Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01566) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Refametinib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Refametinib; 923032-37-5; RDEA119; RDEA 119; BAY 869766; UNII-JPX07AFM0N; (S)-N-(3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)-6-methoxyphenyl)-1-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)cyclopropane-1-sulfonamide; JPX07AFM0N; Refametinib (RDEA119); BAY-869766; BAY 8697661; Refametinib (RDEA119, Bay 86-9766); N-[3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)-6-methoxyphenyl]-1-[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl]cyclopropane-1-sulfonamide; Refametinib R enantiomer; Refametinib [INN]; BAY 86-9766; RDEA-119; 3e8n; BAY 86-97661; Refametinib; RDEA119; SCHEMBL345333; C19H20F3IN2O5S; GTPL7942; Refametinib (BAY86-9766); CHEMBL1236682; DTXSID40238961; BDBM520650; 923032-38-6; AOB87134; EX-A2481; 2254AH; MFCD18633256; NSC800864; s1089; ZINC39187987; AKOS025401896; BAY86-9766; CCG-270103; CS-1818; DB06309; NSC-800864; BAY 86-9766;RDEA119; BAY-86-9766; BAY-8697661; NCGC00188380-01; NCGC00188380-02; NCGC00188380-03; AC-26962; AS-16994; Cyclopropanesulfonamide, N-(3,4-difluoro-2-((2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino)-6-methoxyphenyl)-1-((2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-; HY-14691; SW218136-2; J3.661.482J; F51934; US11147816, Refametinib (RDEA119, Bay; Q27088526; BAY 869766;BAY 86-97661;RDEA-119;RDEA119; (S)-N-(3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodophenylamino)-6-methoxyphenyl)-1-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)cyclopropane-1-sulfonamide; 923032-36-4; N-{3,4-difluoro-2-[(2-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)amino]-6-methoxyphenyl}-1-[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl]cyclopropanesulfonamide; RDEA-119 S enantiomer; ; ; BAY-86-9766 S enantiomer; ; ; N-[3,4-Difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)-6-methoxyphenyl]-1-[(2S)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl]cyclopropane-1-sulfonamide; VRA
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
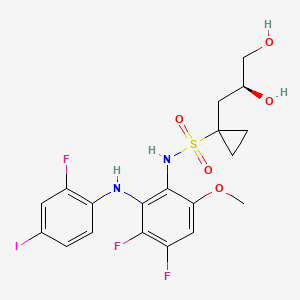
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[2]
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[4]
|
||||
| Target | PI3-kinase beta (PIK3CB) | PK3CB_HUMAN | [4] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
9
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
COC1=CC(=C(C(=C1NS(=O)(=O)C2(CC2)C[C@@H](CO)O)NC3=C(C=C(C=C3)I)F)F)F
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C19H20F3IN2O5S/c1-30-15-7-13(21)16(22)18(24-14-3-2-10(23)6-12(14)20)17(15)25-31(28,29)19(4-5-19)8-11(27)9-26/h2-3,6-7,11,24-27H,4-5,8-9H2,1H3/t11-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
RDSACQWTXKSHJT-NSHDSACASA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Histone H1.4 (H1-4) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Oesophagus adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vivo Model | Patient-derived esophageal cancer model | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Gene expression analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Drug sensitivity analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | The results of drug sensitivity of risk genes showed that the high expression of HIST1H1E made tumor cells resistant to trametinib, selumetinib, RDEA119, Docetaxel and 17-AAG. The high expression of UBE2C makes tumor cells resistant to masitinib. The low expression of ERO1B makes the EC more sensitive to FK866 | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf (BRAF) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V600E (c.1799T>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.55 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
420
|
M
M
D
D
R
R
G
G
S
S
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
430
|
H
H
G
G
S
S
E
E
D
D
R
R
N
N
R
R
M
M
K
K
440
|
T
T
L
L
G
G
R
R
R
R
D
D
S
S
S
S
D
D
D
D
450
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
P
P
D
D
G
G
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
V
V
460
|
G
G
Q
Q
R
R
I
I
G
G
S
S
G
G
S
S
F
F
G
G
470
|
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
K
K
W
W
H
H
G
G
D
D
480
|
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
L
L
N
N
V
V
T
T
A
A
490
|
P
P
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
Q
Q
L
L
Q
Q
A
A
F
F
K
K
500
|
N
N
E
E
V
V
G
G
V
V
L
L
R
R
K
K
T
T
R
R
510
|
H
H
V
V
N
N
I
I
L
L
L
L
F
F
M
M
G
G
Y
Y
520
|
S
S
T
T
K
K
P
P
Q
Q
L
L
A
A
I
I
V
V
T
T
530
|
Q
Q
W
W
C
C
E
E
G
G
S
S
S
S
L
L
Y
Y
H
H
540
|
H
H
L
L
H
H
I
I
I
I
E
E
T
T
K
K
F
F
E
E
550
|
M
M
I
I
K
K
L
L
I
I
D
D
I
I
A
A
R
R
Q
Q
560
|
T
T
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
M
M
D
D
Y
Y
L
L
H
H
A
A
570
|
K
K
S
S
I
I
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
580
|
N
N
N
N
I
I
F
F
L
L
H
H
E
E
D
D
L
L
T
T
590
|
V
V
K
K
I
I
G
G
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
T
T
600
|
V
E
K
K
S
S
R
R
W
W
S
S
G
G
S
S
H
H
Q
Q
610
|
F
F
E
E
Q
Q
L
L
S
S
G
G
S
S
I
I
L
L
W
W
620
|
M
M
A
A
P
P
E
E
V
V
I
I
R
R
M
M
Q
Q
D
D
630
|
K
K
N
N
P
P
Y
Y
S
S
F
F
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
640
|
Y
Y
A
A
F
F
G
G
I
I
V
V
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
L
L
650
|
M
M
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
S
S
N
N
I
I
660
|
N
N
N
N
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
I
I
I
I
F
F
M
M
V
V
670
|
G
G
R
R
G
G
Y
Y
L
L
S
S
P
P
D
D
L
L
S
S
680
|
K
K
V
V
R
R
S
S
N
N
C
C
P
P
K
K
A
A
M
M
690
|
K
K
R
R
L
L
M
M
A
A
E
E
C
C
L
L
K
K
K
K
700
|
K
K
R
R
D
D
E
E
R
R
P
P
L
L
F
F
P
P
Q
Q
710
|
I
I
L
L
A
A
S
S
I
I
E
E
L
L
L
L
A
A
R
R
720
|
S
S
L
L
P
P
K
K
I
I
H
H
R
R
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| HT-29 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0320 | ||||||||||
| A431 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0037 | ||||||||||
| COLO205 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_F402 | ||||||||||
| BxPc3 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0186 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female athymic nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Biochemical kinase assays | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter 96 Aqueous One assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.V600E (c.1799T>A) in gene BRAF cause the sensitivity of Refametinib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 2-alpha (TOP2A) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | S102T |
||
| Mechanism Description | DNA toposomerase 2 (TOP2A) is a ribozyme that controls the topological state of DNA. It is very important for the correct division of ion chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis. The up-regulation of TOP2A expression is related to the shortening of survival time and chemoresistance. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: MAPK/ERK kinase 1 (MEK1) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q56P (c.167A>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 |
| AGS cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0139 | |
| NCI-N87 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1603 | |
| NCI-H508 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1564 | |
| SW48 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1724 | |
| A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| NCI-H1650 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1483 | |
| SW1573 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1720 | |
| SNU-C1 cells | Peritoneum | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1708 | |
| OCUM-1 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3084 | |
| NCI-H226 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1544 | |
| NCI-H196 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1509 | |
| NCI-H1437 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1472 | |
| NCI-H1355 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1464 | |
| MKN7 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1417 | |
| NCI-H1299 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| HCC366 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2059 | |
| NCI-H2126 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1532 | |
| In Vivo Model | Female nu/nu mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf (BRAF) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V600X (c.1798_1799) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.V600X (c.1798_1799) in gene BRAF cause the resistance of Refametinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf (BRAF) | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V600E (c.1799T>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.55 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
420
|
M
M
D
D
R
R
G
G
S
S
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
430
|
H
H
G
G
S
S
E
E
D
D
R
R
N
N
R
R
M
M
K
K
440
|
T
T
L
L
G
G
R
R
R
R
D
D
S
S
S
S
D
D
D
D
450
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
P
P
D
D
G
G
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
V
V
460
|
G
G
Q
Q
R
R
I
I
G
G
S
S
G
G
S
S
F
F
G
G
470
|
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
K
K
W
W
H
H
G
G
D
D
480
|
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
L
L
N
N
V
V
T
T
A
A
490
|
P
P
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
Q
Q
L
L
Q
Q
A
A
F
F
K
K
500
|
N
N
E
E
V
V
G
G
V
V
L
L
R
R
K
K
T
T
R
R
510
|
H
H
V
V
N
N
I
I
L
L
L
L
F
F
M
M
G
G
Y
Y
520
|
S
S
T
T
K
K
P
P
Q
Q
L
L
A
A
I
I
V
V
T
T
530
|
Q
Q
W
W
C
C
E
E
G
G
S
S
S
S
L
L
Y
Y
H
H
540
|
H
H
L
L
H
H
I
I
I
I
E
E
T
T
K
K
F
F
E
E
550
|
M
M
I
I
K
K
L
L
I
I
D
D
I
I
A
A
R
R
Q
Q
560
|
T
T
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
M
M
D
D
Y
Y
L
L
H
H
A
A
570
|
K
K
S
S
I
I
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
580
|
N
N
N
N
I
I
F
F
L
L
H
H
E
E
D
D
L
L
T
T
590
|
V
V
K
K
I
I
G
G
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
T
T
600
|
V
E
K
K
S
S
R
R
W
W
S
S
G
G
S
S
H
H
Q
Q
610
|
F
F
E
E
Q
Q
L
L
S
S
G
G
S
S
I
I
L
L
W
W
620
|
M
M
A
A
P
P
E
E
V
V
I
I
R
R
M
M
Q
Q
D
D
630
|
K
K
N
N
P
P
Y
Y
S
S
F
F
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
640
|
Y
Y
A
A
F
F
G
G
I
I
V
V
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
L
L
650
|
M
M
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
S
S
N
N
I
I
660
|
N
N
N
N
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
I
I
I
I
F
F
M
M
V
V
670
|
G
G
R
R
G
G
Y
Y
L
L
S
S
P
P
D
D
L
L
S
S
680
|
K
K
V
V
R
R
S
S
N
N
C
C
P
P
K
K
A
A
M
M
690
|
K
K
R
R
L
L
M
M
A
A
E
E
C
C
L
L
K
K
K
K
700
|
K
K
R
R
D
D
E
E
R
R
P
P
L
L
F
F
P
P
Q
Q
710
|
I
I
L
L
A
A
S
S
I
I
E
E
L
L
L
L
A
A
R
R
720
|
S
S
L
L
P
P
K
K
I
I
H
H
R
R
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |||||||||
| A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | ||||||||||
| HT-29 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0320 | ||||||||||
| A431 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0037 | ||||||||||
| COLO205 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_F402 | ||||||||||
| BxPc3 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0186 | ||||||||||
| SkMEL28 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0526 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female athymic nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Biochemical kinase assays | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter 96 Aqueous One assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.V600E (c.1799T>A) in gene BRAF cause the sensitivity of Refametinib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-q (GNAQ) | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Uveal melanoma [ICD-11: 2D0Y.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q209L (c.626A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: Electron microscopy | Resolution: 3.50 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: Electron microscopy | Resolution: 2.90 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
0
|
-
H
M
H
T
T
L
L
E
E
S
S
I
I
M
M
A
A
C
C
10
|
C
C
L
L
S
S
E
E
E
E
A
A
K
K
E
E
A
A
R
R
20
|
R
R
I
I
N
N
D
D
E
E
I
I
E
E
R
R
Q
Q
L
L
30
|
R
R
R
R
D
D
K
K
R
R
D
D
A
A
R
R
R
R
E
E
40
|
L
L
K
K
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
G
G
T
T
G
G
E
E
50
|
S
S
G
G
K
K
S
S
T
T
F
F
I
I
K
K
Q
Q
M
M
60
|
R
R
I
I
I
I
H
H
G
G
S
S
G
G
Y
Y
S
S
D
D
70
|
E
E
D
D
K
K
R
R
G
G
F
F
T
T
K
K
L
L
V
V
80
|
Y
Y
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
F
F
T
T
A
A
M
M
Q
Q
A
A
90
|
M
M
I
I
R
R
A
A
M
M
D
D
T
T
L
L
K
K
I
I
100
|
P
P
Y
Y
K
K
Y
Y
E
E
H
H
N
N
K
K
A
A
H
H
110
|
A
A
Q
Q
L
L
V
V
R
R
E
E
V
V
D
D
V
V
E
E
120
|
K
K
V
V
S
S
A
A
F
F
E
E
N
N
P
P
Y
Y
V
V
130
|
D
D
A
A
I
I
K
K
S
S
L
L
W
W
N
N
D
D
P
P
140
|
G
G
I
I
Q
Q
E
E
C
C
Y
Y
D
D
R
R
R
R
R
R
150
|
E
E
Y
Y
Q
Q
L
L
S
S
D
D
S
S
T
T
K
K
Y
Y
160
|
Y
Y
L
L
N
N
D
D
L
L
D
D
R
R
V
V
A
A
D
D
170
|
P
P
A
A
Y
Y
L
L
P
P
T
T
Q
Q
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
180
|
L
L
R
R
V
V
R
Q
V
V
P
P
T
T
T
T
G
G
I
I
190
|
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
P
P
F
F
D
D
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
V
V
200
|
I
I
F
F
R
R
M
M
V
V
D
D
V
V
G
G
G
G
Q
L
210
|
R
R
S
S
E
E
R
R
R
R
K
K
W
W
I
I
H
H
C
C
220
|
F
F
E
E
N
N
V
V
T
T
S
S
I
I
M
M
F
F
L
L
230
|
V
V
A
A
L
L
S
S
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
L
L
240
|
V
V
E
E
S
S
D
D
N
N
E
E
N
N
R
R
M
M
E
E
250
|
E
E
S
S
K
K
A
A
L
L
F
F
R
R
T
T
I
I
I
I
260
|
T
T
Y
Y
P
P
W
W
F
F
Q
Q
N
N
S
S
S
S
V
V
270
|
I
I
L
L
F
F
L
L
N
N
K
K
K
K
D
D
L
L
L
L
280
|
E
E
E
E
K
K
I
I
M
M
Y
Y
S
S
H
H
L
L
V
V
290
|
D
D
Y
Y
F
F
P
P
E
E
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
P
P
Q
Q
300
|
R
R
D
D
A
A
Q
Q
A
A
A
A
R
R
E
E
F
F
I
I
310
|
L
L
K
K
M
M
F
F
V
V
D
D
L
L
N
N
P
P
D
D
320
|
S
S
D
D
K
K
I
I
I
I
Y
Y
S
S
H
H
F
F
T
T
330
|
C
C
A
A
T
T
D
D
T
T
E
E
N
N
I
I
R
R
F
F
340
|
V
V
F
F
A
A
A
A
V
V
K
K
D
D
T
T
I
I
L
L
350
|
Q
Q
L
L
N
N
L
L
K
K
E
E
Y
Y
N
N
L
L
V
V
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q209L (c.626A>T) in gene GNAQ cause the sensitivity of Refametinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
