Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00093)
| Name |
Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
IGF2 mRNA-binding protein 1; IMP-1; IMP1; Coding region determinant-binding protein; CRD-BP; IGF-II mRNA-binding protein 1; VICKZ family member 1; Zipcode-binding protein 1; ZBP-1; CRDBP; VICKZ1; ZBP1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
IGF2BP1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr17:48997385-49056145[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MNKLYIGNLNESVTPADLEKVFAEHKISYSGQFLVKSGYAFVDCPDEHWAMKAIETFSGK
VELQGKRLEIEHSVPKKQRSRKIQIRNIPPQLRWEVLDSLLAQYGTVENCEQVNTESETA VVNVTYSNREQTRQAIMKLNGHQLENHALKVSYIPDEQIAQGPENGRRGGFGSRGQPRQG SPVAAGAPAKQQQVDIPLRLLVPTQYVGAIIGKEGATIRNITKQTQSKIDVHRKENAGAA EKAISVHSTPEGCSSACKMILEIMHKEAKDTKTADEVPLKILAHNNFVGRLIGKEGRNLK KVEQDTETKITISSLQDLTLYNPERTITVKGAIENCCRAEQEIMKKVREAYENDVAAMSL QSHLIPGLNLAAVGLFPASSSAVPPPPSSVTGAAPYSSFMQAPEQEMVQVFIPAQAVGAI IGKKGQHIKQLSRFASASIKIAPPETPDSKVRMVIITGPPEAQFKAQGRIYGKLKEENFF GPKEEVKLETHIRVPASAAGRVIGKGGKTVNELQNLTAAEVVVPRDQTPDENDQVIVKII GHFYASQMAQRKIRDILAQVKQQHQKGQSNQAQARRK Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
RNA-binding factor that recruits target transcripts to cytoplasmic protein-RNA complexes (mRNPs). This transcript 'caging' into mRNPs allows mRNA transport and transient storage. It also modulates the rate and location at which target transcripts encounter the translational apparatus and shields them from endonuclease attacks or microRNA-mediated degradation. Plays a direct role in the transport and translation of transcripts required for axonal regeneration in adult sensory neurons (By similarity). Regulates localized beta-actin/ACTB mRNA translation, a crucial process for cell polarity, cell migration and neurite outgrowth. Co-transcriptionally associates with the ACTB mRNA in the nucleus. This binding involves a conserved 54-nucleotide element in the ACTB mRNA 3'-UTR, known as the 'zipcode'. The RNP thus formed is exported to the cytoplasm, binds to a motor protein and is transported along the cytoskeleton to the cell periphery. During transport, prevents ACTB mRNA from being translated into protein. When the RNP complex reaches its destination near the plasma membrane, IGF2BP1 is phosphorylated. This releases the mRNA, allowing ribosomal 40S and 60S subunits to assemble and initiate ACTB protein synthesis. Monomeric ACTB then assembles into the subcortical actin cytoskeleton (By similarity). During neuronal development, key regulator of neurite outgrowth, growth cone guidance and neuronal cell migration, presumably through the spatiotemporal fine tuning of protein synthesis, such as that of ACTB (By similarity). May regulate mRNA transport to activated synapses (By similarity). Binds to and stabilizes ABCB1/MDR-1 mRNA (By similarity). During interstinal wound repair, interacts with and stabilizes PTGS2 transcript. PTGS2 mRNA stabilization may be crucial for colonic mucosal wound healing (By similarity). Binds to the 3'-UTR of IGF2 mRNA by a mechanism of cooperative and sequential dimerization and regulates IGF2 mRNA subcellular localization and translation. Binds to MYC mRNA, in the coding region instability determinant (CRD) of the open reading frame (ORF), hence prevents MYC cleavage by endonucleases and possibly microRNA targeting to MYC-CRD. Binds to the 3'-UTR of CD44 mRNA and stabilizes it, hence promotes cell adhesion and invadopodia formation in cancer cells. Binds to the oncofetal H19 transcript and to the neuron-specific TAU mRNA and regulates their localizations. Binds to and stabilizes BTRC/FBW1A mRNA. Binds to the adenine-rich autoregulatory sequence (ARS) located in PABPC1 mRNA and represses its translation. PABPC1 mRNA-binding is stimulated by PABPC1 protein. Prevents BTRC/FBW1A mRNA degradation by disrupting microRNA-dependent interaction with AGO2. Promotes the directed movement of tumor-derived cells by fine-tuning intracellular signaling networks. Binds to MAPK4 3'-UTR and inhibits its translation. Interacts with PTEN transcript open reading frame (ORF) and prevents mRNA decay. This combined action on MAPK4 (down-regulation) and PTEN (up-regulation) antagonizes HSPB1 phosphorylation, consequently it prevents G-actin sequestration by phosphorylated HSPB1, allowing F-actin polymerization. Hence enhances the velocity of cell migration and stimulates directed cell migration by PTEN-modulated polarization. Interacts with Hepatitis C virus (HCV) 5'-UTR and 3'-UTR and specifically enhances translation at the HCV IRES, but not 5'-cap-dependent translation, possibly by recruiting eIF3. Interacts with HIV-1 GAG protein and blocks the formation of infectious HIV-1 particles. Reduces HIV-1 assembly by inhibiting viral RNA packaging, as well as assembly and processing of GAG protein on cellular membranes. During cellular stress, such as oxidative stress or heat shock, stabilizes target mRNAs that are recruited to stress granules, including CD44, IGF2, MAPK4, MYC, PTEN, RAPGEF2 and RPS6KA5 transcripts.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
4 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Etoposide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.39E-14 Fold-change: 1.27E-01 Z-score: 8.66E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| c-Myc signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05230 | ||
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-196b overexpression decreased IGF2BP1 RNA expression and protein level. The IGF2BP1 down-regulation by either miR-196b or IGF2BP1 siRNA led to an increase in apoptosis and a decrease in cell viability and proliferation in normal culture conditions. However, IGF2BP1 silencing did not modify the chemoresistance induced by hypoxia, probably because it is not the only target of miR-196b involved in the regulation of apoptosis. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovarian tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.70E-01 Fold-change: -5.15E-02 Z-score: -1.50E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | IGF2BP1/AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05206 | |
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 | |
| SkOV3/DDP cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 | |
| A2780/DDP cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D619 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Caspase-3 activity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR708 increases the susceptibility of ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin by targeting IGF2BP1 and inhibiting Akt signaling. miR708 downregulated the expression of IGF2BP1 and suppressed Akt phosphorylation. Silencing of IGF2BP1 markedly blocked the phosphorylation of Akt. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 |
| IGROV1 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1304 | |
| OVCAR8 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1629 | |
| LOX-IMVI cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1381 | |
| NCI/ADR-RES cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1452 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SRB cytotoxicity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | IMP-1 is an RNA binding protein that acts by stabilizing the mRNA of a number of target genes. In addition, IMP-1 was shown to protect the mRNA of MDR1 from endonucleolytic attack in an in vitro RNA stability assay. Introducing let-7g into ADR-RES cells expressing both IMP-1 and MDR1 reduced expression of both proteins rendering the cells more sensitive to treatment with either Taxol or vinblastine without affecting the sensitivity of the cells to carboplatin. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Vinblastine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 |
| IGROV1 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1304 | |
| OVCAR8 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1629 | |
| LOX-IMVI cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1381 | |
| NCI/ADR-RES cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1452 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SRB cytotoxicity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | IMP-1 is an RNA binding protein that acts by stabilizing the mRNA of a number of target genes. In addition, IMP-1 was shown to protect the mRNA of MDR1 from endonucleolytic attack in an in vitro RNA stability assay. Introducing let-7g into ADR-RES cells expressing both IMP-1 and MDR1 reduced expression of both proteins rendering the cells more sensitive to treatment with either Taxol or vinblastine without affecting the sensitivity of the cells to carboplatin. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.39E-14; Fold-change: 2.58E-01; Z-score: 1.08E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 5.32E-34; Fold-change: 2.78E-01; Z-score: 1.06E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 1.34E-01; Fold-change: 1.82E-01; Z-score: 5.36E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
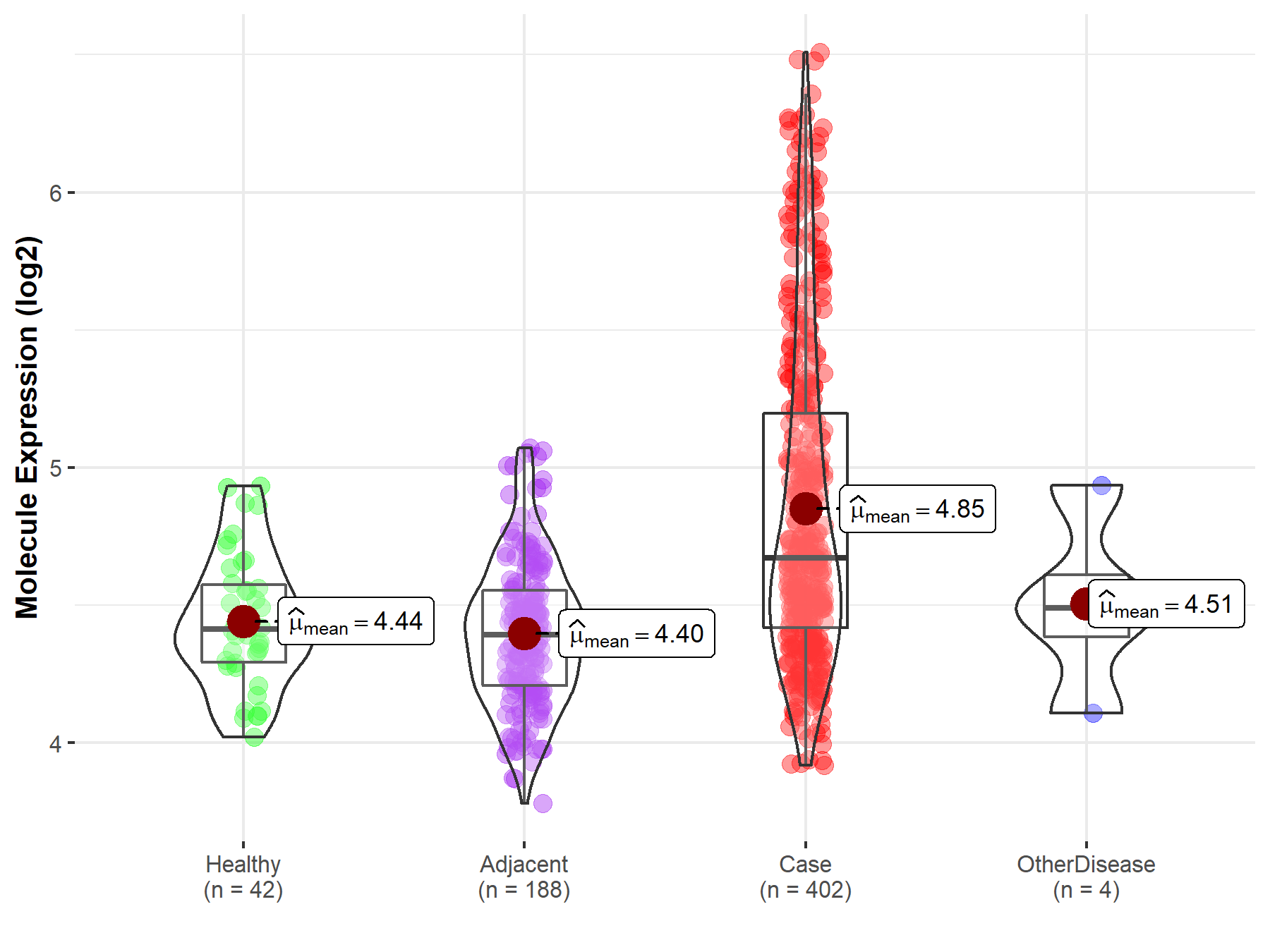
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.70E-01; Fold-change: -1.83E-01; Z-score: -5.37E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 8.76E-01; Fold-change: -3.32E-02; Z-score: -8.70E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
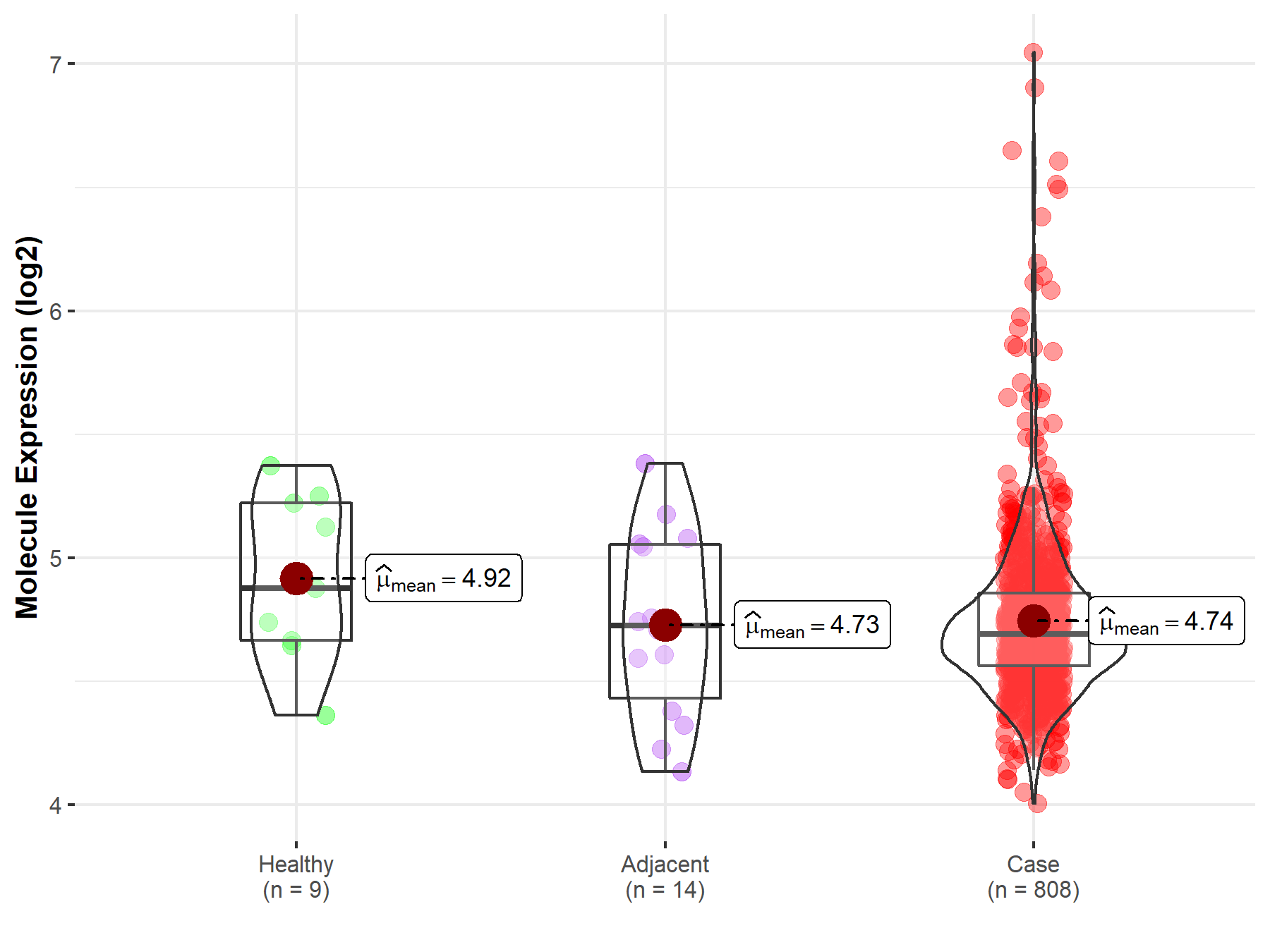
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
