Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01610) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Berzosertib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
VE-822; 1232416-25-9; Berzosertib; VX-970; VE822; UNII-L423PRV3V3; VE 822; VX970; VE-822 (VX-970); 5-(4-(isopropylsulfonyl)phenyl)-3-(3-(4-((methylamino)methyl)phenyl)isoxazol-5-yl)pyrazin-2-amine; L423PRV3V3; 3-(3-{4-[(METHYLAMINO)METHYL]PHENYL}-1,2-OXAZOL-5-YL)-5-[4-(PROPANE-2-SULFONYL)PHENYL]PYRAZIN-2-AMINE; 3-[3-[4-(methylaminomethyl)phenyl]-1,2-oxazol-5-yl]-5-(4-propan-2-ylsulfonylphenyl)pyrazin-2-amine; M6620; 2-Pyrazinamine, 3-(3-(4-((methylamino)methyl)phenyl)-5-isoxazolyl)-5-(4-((1-methylethyl)sulfonyl)phenyl)-; BDBM50226746; 2-Pyrazinamine, 3-[3-[4-[(methylamino)methyl]phenyl]-5-isoxazolyl]-5-[4-[(1-methylethyl)sulfonyl]phenyl]-; 3-(3-(4-((METHYLAMINO)METHYL)PHENYL)-1,2-OXAZOL-5-YL)-5-(4-(PROPANE-2-SULFONYL)PHENYL)PYRAZIN-2-AMINE; 3-[3-[4-[(Methylamino)methyl]phenyl]-5-isoxazolyl]-5-[4-[(1-methylethyl)sulfonyl]phenyl]-2-pyrazinamine; 5-(4-(isopropylsulfonyl)phenyl)-3-(3-(4-((methylamino)methyl)phenyl)isoxazol-5-yl)pyrazin-2-amine.; Berzosertib [USAN]; VX-970;Berzosertib; Berzosertib (USAN/INN); Berzosertib (VE-822); AGN-PC-0CXKB3; GTPL8003; SCHEMBL3061890; CHEMBL3989870; EX-A529; CHEBI:131166; BDBM350085; HMS3653C05; HMS3747I11; AOB87712; BCP07948; 2789AH; MFCD27976794; NSC777718; s7102; US10208027, Compound II-1; US10208027, Compound II-2; US10208027, Compound II-3; US10208027, Compound II-4; VX 970; ZINC96170459; AKOS025404905; CCG-264673; CS-1861; DB11794; NSC-777718; SB17265; NCGC00386313-07; AC-32951; AS-17041; DA-46989; HY-13902; QC-10953; FT-0700136; SW220202-1; A13289; D11148; M-6620; A857986; Q27089129; 5-(4-isopropylsulfonylphenyl)-3-[3-[4-(methylaminomethyl)phenyl]isoxazol-5-yl]pyrazin-2-amine; Synthesis of 3-[3-[4-[dideuterio(methylamino)methyl]phenyl]isoxazol-5-yl]-5-(4-isopropylsulfonylphenyl)pyrazin-2-amine
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
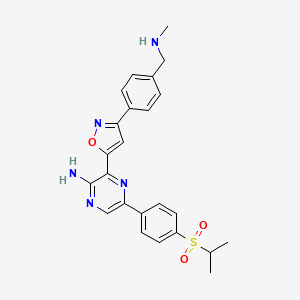
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
7
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC(C)S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=CN=C(C(=N2)C3=CC(=NO3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)CNC)N
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C24H25N5O3S/c1-15(2)33(30,31)19-10-8-18(9-11-19)21-14-27-24(25)23(28-21)22-12-20(29-32-22)17-6-4-16(5-7-17)13-26-3/h4-12,14-15,26H,13H2,1-3H3,(H2,25,27)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
JZCWLJDSIRUGIN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Oxalosuccinate decarboxylase (IDH1) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R132H (c.395G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.88 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
S
S
K
K
K
K
I
I
S
S
G
G
G
G
S
S
10
|
V
V
V
V
E
E
M
M
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
M
M
T
T
20
|
R
R
I
I
I
I
W
W
E
E
L
L
I
I
K
K
E
E
K
K
30
|
L
L
I
I
F
F
P
P
Y
Y
V
V
E
E
L
L
D
D
L
L
40
|
H
H
S
S
Y
Y
D
D
L
L
G
G
I
I
E
E
N
N
R
R
50
|
D
D
A
A
T
T
N
N
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
T
T
K
K
D
D
60
|
A
A
A
A
E
E
A
A
I
I
K
K
K
K
H
H
N
N
V
V
70
|
G
G
V
V
K
K
C
C
A
A
T
T
I
I
T
T
P
P
D
D
80
|
E
E
K
K
R
R
V
V
E
E
E
E
F
F
K
K
L
L
K
K
90
|
Q
Q
M
M
W
W
K
K
S
S
P
P
N
N
G
G
T
T
I
I
100
|
R
R
N
N
I
I
L
L
G
G
G
G
T
T
V
V
F
F
R
R
110
|
E
E
A
A
I
I
I
I
C
C
K
K
N
N
I
I
P
P
R
R
120
|
L
L
V
V
S
S
G
G
W
W
V
V
K
K
P
P
I
I
I
I
130
|
I
I
G
G
R
H
H
H
A
A
Y
Y
G
G
D
D
Q
Q
Y
Y
140
|
R
R
A
A
T
T
D
D
F
F
V
V
V
V
P
P
G
G
P
P
150
|
G
G
K
K
V
V
E
E
I
I
T
T
Y
Y
T
T
P
P
S
S
160
|
D
D
G
G
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
V
V
T
T
Y
Y
L
L
V
V
170
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
E
E
E
E
G
G
G
G
G
G
V
V
A
A
180
|
M
M
G
G
M
M
Y
Y
N
N
Q
Q
D
D
K
K
S
S
I
I
190
|
E
E
D
D
F
F
A
A
H
H
S
S
S
S
F
F
Q
Q
M
M
200
|
A
A
L
L
S
S
K
K
G
G
W
W
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
L
L
210
|
S
S
T
T
K
K
N
N
T
T
I
I
L
L
K
K
K
K
Y
Y
220
|
D
D
G
G
R
R
F
F
K
K
D
D
I
I
F
F
Q
Q
E
E
230
|
I
I
Y
Y
D
D
K
K
Q
Q
Y
Y
K
K
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
240
|
E
E
A
A
Q
Q
K
K
I
I
W
W
Y
Y
E
E
H
H
R
R
250
|
L
L
I
I
D
D
D
D
M
M
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
A
A
M
M
260
|
K
K
S
S
E
E
G
G
G
G
F
F
I
I
W
W
A
A
C
C
270
|
K
K
N
N
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
D
D
V
V
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
280
|
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
Y
Y
G
G
S
S
L
L
G
G
290
|
M
M
M
M
T
T
S
S
V
V
L
L
V
V
C
C
P
P
D
D
300
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
V
V
E
E
A
A
E
E
A
A
A
A
H
H
310
|
G
G
T
T
V
V
T
T
R
R
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
Y
Y
320
|
Q
Q
K
K
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
S
S
T
T
N
N
P
P
330
|
I
I
A
A
S
S
I
I
F
F
A
A
W
W
T
T
R
R
G
G
340
|
L
L
A
A
H
H
R
R
A
A
K
K
L
L
D
D
N
N
N
N
350
|
K
K
E
E
L
L
A
A
F
F
F
F
A
A
N
N
A
A
L
L
360
|
E
E
E
E
V
V
S
S
I
I
E
E
T
T
I
I
E
E
A
A
370
|
G
G
F
F
M
M
T
T
K
K
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
C
C
380
|
I
I
K
K
G
G
L
L
P
P
N
N
V
V
Q
Q
R
R
S
S
390
|
D
D
Y
Y
L
L
N
N
T
T
F
F
E
E
F
F
M
M
D
D
400
|
K
K
L
L
G
G
E
E
N
N
L
L
K
K
I
I
K
K
L
L
410
|
A
A
Q
Q
A
A
K
K
L
L
S
S
L
L
E
E
H
H
H
H
420
|
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | IDH2 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D3DY | |||||||||
| IDH1 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D3DY | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female athymic nu/nu mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The oncometabolite, 2-hydroxyglutarate, renders IDH1/2 mutant cancer cells deficient in homologous recombination and confers vulnerability to synthetic lethal targeting with PARP inhibitors. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 1A (ARID1A) | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Nonsense | p.Q456* (c.1366C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | ES2 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_AX39 |
| TOV21G cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3613 | |
| SMOV2 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_S920 | |
| RMG-1 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1662 | |
| OVTOKO cells | Spleen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3117 | |
| OVSAYO cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3115 | |
| OVMANA cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3111 | |
| OVISE cells | Pelvi | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3116 | |
| OVAS cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0V12 | |
| KOC7C cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5307 | |
| KK cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_F844 | |
| HCH1 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_DF05 | |
| In Vivo Model | CD-1 Nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ApoTox-Glo Triplex assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Defects in ARID1A sensitize tumour cells to clinical inhibitors of the DNA damage checkpoint kinase, ATR, both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, ARID1A deficiency results in topoisomerase 2A and cell cycle defects, which cause an increased reliance on ATR checkpoint activity. In ARID1A mutant tumour cells, inhibition of ATR triggers premature mitotic entry, genomic instability and apoptosis. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
