Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00060) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Pyrimethamine/Sulfadoxine
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Fansidar; Suldox; Pyrimethamine-sulfadoxine; 37338-39-9; Pyrimethamine mixture with sulfadoxine; Pyrimethamine combination with sulfadoxine; Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-N-(5,6-dimethoxy-4-pyrimidinyl)-, mixt. with 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-ethyl-2,4-pyrimidinediamine; sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine; sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine; Sulphadoxyne-pyrimethamine; sulfadoxine / pyrimethamine; Pyrimethamine / sulfadoxine; Sulphadoxine / pyrimethamine; Pyrimethamine-sulfadoxine mixt.; Sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine mixt.; Fansidar (TN)
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
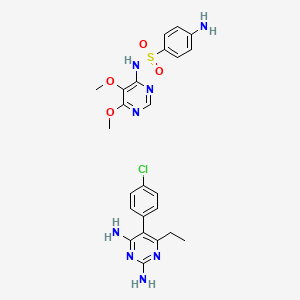
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[2]
[3]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C24H27ClN8O4S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CCC1=C(C(=NC(=N1)N)N)C2=CC=C(C=C2)Cl.COC1=C(N=CN=C1OC)NS(=O)(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C12H13ClN4.C12H14N4O4S/c1-2-9-10(11(14)17-12(15)16-9)7-3-5-8(13)6-4-7;1-19-10-11(14-7-15-12(10)20-2)16-21(17,18)9-5-3-8(13)4-6-9/h3-6H,2H2,1H3,(H4,14,15,16,17);3-7H,13H2,1-2H3,(H,14,15,16)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
LUBUTTBEBGYNJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Bifunctional dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase (PVDHFR) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Plasmodium vivax malaria [ICD-11: 1F41.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Red blood cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Giemsa stain assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The lack of copy number variation of pvgch1 suggests that SP-resistant P. vivax may harbor alternative mechanisms to secure sufficient folate.The quadruple mutant haplotypes 57I/L/58R/61M/117T of pvdhfr gene were the most common (comprising 76% of cases in Myitsone and 43.7% of case in Laiza). The double mutant haplotype 383G/553G of pvdhps gene was also prevalent at each site. | |||
| Key Molecule: Hydroxymethylpterin pyrophosphokinase-dihydropteroate synthetase (DHPS) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Plasmodium vivax malaria [ICD-11: 1F41.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | SNP | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Red blood cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Giemsa stain assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The lack of copy number variation of pvgch1 suggests that SP-resistant P. vivax may harbor alternative mechanisms to secure sufficient folate.The quadruple mutant haplotypes 57I/L/58R/61M/117T of pvdhfr gene were the most common (comprising 76% of cases in Myitsone and 43.7% of case in Laiza). The double mutant haplotype 383G/553G of pvdhps gene was also prevalent at each site. | |||
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C59R |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum strains | 5833 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | The quintuple mutant of pfdhfr (S108N, N51I and C59R) and pfdhps (A437G and k540E) were associated with a high relative risk of treatment failure, and this haplotype was suggested as a relevant molecular marker for failure of SP treatment in uncomplicated P. falciparum. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C59R+I164L |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum strains | 5833 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | The quintuple mutant of pfdhfr (S108N, N51I and C59R) and pfdhps (A437G and k540E) were associated with a high relative risk of treatment failure, and this haplotype was suggested as a relevant molecular marker for failure of SP treatment in uncomplicated P. falciparum. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C59R+S108N |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum strains | 5833 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | The quintuple mutant of pfdhfr (S108N, N51I and C59R) and pfdhps (A437G and k540E) were associated with a high relative risk of treatment failure, and this haplotype was suggested as a relevant molecular marker for failure of SP treatment in uncomplicated P. falciparum. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C59R+S108N+I164L |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum strains | 5833 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | The quintuple mutant of pfdhfr (S108N, N51I and C59R) and pfdhps (A437G and k540E) were associated with a high relative risk of treatment failure, and this haplotype was suggested as a relevant molecular marker for failure of SP treatment in uncomplicated P. falciparum. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N51I+C59R |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum strains | 5833 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | The quintuple mutant of pfdhfr (S108N, N51I and C59R) and pfdhps (A437G and k540E) were associated with a high relative risk of treatment failure, and this haplotype was suggested as a relevant molecular marker for failure of SP treatment in uncomplicated P. falciparum. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N51I+C59R+I164L |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum strains | 5833 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | The quintuple mutant of pfdhfr (S108N, N51I and C59R) and pfdhps (A437G and k540E) were associated with a high relative risk of treatment failure, and this haplotype was suggested as a relevant molecular marker for failure of SP treatment in uncomplicated P. falciparum. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N51I+C59R+S108N |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum strains | 5833 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | The quintuple mutant of pfdhfr (S108N, N51I and C59R) and pfdhps (A437G and k540E) were associated with a high relative risk of treatment failure, and this haplotype was suggested as a relevant molecular marker for failure of SP treatment in uncomplicated P. falciparum. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N51I+C59R+S108N+I164L |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum strains | 5833 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | The quintuple mutant of pfdhfr (S108N, N51I and C59R) and pfdhps (A437G and k540E) were associated with a high relative risk of treatment failure, and this haplotype was suggested as a relevant molecular marker for failure of SP treatment in uncomplicated P. falciparum. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A437G |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum strains | 5833 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | The quintuple mutant of pfdhfr (S108N, N51I and C59R) and pfdhps (A437G and k540E) were associated with a high relative risk of treatment failure, and this haplotype was suggested as a relevant molecular marker for failure of SP treatment in uncomplicated P. falciparum. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I158V+p.V79I |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pneumocystis jirovecii strain | 42068 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in DHFR may contribute to P. jirovecii emerging drug (Trimethoprim, Pyrimethamine) resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y197L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pneumocystis jirovecii strain | 42068 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in DHFR may contribute to P. jirovecii emerging drug (Trimethoprim, Pyrimethamine) resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T14A+p.P26Q |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pneumocystis jirovecii strain | 42068 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in DHFR may contribute to P. jirovecii emerging drug (Trimethoprim, Pyrimethamine) resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.M52I+p.E63G+p.T144A+p.K171E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pneumocystis jirovecii strain | 42068 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in DHFR may contribute to P. jirovecii emerging drug (Trimethoprim, Pyrimethamine) resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pneumocystis jirovecii infection [ICD-11: CA40.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S106P+p.E127G+p.R170G |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Pneumocystis jirovecii strain | 42068 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in DHFR may contribute to P. jirovecii emerging drug (Trimethoprim, Pyrimethamine) resistance. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
