Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01291) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Trilaciclib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Trilaciclib; 1374743-00-6; G1T28; UNII-U6072DO9XG; U6072DO9XG; 2'-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)amino)-7',8'-dihydro-6'H-spiro[cyclohexane-1,9'-pyrazino[1',2':1,5]pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin]-6'-one; Cosela; 2'-((5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)amino)-7',8'-dihydro-6'H-spiro(cyclohexane-1,9'-pyrazino(1',2':1,5)pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidin)-6'-one; Trilaciclib [USAN]; G1T28(Trilaciclib); G1T28 di-HCl; Trilaciclib (USAN/INN); GTPL9626; CHEMBL3894860; SCHEMBL10082028; BDBM253928; BCP25013; EX-A4297; NSC816987; DB15442; NSC-816987; SB19783; US9464092, T; HY-101467; CS-0021431; A17084; D11130; 2'-((5-(4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-pyridinyl)amino)-7',8'-dihydro-6'H-spiro(cyclohexane-1,9'-pyrazino(1',2':1,5)pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidin)-6'-one; 2-[[5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]amino]spiro[7,8-dihydropyrazino[5,6]pyrrolo[1,2-d]pyrimidine-9,1'-cyclohexane]-6-one; 4-[[5-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl]amino]spiro[1,3,5,11-tetrazatricyclo[7.4.0.02,7]trideca-2,4,6,8-tetraene-13,1'-cyclohexane]-10-one; Spiro(cyclohexane-1,9'(6'H)-pyrazino(1',2':1,5)pyrrolo(2,3-d)pyrimidin)-6'-one, 7',8'-dihydro-2'-((5-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-pyridinyl)amino)-
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 2 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
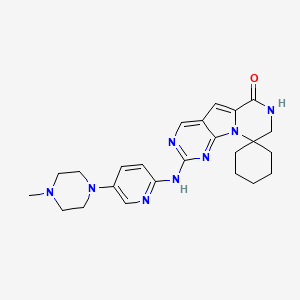
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) | CDK4_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6) | CDK6_HUMAN | [1] | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C24H30N8O
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CN1CCN(CC1)C2=CN=C(C=C2)NC3=NC=C4C=C5C(=O)NCC6(N5C4=N3)CCCCC6
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C24H30N8O/c1-30-9-11-31(12-10-30)18-5-6-20(25-15-18)28-23-26-14-17-13-19-22(33)27-16-24(7-3-2-4-8-24)32(19)21(17)29-23/h5-6,13-15H,2-4,7-12,16H2,1H3,(H,27,33)(H,25,26,28,29)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
PDGKHKMBHVFCMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Triple negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.9] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | |
| Mechanism Description | Trilaciclib, a small molecule short-acting inhibitor of CDK4/6, has also been approved recently for people with small cell lung cancer, and is also expected to be clinically effective against breast cancer. r\Reducing Rb phosphorylation promotes AKT pathway activity, which may result in CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance. Trilaciclib, an intravenous and competitive CDK4/6 inhibitor, has been shown to reduce the myelotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents by inducing transient cell cycle arrest. This drug can differentially inhibit both cytotoxic and regulatory T cells. | |||
| Key Molecule: Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Triple negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.9] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Inhibition |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | |
| Mechanism Description | Trilaciclib, a small molecule short-acting inhibitor of CDK4/6, has also been approved recently for people with small cell lung cancer, and is also expected to be clinically effective against breast cancer. r\Reducing Rb phosphorylation promotes AKT pathway activity, which may result in CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance. Trilaciclib, an intravenous and competitive CDK4/6 inhibitor, has been shown to reduce the myelotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents by inducing transient cell cycle arrest. This drug can differentially inhibit both cytotoxic and regulatory T cells. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
