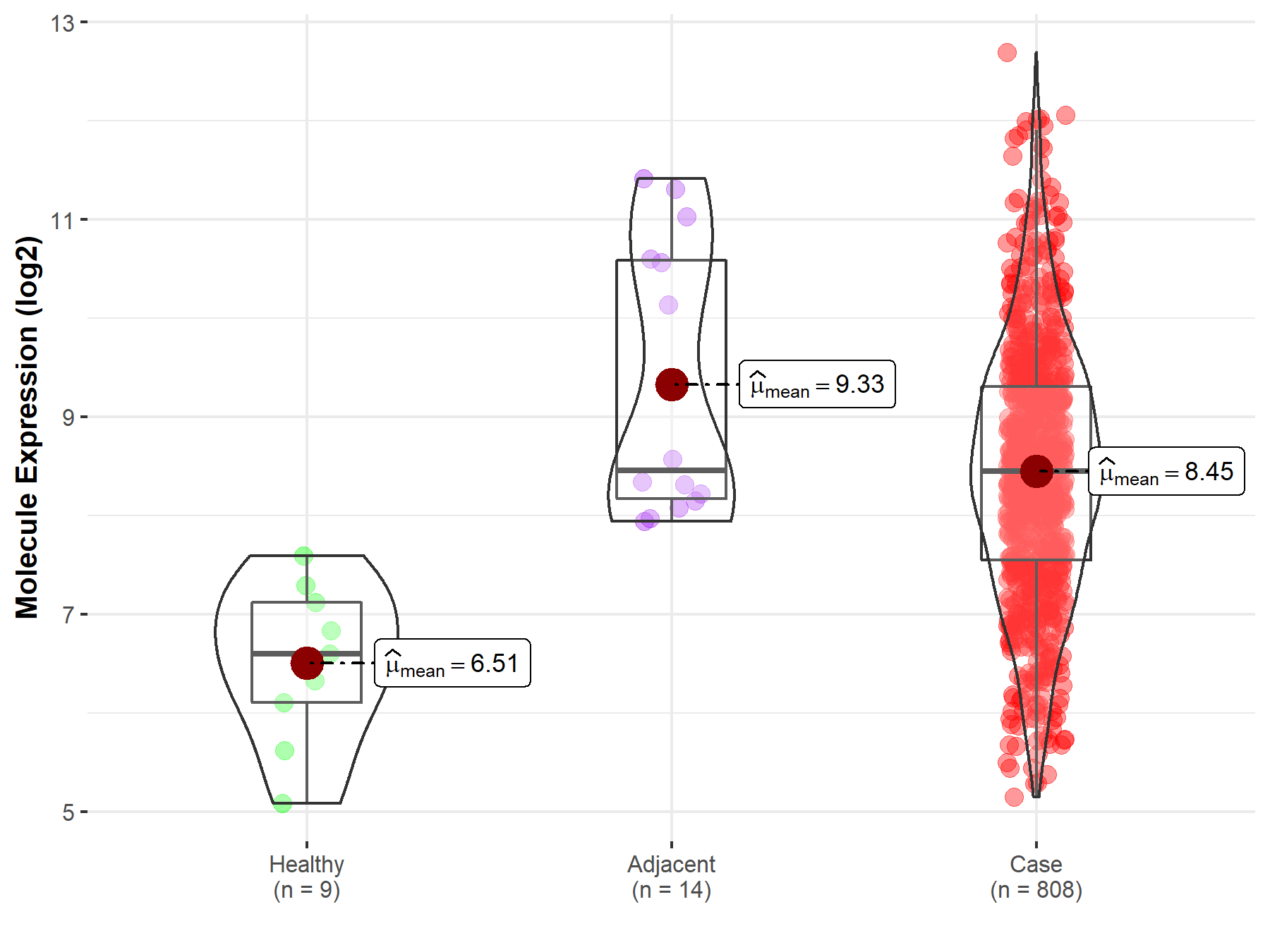
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

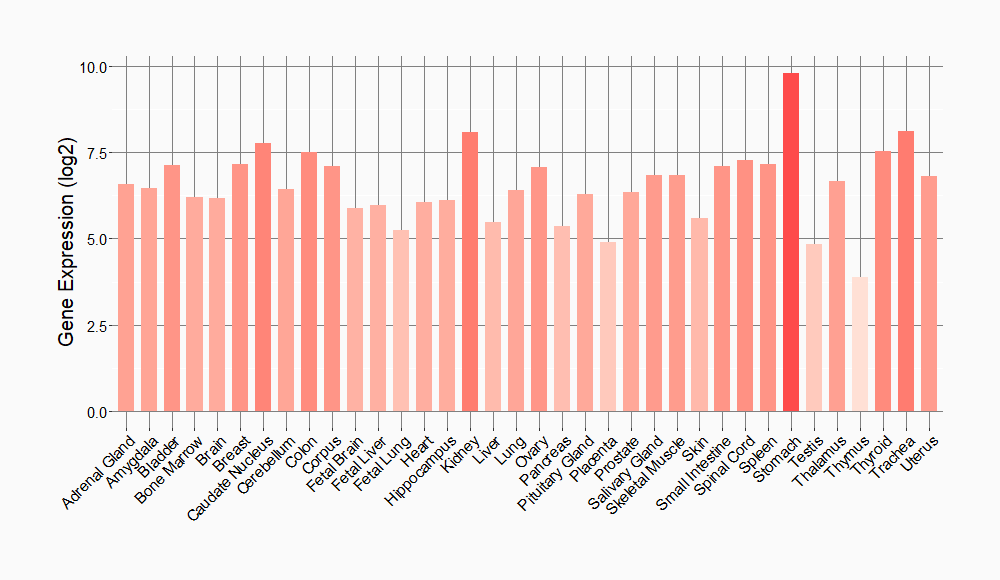
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
