Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00029) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Glutathione
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Glutathione; 70-18-8; Glutathion; Isethion; Tathion; Glutathione-SH; Glutinal; reduced glutathione; Neuthion; Deltathione; Copren; L-Glutathione reduced; Glutide; Tathione; Triptide; Ledac; Glutatione; GSH; Glutatiol; Panaron; gamma-L-Glutamyl-L-cysteinylglycine; Glutathione SH; L-Glutatione; Glutathione (reduced); Agifutol S; L-gamma-glutamyl-L-cysteinylglycine; gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl-glycine; 5-L-Glutamyl-L-cysteinylglycine; Glutathione [JAN]; glutathione red; gamma-L-Glutamylcysteinylglycine; red. glutathione
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
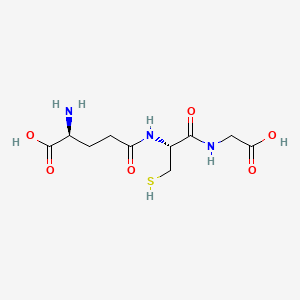
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[2]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[3]
|
||||
| Target | Enzyme unspecific (Enz) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C10H17N3O6S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C(CC(=O)N[C@@H](CS)C(=O)NCC(=O)O)[C@@H](C(=O)O)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C10H17N3O6S/c11-5(10(18)19)1-2-7(14)13-6(4-20)9(17)12-3-8(15)16/h5-6,20H,1-4,11H2,(H,12,17)(H,13,14)(H,15,16)(H,18,19)/t5-,6-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
RWSXRVCMGQZWBV-WDSKDSINSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Glutathione S-transferase P (GSTP1) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bladder carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C94.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Bladder cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Bladder tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.13E-03 Fold-change: 6.48E-02 Z-score: 3.58E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SABC immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In the 119 cases of bladder carcinoma, the positive rate of HIF-1alpha was 57.9%, the positive rate of GST-Pi was 67.2%. Co-expression of HIF-1alpha and GST-Pi is a object index for judging differentiation and chemoresistance of bladder cancer. GTS-Pi catalyzes the combination of glutathione and drugs to form gh-x, which makes it easier to excrete cells and cause drug resistance of cancer. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Chloroquine resistance transporter (CRT) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K76T |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium falciparum C-1Dd2 | 5833 | ||
| Plasmodium falciparum C2GC03 | 5833 | |||
| Plasmodium falciparum C3Dd2 | 5833 | |||
| Plasmodium falciparum C67G8 | 5833 | |||
| Plasmodium falciparum GC03 | 5833 | |||
| Plasmodium falciparum T76k-1Dd2 | 5833 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
[3H]-hypoxanthine assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The k76T mutation in PfCRT generates structural changes that are sufficient to allow GSH transport, but not CQ transport. mutant pfcrt allows enhanced transport of GSH into the parasite's DV. The elevated levels of GSH in the DV reduce the level of free heme available for CQ binding, which mediates the lower susceptibility to CQ in the PfCRT mutant parasites. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase (GGCS) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Malaria [ICD-11: 1F45.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Plasmodium berghei ANkA 2.34 | 5823 | ||
| Plasmodium berghei pbggcs-ko | 5821 | |||
| Plasmodium berghei pbggcs-oe | 5821 | |||
| In Vivo Model | Swiss albino CD-1 female mice xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
In vivo drug suppressive test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | To analyze the role of GSH levels in CQ and ART resistance, we generated transgenic Plasmodium berghei parasites either deficient in or overexpressing the gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase gene (pbggcs) encoding the rate-limiting enzyme in GSH biosynthesis. These lines produce either lower (pbggcs-ko) or higher (pbggcs-oe) levels of GSH than wild type parasites. Recrudescence assays after the parasites have been exposed to a sub-lethal dose of ART showed that parasites with low levels of GSH are more sensitive to ART tre. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
