Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00335)
| Name |
Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
DHFR
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr5:80626226-80654983[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MVGSLNCIVAVSQNMGIGKNGDLPWPPLRNEFRYFQRMTTTSSVEGKQNLVIMGKKTWFS
IPEKNRPLKGRINLVLSRELKEPPQGAHFLSRSLDDALKLTEQPELANKVDMVWIVGGSS VYKEAMNHPGHLKLFVTRIMQDFESDTFFPEIDLEKYKLLPEYPGVLSDVQEEKGIKYKF EVYEKND Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
Key enzyme in folate metabolism. Contributes to the de novo mitochondrial thymidylate biosynthesis pathway. Catalyzes an essential reaction for de novo glycine and purine synthesis, and for DNA precursor synthesis. Binds its own mRNA and that of DHFR2.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
5 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Co-trimoxazole | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S37T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pneumocystis jirovecii strain | 42068 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in DHFR may contribute to P. jirovecii emerging drug (Trimethoprim, Pyrimethamine) resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Methotrexate | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| p53 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04115 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MG63 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0426 |
| U2OS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0042 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Immunofluorescence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-215, through the suppression of DTL expression, induces a decreased cell proliferation by causing G2-arrest, thereby leading to an increase in chemoresistance to MTX and TDX. | |||
| Disease Class: Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Methotrexate | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| p53 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04115 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Immunofluorescence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-215, through the suppression of DTL expression, induces a decreased cell proliferation by causing G2-arrest, thereby leading to an increase in chemoresistance to MTX and TDX. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pentamidine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D153V |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pneumocystis jirovecii strain | 42068 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in DHFR may contribute to P. jirovecii emerging drug (Trimethoprim, Pyrimethamine) resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pyrimethamine/Sulfadoxine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I158V+p.V79I |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pneumocystis jirovecii strain | 42068 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in DHFR may contribute to P. jirovecii emerging drug (Trimethoprim, Pyrimethamine) resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pyrimethamine/Sulfadoxine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y197L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pneumocystis jirovecii strain | 42068 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in DHFR may contribute to P. jirovecii emerging drug (Trimethoprim, Pyrimethamine) resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pyrimethamine/Sulfadoxine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T14A+p.P26Q |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pneumocystis jirovecii strain | 42068 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in DHFR may contribute to P. jirovecii emerging drug (Trimethoprim, Pyrimethamine) resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pyrimethamine/Sulfadoxine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.M52I+p.E63G+p.T144A+p.K171E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pneumocystis jirovecii strain | 42068 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in DHFR may contribute to P. jirovecii emerging drug (Trimethoprim, Pyrimethamine) resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pyrimethamine/Sulfadoxine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S106P+p.E127G+p.R170G |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pneumocystis jirovecii strain | 42068 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in DHFR may contribute to P. jirovecii emerging drug (Trimethoprim, Pyrimethamine) resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Raltitrexed | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| p53 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04115 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MG63 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0426 |
| U2OS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0042 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Immunofluorescence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-215, through the suppression of DTL expression, induces a decreased cell proliferation by causing G2-arrest, thereby leading to an increase in chemoresistance to MTX and TDX. | |||
| Disease Class: Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Raltitrexed | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| p53 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04115 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Immunofluorescence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-215, through the suppression of DTL expression, induces a decreased cell proliferation by causing G2-arrest, thereby leading to an increase in chemoresistance to MTX and TDX. | |||
Investigative Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Pyrimethamine/Atovaquone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S37T |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pneumocystis jirovecii strain | 42068 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in DHFR may contribute to P. jirovecii emerging drug (Trimethoprim, Pyrimethamine) resistance. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Colon | |
| The Specified Disease | Colon cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.35E-17; Fold-change: 4.30E-01; Z-score: 8.72E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.77E-24; Fold-change: 7.42E-01; Z-score: 1.32E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

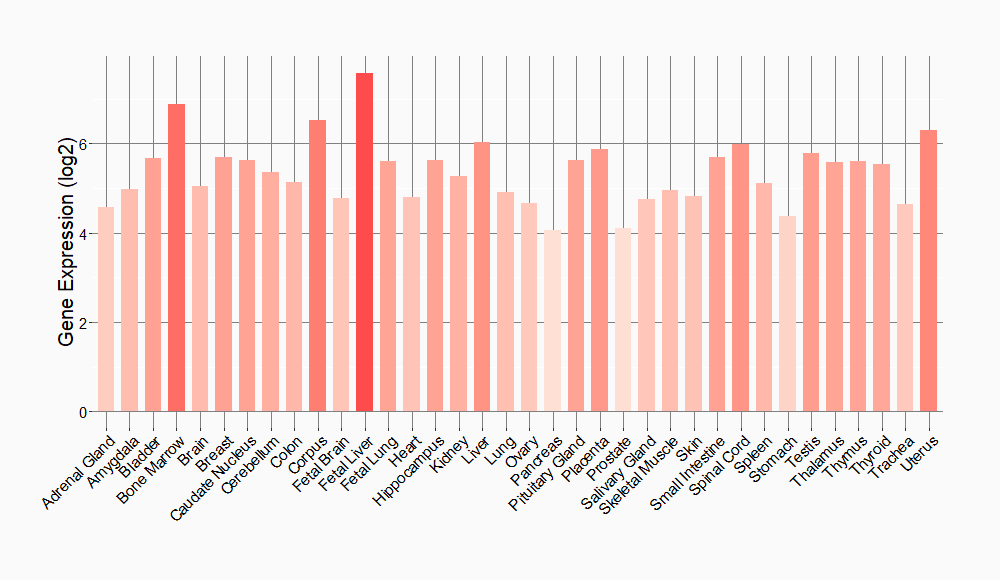
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
