Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00234)
| Name |
AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 1A (ARID1A)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
ARID domain-containing protein 1A; B120; BRG1-associated factor 250; BAF250; BRG1-associated factor 250a; BAF250A; Osa homolog 1; hOSA1; SWI-like protein; SWI/SNF complex protein p270; SWI/SNF-related; matrix-associated; actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily F member 1; hELD; BAF250; BAF250A; C1orf4; OSA1; SMARCF1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
ARID1A
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr1:26693236-26782104[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MAAQVAPAAASSLGNPPPPPPSELKKAEQQQREEAGGEAAAAAAAERGEMKAAAGQESEG
PAVGPPQPLGKELQDGAESNGGGGGGGAGSGGGPGAEPDLKNSNGNAGPRPALNNNLTEP PGGGGGGSSDGVGAPPHSAAAALPPPAYGFGQPYGRSPSAVAAAAAAVFHQQHGGQQSPG LAALQSGGGGGLEPYAGPQQNSHDHGFPNHQYNSYYPNRSAYPPPAPAYALSSPRGGTPG SGAAAAAGSKPPPSSSASASSSSSSFAQQRFGAMGGGGPSAAGGGTPQPTATPTLNQLLT SPSSARGYQGYPGGDYSGGPQDGGAGKGPADMASQCWGAAAAAAAAAAASGGAQQRSHHA PMSPGSSGGGGQPLARTPQPSSPMDQMGKMRPQPYGGTNPYSQQQGPPSGPQQGHGYPGQ PYGSQTPQRYPMTMQGRAQSAMGGLSYTQQIPPYGQQGPSGYGQQGQTPYYNQQSPHPQQ QQPPYSQQPPSQTPHAQPSYQQQPQSQPPQLQSSQPPYSQQPSQPPHQQSPAPYPSQQST TQQHPQSQPPYSQPQAQSPYQQQQPQQPAPSTLSQQAAYPQPQSQQSQQTAYSQQRFPPP QELSQDSFGSQASSAPSMTSSKGGQEDMNLSLQSRPSSLPDLSGSIDDLPMGTEGALSPG VSTSGISSSQGEQSNPAQSPFSPHTSPHLPGIRGPSPSPVGSPASVAQSRSGPLSPAAVP GNQMPPRPPSGQSDSIMHPSMNQSSIAQDRGYMQRNPQMPQYSSPQPGSALSPRQPSGGQ IHTGMGSYQQNSMGSYGPQGGQYGPQGGYPRQPNYNALPNANYPSAGMAGGINPMGAGGQ MHGQPGIPPYGTLPPGRMSHASMGNRPYGPNMANMPPQVGSGMCPPPGGMNRKTQETAVA MHVAANSIQNRPPGYPNMNQGGMMGTGPPYGQGINSMAGMINPQGPPYSMGGTMANNSAG MAASPEMMGLGDVKLTPATKMNNKADGTPKTESKSKKSSSSTTTNEKITKLYELGGEPER KMWVDRYLAFTEEKAMGMTNLPAVGRKPLDLYRLYVSVKEIGGLTQVNKNKKWRELATNL NVGTSSSAASSLKKQYIQCLYAFECKIERGEDPPPDIFAAADSKKSQPKIQPPSPAGSGS MQGPQTPQSTSSSMAEGGDLKPPTPASTPHSQIPPLPGMSRSNSVGIQDAFNDGSDSTFQ KRNSMTPNPGYQPSMNTSDMMGRMSYEPNKDPYGSMRKAPGSDPFMSSGQGPNGGMGDPY SRAAGPGLGNVAMGPRQHYPYGGPYDRVRTEPGIGPEGNMSTGAPQPNLMPSNPDSGMYS PSRYPPQQQQQQQQRHDSYGNQFSTQGTPSGSPFPSQQTTMYQQQQQNYKRPMDGTYGPP AKRHEGEMYSVPYSTGQGQPQQQQLPPAQPQPASQQQAAQPSPQQDVYNQYGNAYPATAT AATERRPAGGPQNQFPFQFGRDRVSAPPGTNAQQNMPPQMMGGPIQASAEVAQQGTMWQG RNDMTYNYANRQSTGSAPQGPAYHGVNRTDEMLHTDQRANHEGSWPSHGTRQPPYGPSAP VPPMTRPPPSNYQPPPSMQNHIPQVSSPAPLPRPMENRTSPSKSPFLHSGMKMQKAGPPV PASHIAPAPVQPPMIRRDITFPPGSVEATQPVLKQRRRLTMKDIGTPEAWRVMMSLKSGL LAESTWALDTINILLYDDNSIMTFNLSQLPGLLELLVEYFRRCLIEIFGILKEYEVGDPG QRTLLDPGRFSKVSSPAPMEGGEEEEELLGPKLEEEEEEEVVENDEEIAFSGKDKPASEN SEEKLISKFDKLPVKIVQKNDPFVVDCSDKLGRVQEFDSGLLHWRIGGGDTTEHIQTHFE SKTELLPSRPHAPCPPAPRKHVTTAEGTPGTTDQEGPPPDGPPEKRITATMDDMLSTRSS TLTEDGAKSSEAIKESSKFPFGISPAQSHRNIKILEDEPHSKDETPLCTLLDWQDSLAKR CVCVSNTIRSLSFVPGNDFEMSKHPGLLLILGKLILLHHKHPERKQAPLTYEKEEEQDQG VSCNKVEWWWDCLEMLRENTLVTLANISGQLDLSPYPESICLPVLDGLLHWAVCPSAEAQ DPFSTLGPNAVLSPQRLVLETLSKLSIQDNNVDLILATPPFSRLEKLYSTMVRFLSDRKN PVCREMAVVLLANLAQGDSLAARAIAVQKGSIGNLLGFLEDSLAATQFQQSQASLLHMQN PPFEPTSVDMMRRAARALLALAKVDENHSEFTLYESRLLDISVSPLMNSLVSQVICDVLF LIGQS Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Involved in transcriptional activation and repression of select genes by chromatin remodeling (alteration of DNA-nucleosome topology). Component of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes that carry out key enzymatic activities, changing chromatin structure by altering DNA-histone contacts within a nucleosome in an ATP-dependent manner. Binds DNA non-specifically. Belongs to the neural progenitors-specific chromatin remodeling complex (npBAF complex) and the neuron-specific chromatin remodeling complex (nBAF complex). During neural development a switch from a stem/progenitor to a postmitotic chromatin remodeling mechanism occurs as neurons exit the cell cycle and become committed to their adult state. The transition from proliferating neural stem/progenitor cells to postmitotic neurons requires a switch in subunit composition of the npBAF and nBAF complexes. As neural progenitors exit mitosis and differentiate into neurons, npBAF complexes which contain ACTL6A/BAF53A and PHF10/BAF45A, are exchanged for homologous alternative ACTL6B/BAF53B and DPF1/BAF45B or DPF3/BAF45C subunits in neuron-specific complexes (nBAF). The npBAF complex is essential for the self-renewal/proliferative capacity of the multipotent neural stem cells. The nBAF complex along with CREST plays a role regulating the activity of genes essential for dendrite growth (By similarity).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.Y] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Sunitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Kidney cancer [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Renal cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Kidney | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.33E-04 Fold-change: -1.74E-01 Z-score: -5.03E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell metastasis | Activation | hsa05205 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| Chemoresistance | Activation | hsa05207 | ||
| In Vitro Model | 786-O cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1051 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Luciferase reporter assay; Western blot analysis; Immunohistochemical staining assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR144-3p promotes cell proliferation, metastasis, sunitinib resistance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma by downregulating ARID1A. and the downregulation of ARIDIA could promote the function of mir144-3p in cell proliferation, metastasis and chemoresistance. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Rucaparib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Nonsense | p.Q456* (c.1366C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF10A cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0598 | |
| U2OS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0042 | |
| HMEC cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| ARID1A-knockout (Q456*/Q456*) cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | Male athymic nu/nu mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; ChIP assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor volume measurement assay | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Talazoparib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Nonsense | p.Q456* (c.1366C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| MCF10A cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0598 | |
| U2OS cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0042 | |
| HMEC cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| ARID1A-knockout (Q456*/Q456*) cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | Male athymic nu/nu mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; ChIP assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor volume measurement assay | |||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Berzosertib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Nonsense | p.Q456* (c.1366C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | ES2 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_AX39 |
| TOV21G cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3613 | |
| SMOV2 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_S920 | |
| RMG-1 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1662 | |
| OVTOKO cells | Spleen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3117 | |
| OVSAYO cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3115 | |
| OVMANA cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3111 | |
| OVISE cells | Pelvi | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3116 | |
| OVAS cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0V12 | |
| KOC7C cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5307 | |
| KK cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_F844 | |
| HCH1 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_DF05 | |
| In Vivo Model | CD-1 Nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ApoTox-Glo Triplex assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Defects in ARID1A sensitize tumour cells to clinical inhibitors of the DNA damage checkpoint kinase, ATR, both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, ARID1A deficiency results in topoisomerase 2A and cell cycle defects, which cause an increased reliance on ATR checkpoint activity. In ARID1A mutant tumour cells, inhibition of ATR triggers premature mitotic entry, genomic instability and apoptosis. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | JQ1 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Nonsense | p.Q1148* (c.3442C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | ES2 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_AX39 |
| TOV21G cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3613 | |
| OVCA429 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3936 | |
| TUOC1 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_L700 | |
| SMOV2 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_S920 | |
| RMGII cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2803 | |
| RMGI cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1662 | |
| OVTOKO cells | Spleen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3117 | |
| OVMANA cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3111 | |
| OVAS cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0V12 | |
| OV207 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A404 | |
| KOC7C cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5307 | |
| HAC2 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8354 | |
| In Vivo Model | NSG mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The inhibitory effects on residual SWI/SNF function, specifically via reduced ARID1B expression, may explain the enhanced sensitivity of ARID1A mutant cells to BET inhibitors. | |||
Investigative Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | VE-821 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Nonsense | p.Q456* (c.1366C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | ES2 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_AX39 |
| TOV21G cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3613 | |
| SMOV2 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_S920 | |
| RMG-1 cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1662 | |
| OVTOKO cells | Spleen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3117 | |
| OVSAYO cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3115 | |
| OVMANA cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3111 | |
| OVISE cells | Pelvi | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3116 | |
| OVAS cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0V12 | |
| KOC7C cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5307 | |
| KK cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_F844 | |
| HCH1 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_DF05 | |
| In Vivo Model | CD-1 Nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ApoTox-Glo triplex assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Defects in ARID1A sensitize tumour cells to clinical inhibitors of the DNA damage checkpoint kinase, ATR, both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, ARID1A deficiency results in topoisomerase 2A and cell cycle defects, which cause an increased reliance on ATR checkpoint activity. In ARID1A mutant tumour cells, inhibition of ATR triggers premature mitotic entry, genomic instability and apoptosis. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.93E-01; Fold-change: -5.38E-03; Z-score: -1.32E-02 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.08E-08; Fold-change: 2.06E+00; Z-score: 3.59E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
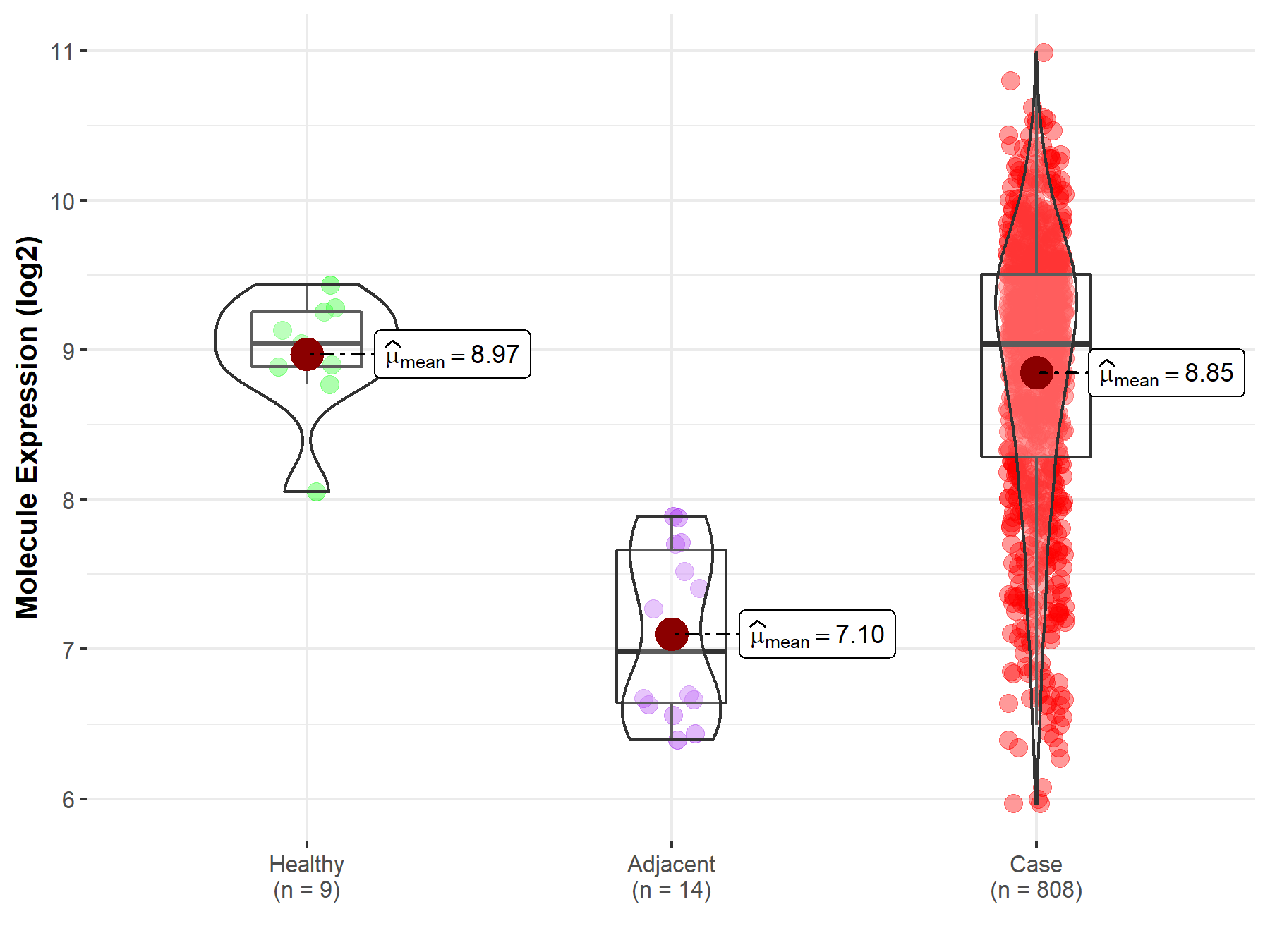
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Kidney | |
| The Specified Disease | Kidney cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.33E-04; Fold-change: -7.77E-01; Z-score: -1.18E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.70E-01; Fold-change: -1.93E-01; Z-score: -3.67E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
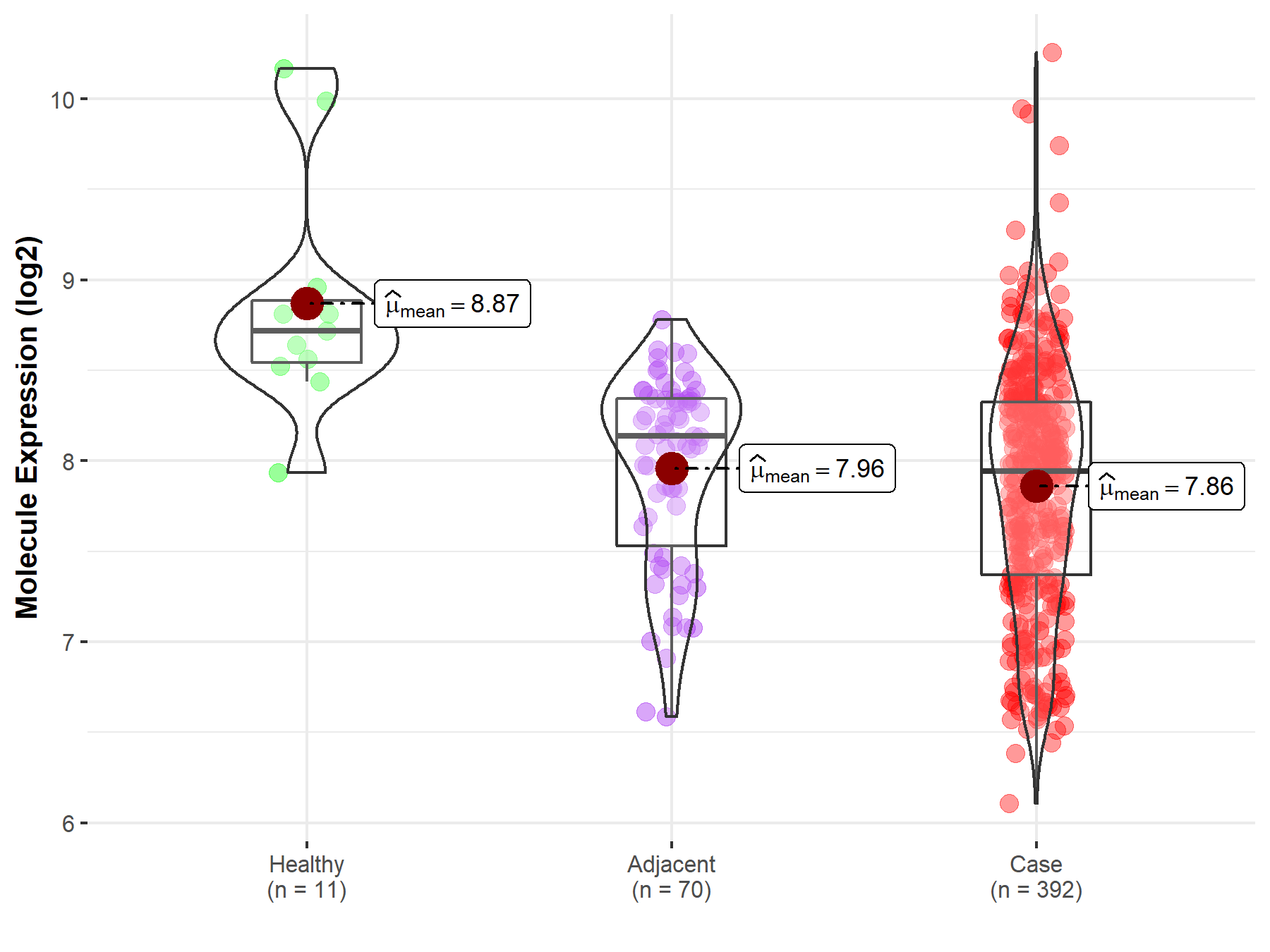
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

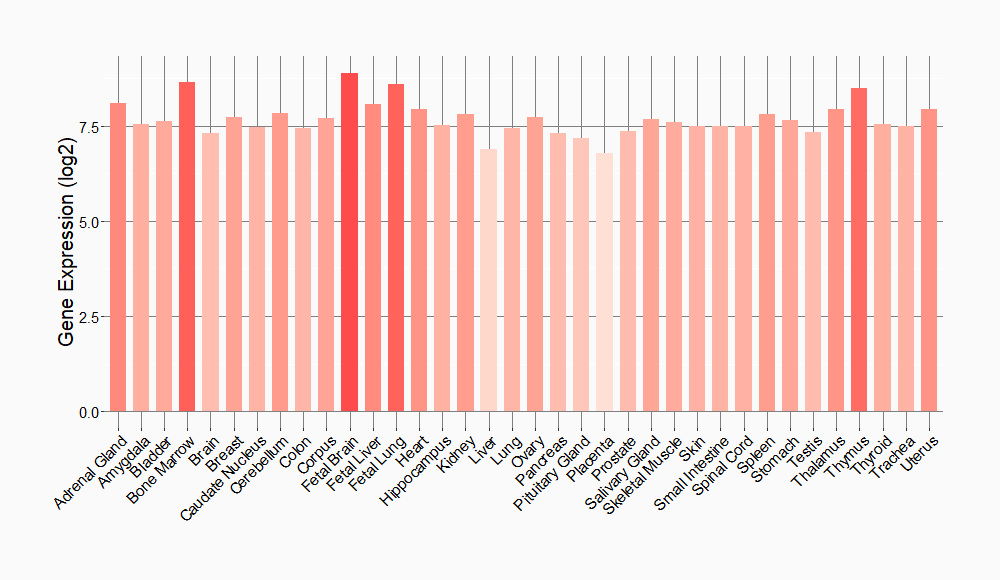
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
