Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00078)
| Name |
Glutathione S-transferase P (GSTP1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
GST class-pi; GSTP1-1; FAEES3; GST3
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
GSTP1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr11:67583742-67586656[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MPPYTVVYFPVRGRCAALRMLLADQGQSWKEEVVTVETWQEGSLKASCLYGQLPKFQDGD
LTLYQSNTILRHLGRTLGLYGKDQQEAALVDMVNDGVEDLRCKYISLIYTNYEAGKDDYV KALPGQLKPFETLLSQNQGGKTFIVGDQISFADYNLLDLLLIHEVLAPGCLDAFPLLSAY VGRLSARPKLKAFLASPEYVNLPINGNGKQ Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Conjugation of reduced glutathione to a wide number of exogenous and endogenous hydrophobic electrophiles. Involved in the formation of glutathione conjugates of both prostaglandin A2 (PGA2) and prostaglandin J2 (PGJ2). Participates in the formation of novel hepoxilin regioisomers. Regulates negatively CDK5 activity via p25/p35 translocation to prevent neurodegeneration.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
10 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Anaplastic astrocytoma [ICD-11: 2A00.04] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Anaplastic astrocytoma [ICD-11: 2A00.04] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Carmustine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Anaplastic astrocytoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.99E-02 Fold-change: 1.21E-01 Z-score: 2.07E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Malignant gliomas tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Oncotech EDR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | GSTP1 is the first major mechanism of resistance alkylator agents encounter after entering the cancer cell cytoplasm. GSTP1 acts to enzymatically conjugate glutathione to the reactive metabolites of BCNU. The mechanisms by which GSTP1 may be up-regulated in gliomas are under investigation. Constitutive expression is thought to be influenced by the proximal promoter factor Sp1, whereas increased expression levels may result from stabilization of GSTP1 mRNA. GSTP1 expression has been reported to be induced by drug exposure, indicating that it may play a role in acquired drug resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Carmustine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Malignant glioma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.99E-02 Fold-change: 1.21E-01 Z-score: 2.07E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Malignant gliomas tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EDR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In vitro drug resistance in malignant gliomas was independent of prior therapy. High-grade glioblastomas showed a lower level of extreme drug resistance than low-grade astrocytomas to cisplatin (11% versus 27%), temozolomide (14% versus 27%), irinotecan (33% versus 53%), and BCNU (29% versus 38%). A substantial percentage of brain tumors overexpressed biomarkers associated with drug resistance, including MGMT (67%), GSTP1 (49%), and mutant p53 (41%). MGMT and GSTP1 overexpression was independently associated with in vitro resistance to BCNU, whereas coexpression of these two markers was associated with the greatest degree of BCNU resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Irinotecan | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Malignant glioma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.99E-02 Fold-change: 1.21E-01 Z-score: 2.07E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Malignant gliomas tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EDR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In vitro drug resistance in malignant gliomas was independent of prior therapy. High-grade glioblastomas showed a lower level of extreme drug resistance than low-grade astrocytomas to cisplatin (11% versus 27%), temozolomide (14% versus 27%), irinotecan (33% versus 53%), and BCNU (29% versus 38%). A substantial percentage of brain tumors overexpressed biomarkers associated with drug resistance, including MGMT (67%), GSTP1 (49%), and mutant p53 (41%). MGMT and GSTP1 overexpression was independently associated with in vitro resistance to BCNU, whereas coexpression of these two markers was associated with the greatest degree of BCNU resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Vincristine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Malignant glioma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.99E-02 Fold-change: 1.21E-01 Z-score: 2.07E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Malignant gliomas tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EDR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In vitro drug resistance in malignant gliomas was independent of prior therapy. High-grade glioblastomas showed a lower level of extreme drug resistance than low-grade astrocytomas to cisplatin (11% versus 27%), temozolomide (14% versus 27%), irinotecan (33% versus 53%), and BCNU (29% versus 38%). A substantial percentage of brain tumors overexpressed biomarkers associated with drug resistance, including MGMT (67%), GSTP1 (49%), and mutant p53 (41%). MGMT and GSTP1 overexpression was independently associated with in vitro resistance to BCNU, whereas coexpression of these two markers was associated with the greatest degree of BCNU resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Malignant glioma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.99E-02 Fold-change: 1.21E-01 Z-score: 2.07E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Malignant gliomas tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EDR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In vitro drug resistance in malignant gliomas was independent of prior therapy. High-grade glioblastomas showed a lower level of extreme drug resistance than low-grade astrocytomas to cisplatin (11% versus 27%), temozolomide (14% versus 27%), irinotecan (33% versus 53%), and BCNU (29% versus 38%). A substantial percentage of brain tumors overexpressed biomarkers associated with drug resistance, including MGMT (67%), GSTP1 (49%), and mutant p53 (41%). MGMT and GSTP1 overexpression was independently associated with in vitro resistance to BCNU, whereas coexpression of these two markers was associated with the greatest degree of BCNU resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.41E-06 Fold-change: 3.22E-01 Z-score: 4.97E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ovarian cancer tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Efficacy evaluation of chemotherapy | |||
| Mechanism Description | Ovarian cancer tissues had much higher expression levels of MRP1, GST-pai, and GSK3beta mRNA than normal ovarian tissues (P<0.05). The expression levels of MRP1, GST-pai, and GSK3beta mRNA in the Chemotherapy-sensitive group were significantly lower than those in the Chemotherapy-resistant group (P<0.05). Patients with high expression of MRP1, GST-pai, and GSK3beta mRNA had a much lower 3-year survival rate than patients with low expression of the genes (P<0.05). Highly expressed in patients with ovarian cancer, MRP1, GST-pai, and GSK3beta mRNA play an important role in the development and drug resistance of ovarian cancer. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Dacarbazine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Malignant glioma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.99E-02 Fold-change: 1.21E-01 Z-score: 2.07E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Malignant gliomas tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EDR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In vitro drug resistance in malignant gliomas was independent of prior therapy. High-grade glioblastomas showed a lower level of extreme drug resistance than low-grade astrocytomas to cisplatin (11% versus 27%), temozolomide (14% versus 27%), irinotecan (33% versus 53%), and BCNU (29% versus 38%). A substantial percentage of brain tumors overexpressed biomarkers associated with drug resistance, including MGMT (67%), GSTP1 (49%), and mutant p53 (41%). MGMT and GSTP1 overexpression was independently associated with in vitro resistance to BCNU, whereas coexpression of these two markers was associated with the greatest degree of BCNU resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malignant glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Malignant glioma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.99E-02 Fold-change: 1.21E-01 Z-score: 2.07E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Malignant gliomas tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EDR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In vitro drug resistance in malignant gliomas was independent of prior therapy. High-grade glioblastomas showed a lower level of extreme drug resistance than low-grade astrocytomas to cisplatin (11% versus 27%), temozolomide (14% versus 27%), irinotecan (33% versus 53%), and BCNU (29% versus 38%). A substantial percentage of brain tumors overexpressed biomarkers associated with drug resistance, including MGMT (67%), GSTP1 (49%), and mutant p53 (41%). MGMT and GSTP1 overexpression was independently associated with in vitro resistance to BCNU, whereas coexpression of these two markers was associated with the greatest degree of BCNU resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.61E-12 Fold-change: 3.86E-01 Z-score: 7.08E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |
| Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Vi-cell cell viability analyzer assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-21 achieves the drug resistance effect through three mechanisms: Increasing MDR1 and MPR1 expression levels, and enhancing drug efflux from the cells; increasing GSH, superoxide dismutase and GST-Pi expression levels and promoting drug inactivation; and inhibiting the PI3k signaling pathway and in turn inhibiting apoptotic signaling. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.41E-06 Fold-change: 3.22E-01 Z-score: 4.97E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | A2780-DR cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_EG64 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Clonogenic assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The Essential Role of H19 Contributing to Cisplatin Resistance by Regulating Glutathione Metabolism in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer.Additionally, we verified that different H19 expression levels in HGSC tissues showed strong correlation with cancer recurrence. H19 knockdown in A2780-DR cells resulted in recovery of cisplatin sensitivity in vitro and in vivo. Quantitative proteomics analysis indicated that six NRF2-targeted proteins, including NQO1, GSR, G6PD, GCLC, GCLM and GSTP1 involved in the glutathione metabolism pathway, were reduced in H19-knockdown cells. Furthermore, H19-knockdown cells were markedly more sensitive to hydrogen-peroxide treatment and exhibited lower glutathione levels. Our results reveal a previously unknown link between H19 and glutathione metabolism in the regulation of cancer-drug resistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovarian tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.41E-03 Fold-change: 1.16E-01 Z-score: 4.28E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ovarian cancer tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Efficacy evaluation of chemotherapy | |||
| Mechanism Description | Ovarian cancer tissues had much higher expression levels of MRP1, GST-pai, and GSK3beta mRNA than normal ovarian tissues (P<0.05). The expression levels of MRP1, GST-pai, and GSK3beta mRNA in the Chemotherapy-sensitive group were significantly lower than those in the Chemotherapy-resistant group (P<0.05). Patients with high expression of MRP1, GST-pai, and GSK3beta mRNA had a much lower 3-year survival rate than patients with low expression of the genes (P<0.05). Highly expressed in patients with ovarian cancer, MRP1, GST-pai, and GSK3beta mRNA play an important role in the development and drug resistance of ovarian cancer. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.64E-02 Fold-change: -7.77E-02 Z-score: -1.79E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell colony | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549/DPP cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| H1299/DDP cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-qPCR; Western blot analysis; Luciferase reporter assay; Dual-luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR133b reduces cisplatin resistance and its overexpression contributes to the suppression of the malignant growth and aggressiveness of cisplatin-resistant NSCLC cells by targeting GSTP1. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [10] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR-133b increases ovarian cancer cell sensitivity to cisplatin and paclitaxel by decreasing GST-Pi and MDR1 expression. | |||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [9] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.91E-01 Fold-change: -3.20E-03 Z-score: -5.38E-01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| SPC-A1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6955 | |
| A549/CDDP cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | GSTP1 augment drug resistance by catalyzing GSH-drug binding, exogenous miR-513a-3p plays a role in sensitizing human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines to cisplatin by repressing GSTP1 expression at the translational level. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.41E-06 Fold-change: 3.22E-01 Z-score: 4.97E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The upregulation of GST-Pi cause excessive intensity of detoxification of cytostatics, affect drug metabolism and influence the effects of chemotherapy, which results in resistance for paclitaxel in the ovarian cancer cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [10] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of miR-133b increases ovarian cancer cell sensitivity to cisplatin and paclitaxel by decreasing GST-Pi and MDR1 expression. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.64E-02 Fold-change: -7.77E-02 Z-score: -1.79E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT/ERK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | |
| Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | ||
| Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Luciferase reporter assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Suppression of miR-155 in this cell line considerably reversed doxorubicin resistance, and doxorubicin-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest were recovered. Furthermore, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and western blot analysis revealed that miR-155 suppression downregulated the expression of multidrug resistance protein 1, multidrug resistance-associated protein 1, breast cancer resistance protein, glutathione S-transferase-Pi, Survivin and B-cell lymphoma 2, and upregulated the expression of caspase-3 and caspase-8. In addition, it was found that miR-155 suppression inhibited the activation of AkT and extracellular signal-regulated kinase. The transcriptional activity of nuclear factor-kB and activator protein-1 was also downregulated. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Anaplastic astrocytoma [ICD-11: 2A00.04] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Anaplastic astrocytoma [ICD-11: 2A00.04] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Temozolomide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.43E-75 Fold-change: 9.33E-02 Z-score: 2.02E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Malignant gliomas tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Oncotech EDR assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | GSTP1 is the first major mechanism of resistance alkylator agents encounter after entering the cancer cell cytoplasm. GSTP1 acts to enzymatically conjugate glutathione to the reactive metabolites of BCNU. The mechanisms by which GSTP1 may be up-regulated in gliomas are under investigation. Constitutive expression is thought to be influenced by the proximal promoter factor Sp1, whereas increased expression levels may result from stabilization of GSTP1 mRNA. GSTP1 expression has been reported to be induced by drug exposure, indicating that it may play a role in acquired drug resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Bladder carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C94.1] | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bladder carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C94.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Glutathione | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Bladder cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Bladder tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.13E-03 Fold-change: 6.48E-02 Z-score: 3.58E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SABC immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In the 119 cases of bladder carcinoma, the positive rate of HIF-1alpha was 57.9%, the positive rate of GST-Pi was 67.2%. Co-expression of HIF-1alpha and GST-Pi is a object index for judging differentiation and chemoresistance of bladder cancer. GTS-Pi catalyzes the combination of glutathione and drugs to form gh-x, which makes it easier to excrete cells and cause drug resistance of cancer. | |||
Investigative Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Folfox protocol | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I105V (c.313A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.40 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.80 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
P
P
P
P
Y
Y
T
T
V
V
V
V
Y
Y
F
F
10
|
P
P
V
V
R
R
G
G
R
R
C
C
A
A
A
A
L
L
R
R
20
|
M
M
L
L
L
L
A
A
D
D
Q
Q
G
G
Q
Q
S
S
W
W
30
|
K
K
E
E
E
E
V
V
V
V
T
T
V
V
E
E
T
T
W
W
40
|
Q
Q
E
E
G
G
S
S
L
L
K
K
A
A
S
S
C
C
L
L
50
|
Y
Y
G
G
Q
Q
L
L
P
P
K
K
F
F
Q
Q
D
D
G
G
60
|
D
D
L
L
T
T
L
L
Y
Y
Q
Q
S
S
N
N
T
T
I
I
70
|
L
L
R
R
H
H
L
L
G
G
R
R
T
T
L
L
G
G
L
L
80
|
Y
Y
G
G
K
K
D
D
Q
Q
Q
Q
E
E
A
A
A
A
L
L
90
|
V
V
D
D
M
M
V
V
N
N
D
D
G
G
V
V
E
E
D
D
100
|
L
L
R
R
C
C
K
K
Y
Y
I
V
S
S
L
L
I
I
Y
Y
110
|
T
T
N
N
Y
Y
E
E
A
A
G
G
K
K
D
D
D
D
Y
Y
120
|
V
V
K
K
A
A
L
L
P
P
G
G
Q
Q
L
L
K
K
P
P
130
|
F
F
E
E
T
T
L
L
L
L
S
S
Q
Q
N
N
Q
Q
G
G
140
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
F
F
I
I
V
V
G
G
D
D
Q
Q
I
I
150
|
S
S
F
F
A
A
D
D
Y
Y
N
N
L
L
L
L
D
D
L
L
160
|
L
L
L
L
I
I
H
H
E
E
V
V
L
L
A
A
P
P
G
G
170
|
C
C
L
L
D
D
A
A
F
F
P
P
L
L
L
L
S
S
A
A
180
|
Y
Y
V
V
G
G
R
R
L
L
S
S
A
A
R
R
P
P
K
K
190
|
L
L
K
K
A
A
F
F
L
L
A
A
S
S
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
200
|
V
V
N
N
L
L
P
P
I
I
N
N
G
G
N
N
G
G
K
K
210
|
Q
Q
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Human colorectal carcinoma tissue | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.I105V (c.313A>G) in gene GSTP1 cause the sensitivity of Folfox Protocol by drug inactivation by structure modification | ||||||||||||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.43E-75; Fold-change: 6.27E-01; Z-score: 1.37E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.28E-01; Fold-change: -1.93E-01; Z-score: -6.79E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
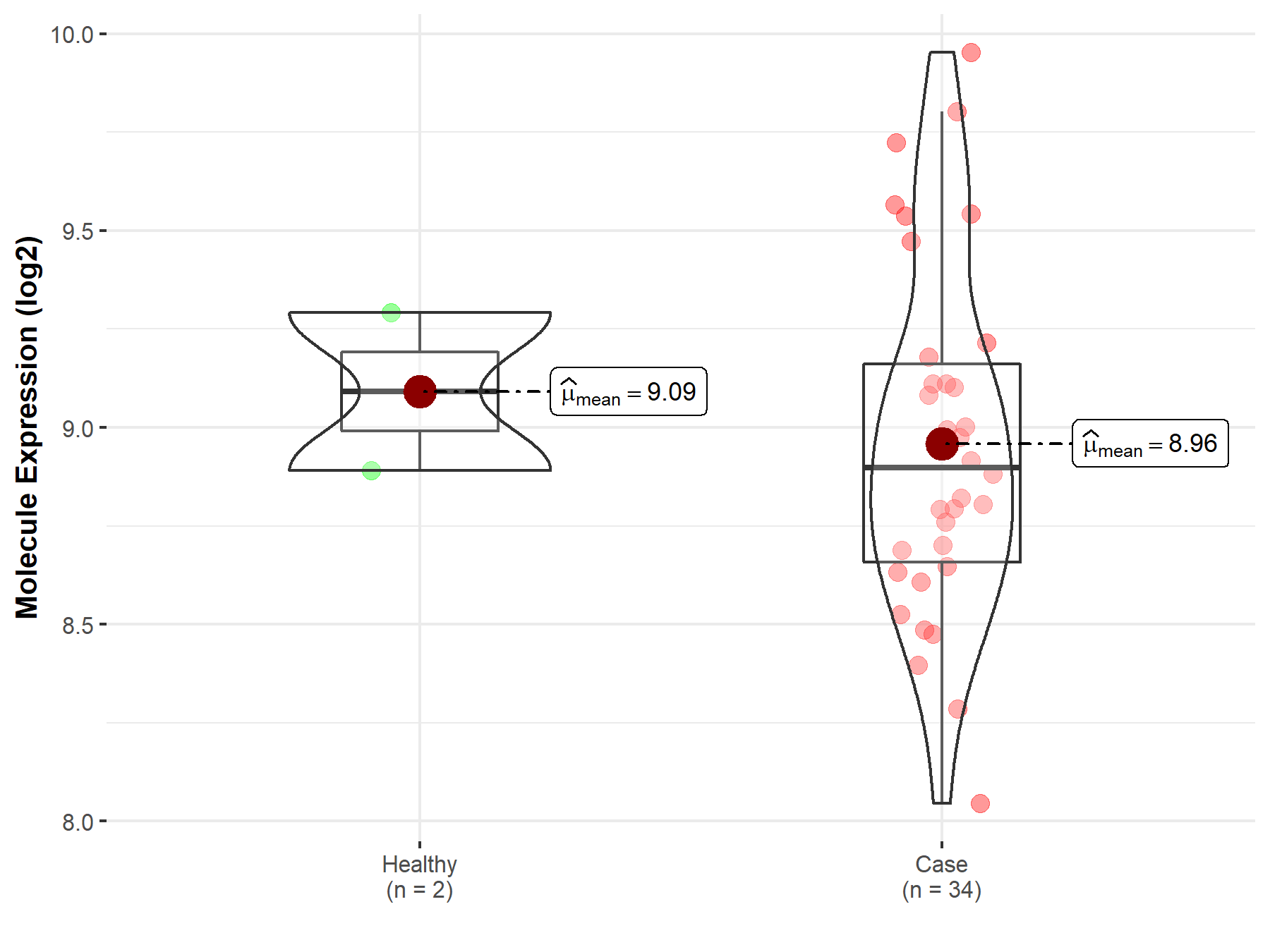
| The Studied Tissue | White matter | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.70E-02; Fold-change: 9.41E-01; Z-score: 1.36E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
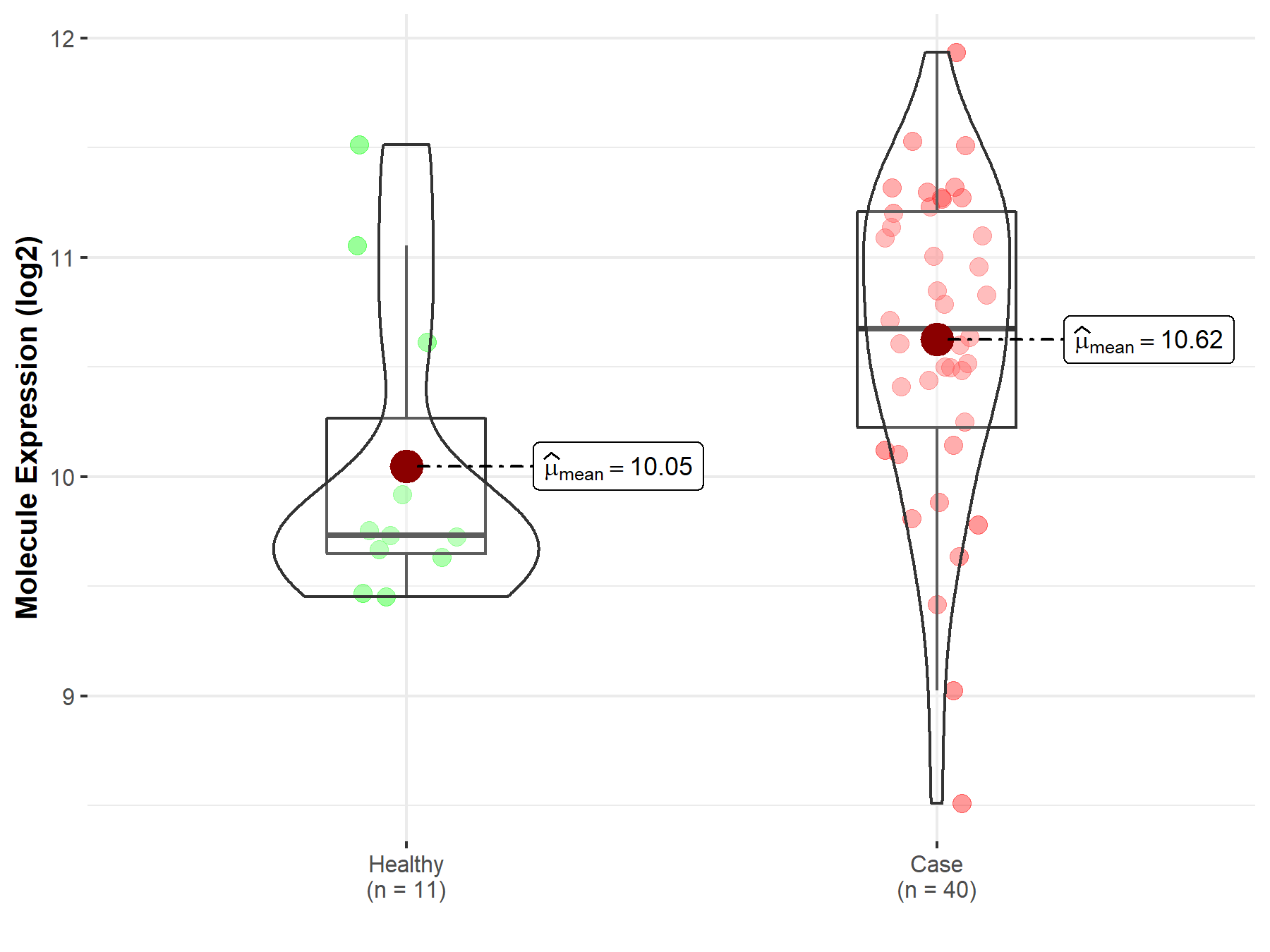
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Neuroectodermal tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.35E-05; Fold-change: 7.82E-01; Z-score: 2.29E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
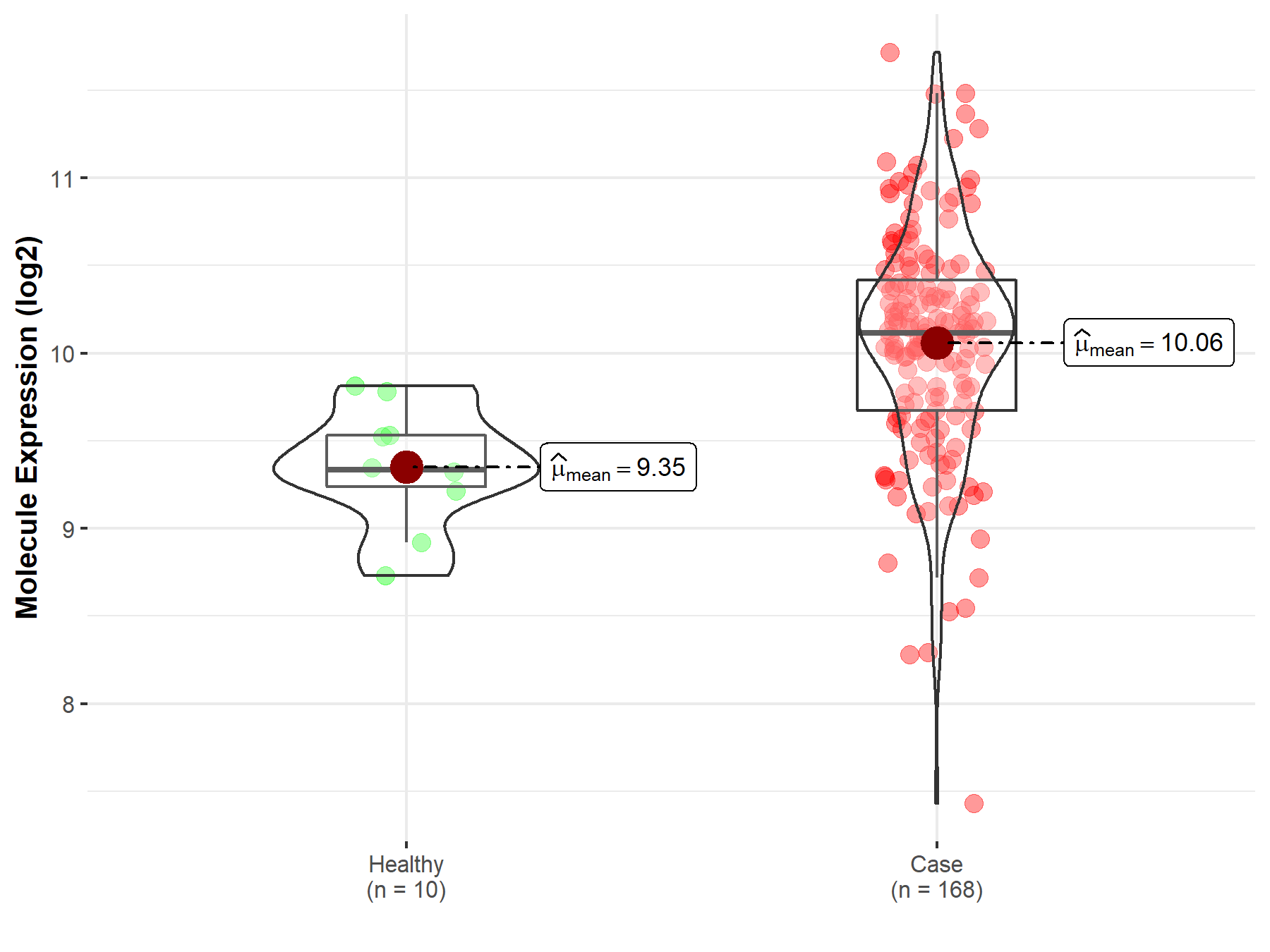
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.91E-01; Fold-change: 1.98E-01; Z-score: 4.79E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.63E-01; Fold-change: 1.44E-01; Z-score: 1.97E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
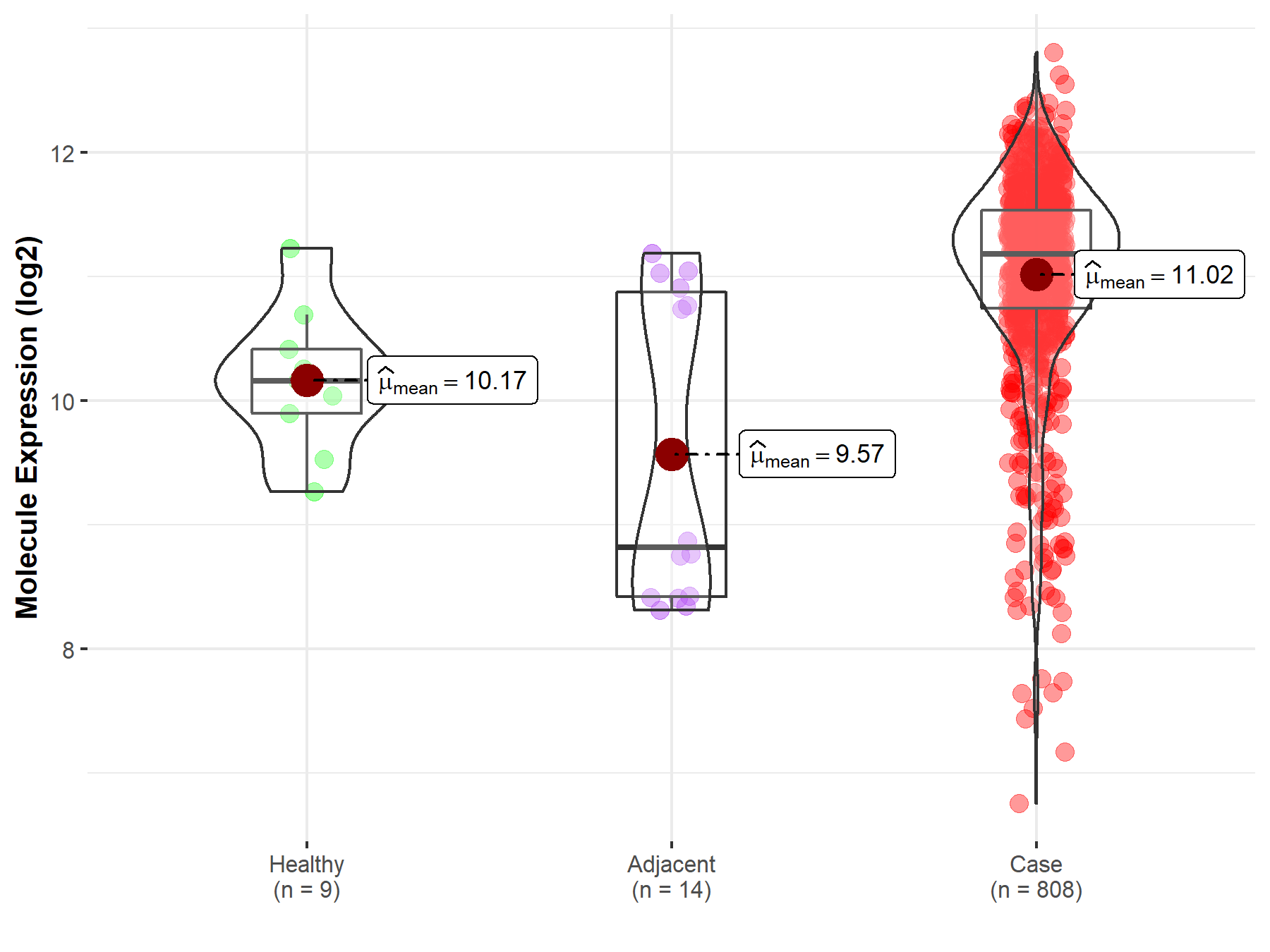
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.41E-03; Fold-change: 1.02E+00; Z-score: 1.73E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 8.18E-04; Fold-change: 2.36E+00; Z-score: 1.89E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Bladder tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Bladder cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.13E-03; Fold-change: 5.14E-01; Z-score: 1.60E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
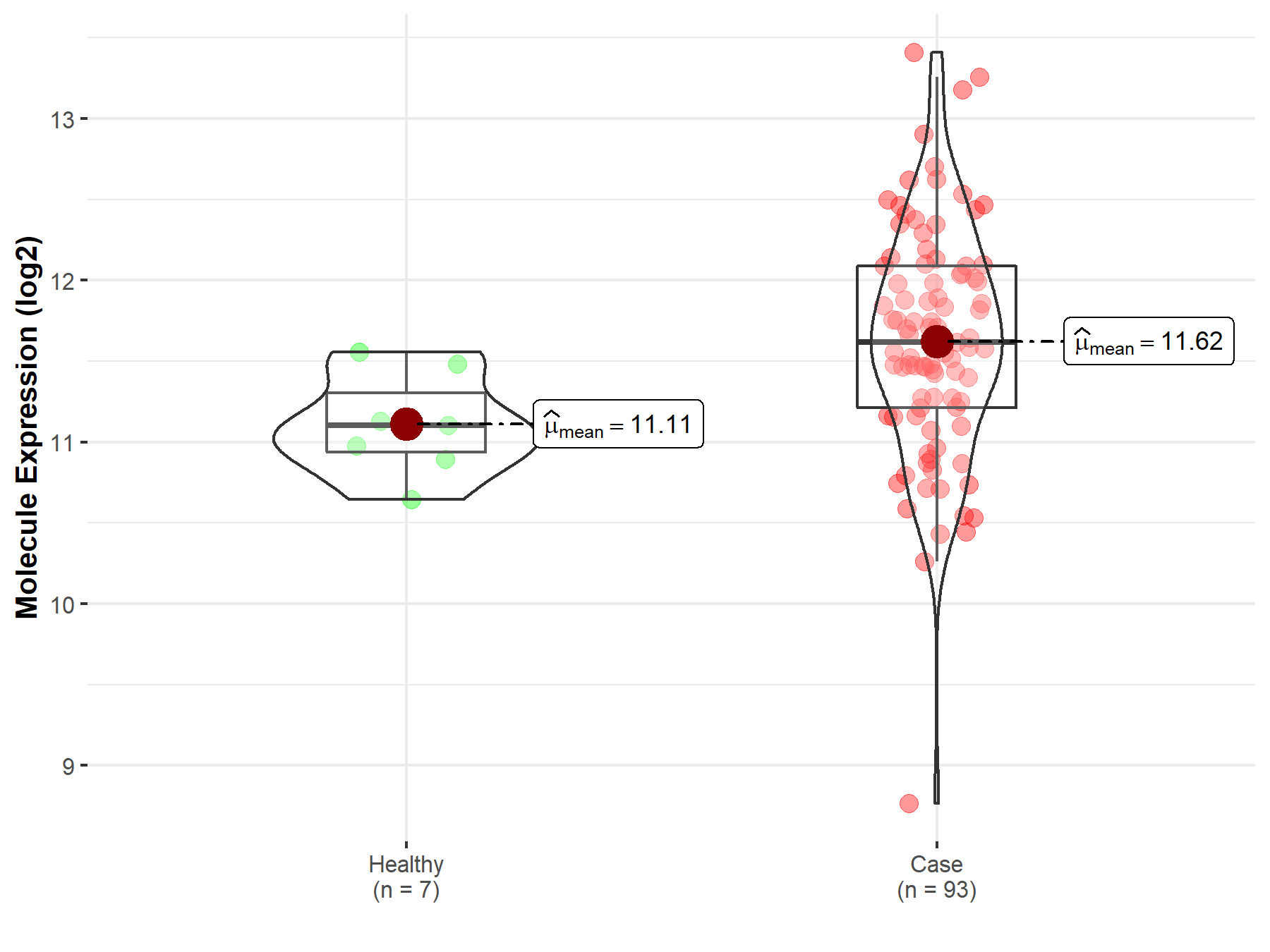
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

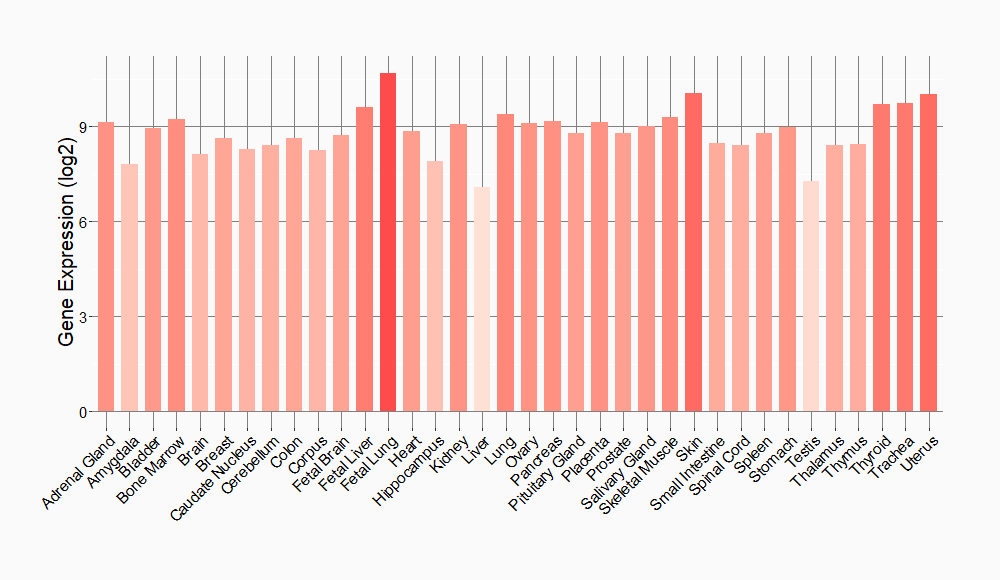
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
