Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00043)
| Name |
Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cell division protein kinase 6; Serine/threonine-protein kinase PLSTIRE; CDKN6
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
CDK6
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr7:92604921-92836573[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MEKDGLCRADQQYECVAEIGEGAYGKVFKARDLKNGGRFVALKRVRVQTGEEGMPLSTIR
EVAVLRHLETFEHPNVVRLFDVCTVSRTDRETKLTLVFEHVDQDLTTYLDKVPEPGVPTE TIKDMMFQLLRGLDFLHSHRVVHRDLKPQNILVTSSGQIKLADFGLARIYSFQMALTSVV VTLWYRAPEVLLQSSYATPVDLWSVGCIFAEMFRRKPLFRGSSDVDQLGKILDVIGLPGE EDWPRDVALPRQAFHSKSAQPIEKFVTDIDELGKDLLLKCLTFNPAKRISAYSALSHPYF QDLERCKENLDSHLPPSQNTSELNTA Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase involved in the control of the cell cycle and differentiation; promotes G1/S transition. Phosphorylates pRB/RB1 and NPM1. Interacts with D-type G1 cyclins during interphase at G1 to form a pRB/RB1 kinase and controls the entrance into the cell cycle. Involved in initiation and maintenance of cell cycle exit during cell differentiation; prevents cell proliferation and regulates negatively cell differentiation, but is required for the proliferation of specific cell types (e.g. erythroid and hematopoietic cells). Essential for cell proliferation within the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus and the subventricular zone of the lateral ventricles. Required during thymocyte development. Promotes the production of newborn neurons, probably by modulating G1 length. Promotes, at least in astrocytes, changes in patterns of gene expression, changes in the actin cytoskeleton including loss of stress fibers, and enhanced motility during cell differentiation. Prevents myeloid differentiation by interfering with RUNX1 and reducing its transcription transactivation activity, but promotes proliferation of normal myeloid progenitors. Delays senescence. Promotes the proliferation of beta-cells in pancreatic islets of Langerhans. May play a role in the centrosome organization during the cell cycle phases.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
6 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.73E-01 Fold-change: -7.96E-03 Z-score: -1.36E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LINC00511 positively regulated CDk6 expression in breast cancer cells. And LINC00511 knockdown enhanced paclitaxel cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells by upregulating miR-29c. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 | |
| A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 | |
| MCF-7/ADM cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | |
| A2780/PTX cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_IJ13 | |
| HOEC cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| SkOV3/PTX cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_HF69 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-145 modulates the cellular response to anticancer drugs, Down-regulation of miR-145 is correlated with overexpression of Sp1 and Cdk6, Sp1 and Cdk6 are targets of miR-145, miR-145 downregulated P-gp and pRb through inhibition of Sp1 and Cdk6, miR-145 sensitized EOC cells to paclitaxel via Sp1 and Cdk6 inhibition, Overexpression of miR-145 enhanced paclitaxel sensitivity in vivo. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | CDk6 knockdown attenuated the effects of miR-29c inhibition on paclitaxel cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Bladder cancer [ICD-11: 2C94.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | 5637 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0126 |
| T24 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0554 | |
| TCCSuP cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1738 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
WST-1 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Cdk6, in complex with Cdk4 and cyclin D1, is a key regulator of Rb activity and thereby G1/S transition, SIRT-1 is a deacetylase whose targets including p53, FOXO, SFRP1 and PGC1. Transfection with pre-miR-34a increases chemo-sensitivity to cisplatin through inhibition of Cdk6 and SIRT-1. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | LY2835219 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | In some studies, CDK6 overexpression was reported to promote resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in preclinical models. Possible mechanisms how CDK6 amplification confers resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitor might be due to kinase-independent function of CDK6, which involves VEGF-A or p16. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Palbociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | In some studies, CDK6 overexpression was reported to promote resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in preclinical models. Possible mechanisms how CDK6 amplification confers resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitor might be due to kinase-independent function of CDK6, which involves VEGF-A or p16. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Ribociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | In some studies, CDK6 overexpression was reported to promote resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in preclinical models. Possible mechanisms how CDK6 amplification confers resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitor might be due to kinase-independent function of CDK6, which involves VEGF-A or p16. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Triple negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.9] | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Triple negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.9] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Trilaciclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | |
| Mechanism Description | Trilaciclib, a small molecule short-acting inhibitor of CDK4/6, has also been approved recently for people with small cell lung cancer, and is also expected to be clinically effective against breast cancer. r\Reducing Rb phosphorylation promotes AKT pathway activity, which may result in CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance. Trilaciclib, an intravenous and competitive CDK4/6 inhibitor, has been shown to reduce the myelotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents by inducing transient cell cycle arrest. This drug can differentially inhibit both cytotoxic and regulatory T cells. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.73E-01; Fold-change: -9.95E-02; Z-score: -3.50E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 6.18E-01; Fold-change: -1.33E-01; Z-score: -4.70E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
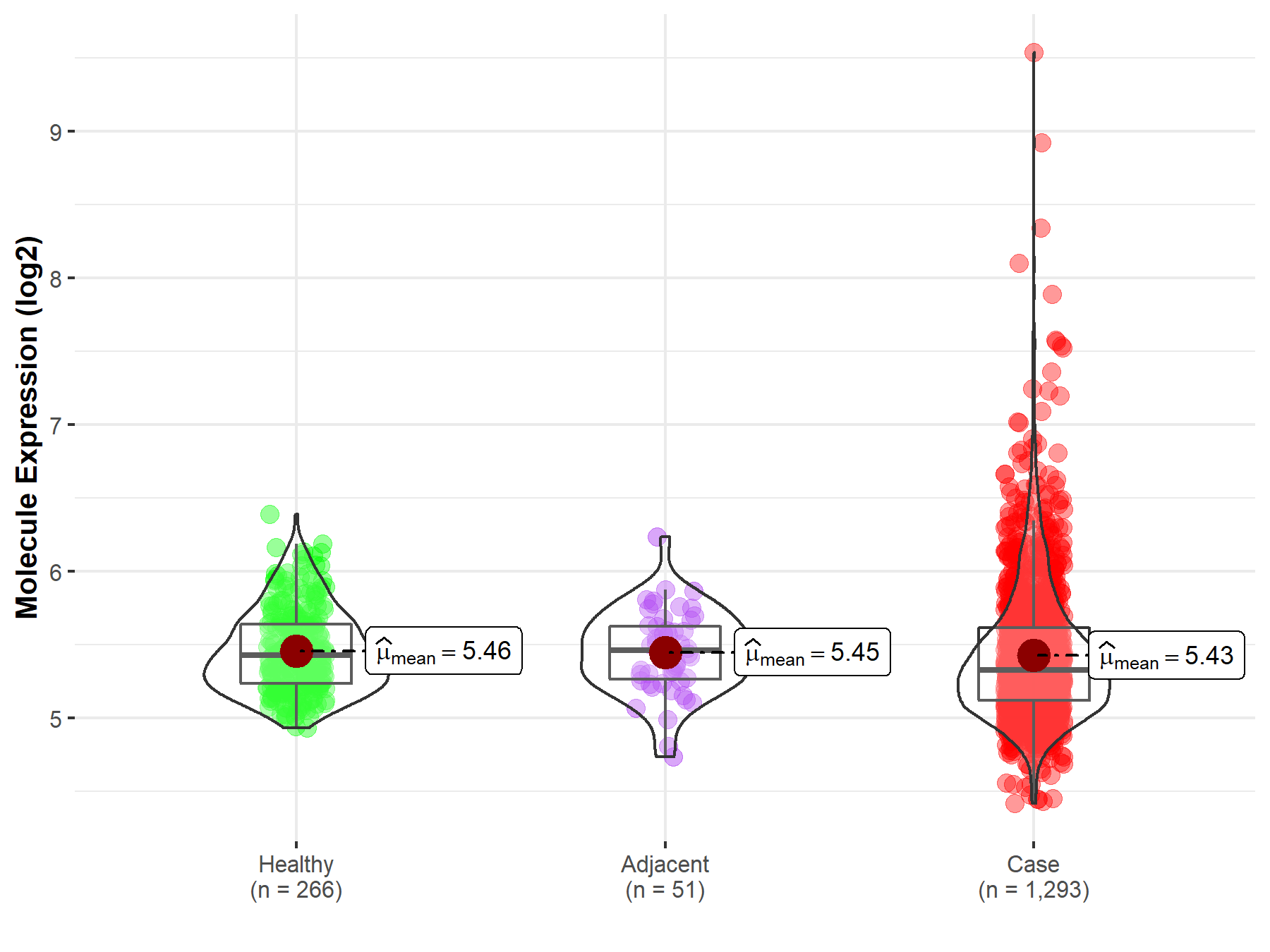
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.02E-02; Fold-change: 1.24E-03; Z-score: 5.44E-03 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.80E-02; Fold-change: -3.72E-01; Z-score: -4.61E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
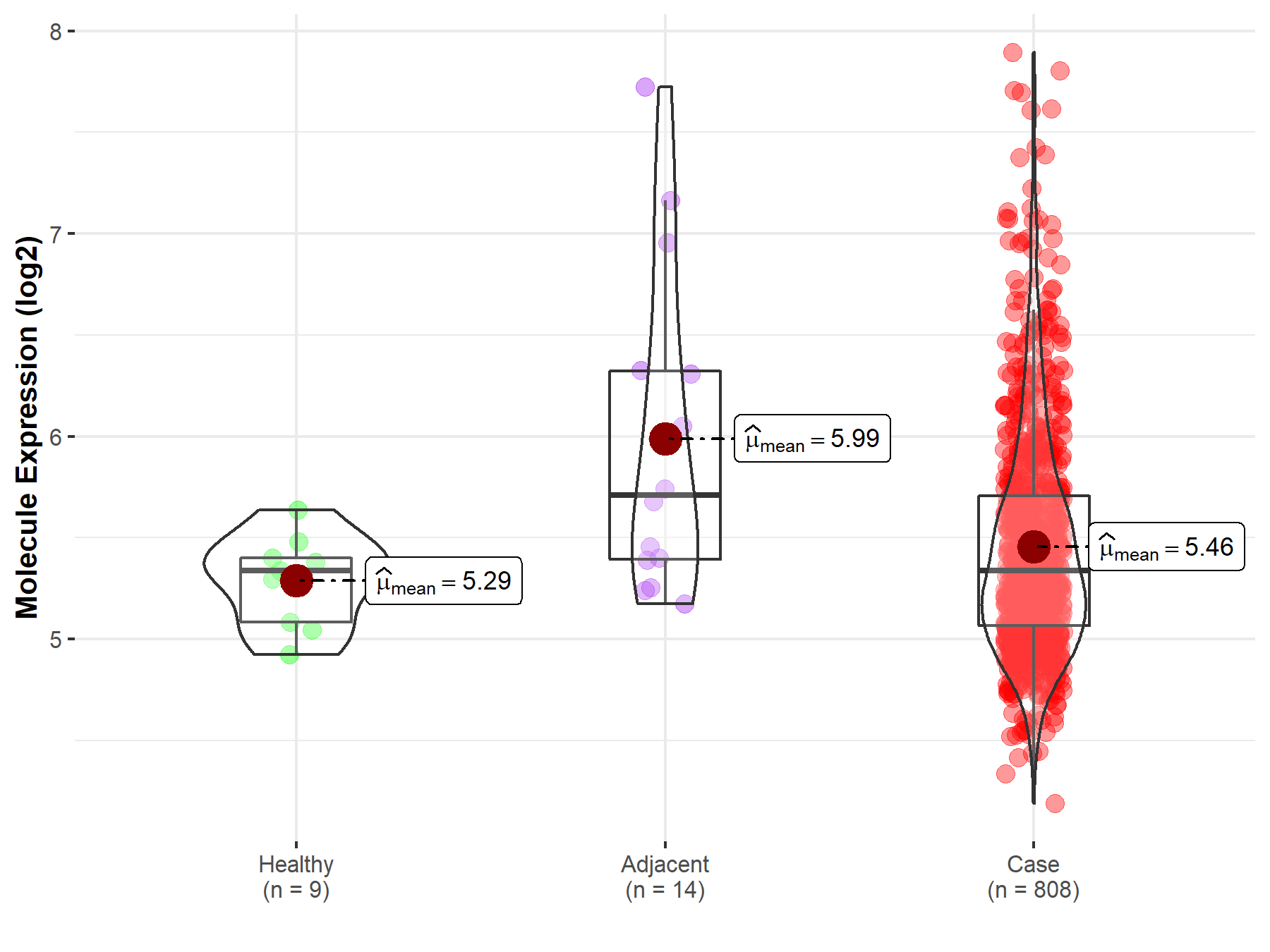
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Bladder tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Bladder cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.88E-01; Fold-change: 3.30E-01; Z-score: 1.17E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
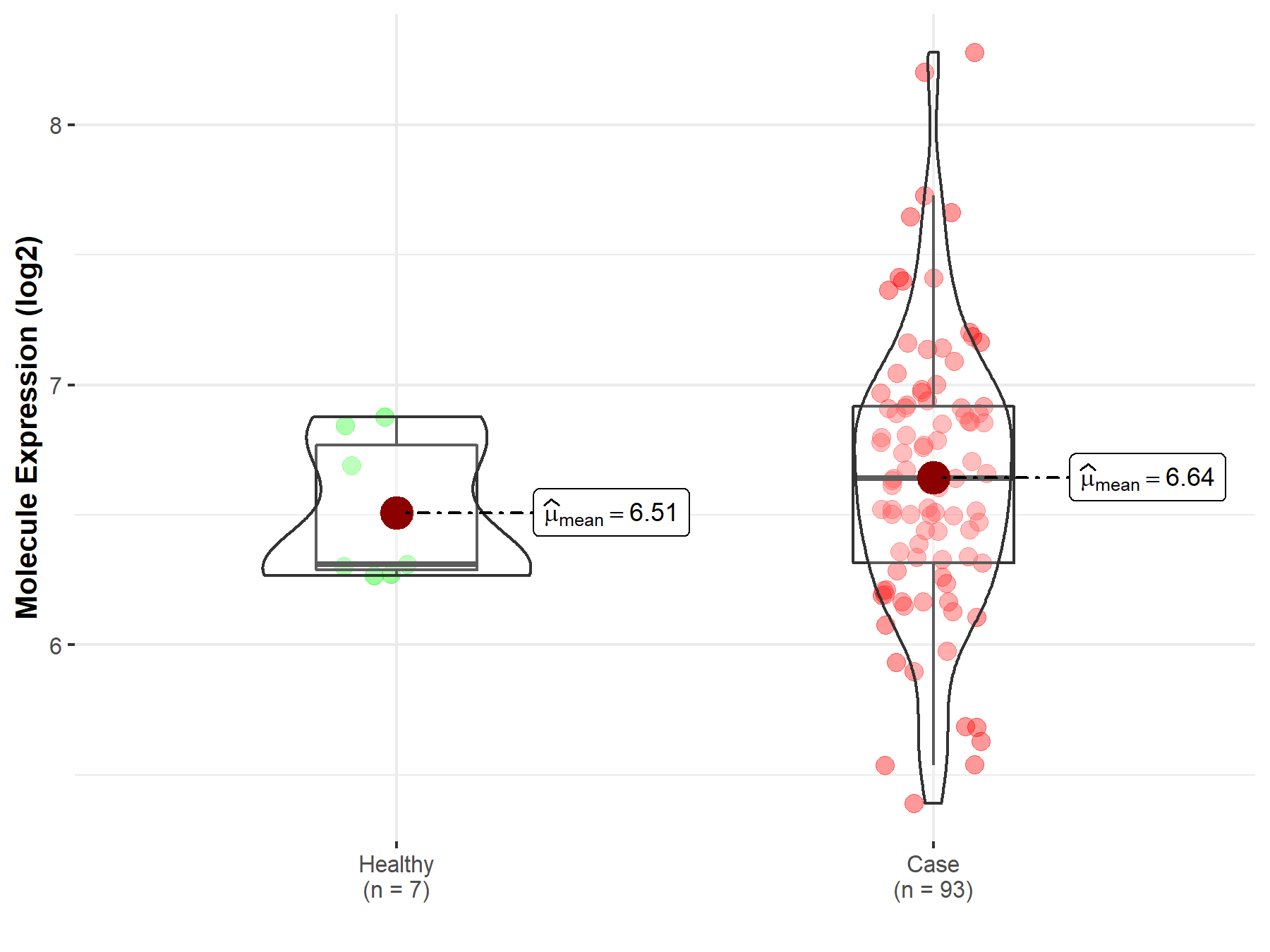
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

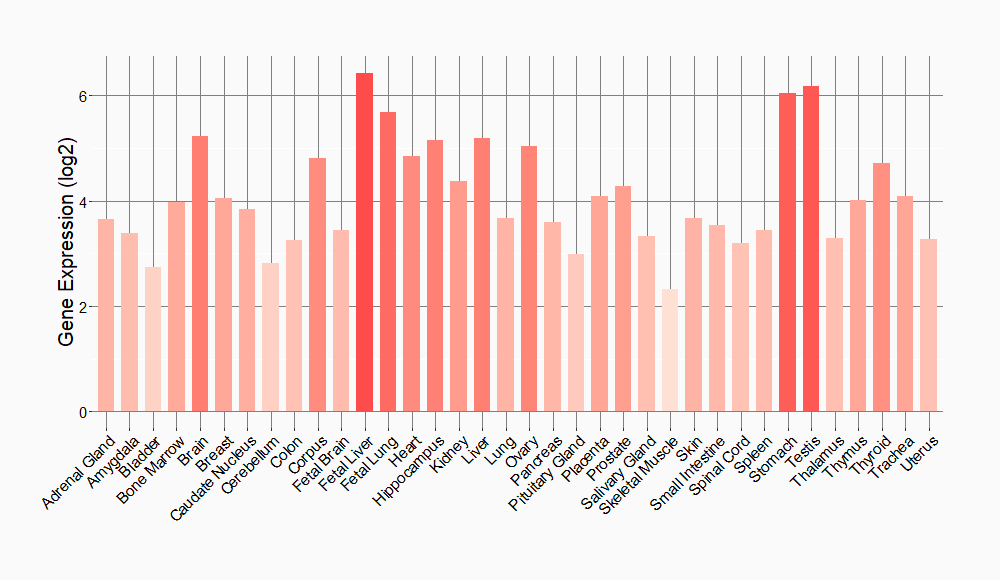
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
