Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01551) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Omipalisib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Omipalisib; 1086062-66-9; GSK2126458; GSK-2126458; GSK 2126458; 2,4-difluoro-N-(2-methoxy-5-(4-(pyridazin-4-yl)quinolin-6-yl)pyridin-3-yl)benzenesulfonamide; 2,4-difluoro-N-[2-methoxy-5-(4-pyridazin-4-ylquinolin-6-yl)pyridin-3-yl]benzenesulfonamide; UNII-1X8F5A3NA0; 2,4-Difluoro-N-[2-methoxy-5-[4-(4-pyridazinyl)-6-quinolinyl]-3-pyridinyl]benzenesulfonamide; 1X8F5A3NA0; Omipalisib (GSK2126458, GSK458); C25H17F2N5O3S; 2,4-difluoro-N-(2-(methyloxy)-5-(4-(4-pyridazinyl)-6-quinolinyl)-3-pyridinyl)benzenesulfonamide; GSK-212; Omipalisib [USAN:INN]; GSK458; GSK 212; 2,4-difluoro-N-{2-(methyloxy)-5-[4-(4-pyridazinyl)-6-quinolinyl]-3-pyridinyl}benzenesulfonamide; Omipalisib (USAN/INN); MLS006011258; Omipalisib; GSK2126458; SCHEMBL623194; GTPL8974; Omipalisib (GSK2126458); CHEMBL1236962; CHEBI:95093; DTXSID10148604; EX-A003; GSK-458; SYN1126; 3l08; HMS3656D09; AOB87781; BCP02252; BDBM50145416; MFCD16038929; NSC764092; NSC800807; s2658; ZINC43208634; AKOS015904655; CCG-264973; CS-0085; DB12703; NSC-764092; NSC-800807; QC-7243; SB16572; NCGC00250408-01; NCGC00250408-05; AC-28458; AS-16266; Benzenesulfonamide, 2,4-difluoro-N-(2-methoxy-5-(4-(4-pyridazinyl)-6-quinolinyl)-3-pyridinyl)-; GSK2126458 (GSK458); HY-10297; SMR004703011; FT-0669061; SW219502-1; X7449; A25172; D10718; GSK-2126458;GSK 2126458; Omipalisib; J-507217; Q27088179; N-[2-Methoxy-5-[4-(4-pyridazinyl)-6-quinolinyl]-3-pyridinyl]benzenesulfonamide; ZIG
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 2 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
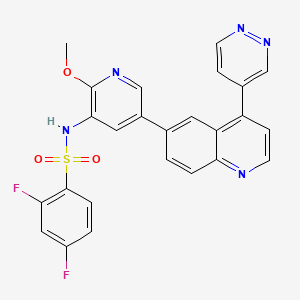
|
||||
| Target | Hepatitis C virus Non-structural 5A (HCV NS5A) | POLG_HCV1 | [2] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
6
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
COC1=C(C=C(C=N1)C2=CC3=C(C=CN=C3C=C2)C4=CN=NC=C4)NS(=O)(=O)C5=C(C=C(C=C5)F)F
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C25H17F2N5O3S/c1-35-25-23(32-36(33,34)24-5-3-18(26)12-21(24)27)11-17(13-29-25)15-2-4-22-20(10-15)19(7-8-28-22)16-6-9-30-31-14-16/h2-14,32H,1H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
CGBJSGAELGCMKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y288C (c.863A>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF10A cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0598 |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Presto blue assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | PDGFRA Y288C induces constitutive phosphorylation of Akt, ERK1/2, and STAT3. PDGFRA Y288C is resistant to PDGFR inhibitors, such as crenolanib, but sensitive to PI3K/mTOR and MEK inhibitors, such as omipalisib and trametinib, consistent with pathway activation results. | |||
| Key Molecule: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V561D (c.1682T>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF10A cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0598 |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Presto blue assay | |||
| Key Molecule: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D842V (c.2525A>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF10A cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0598 |
| Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Presto blue assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | PDGFRA Y288C induces constitutive phosphorylation of Akt, ERK1/2, and STAT3. PDGFRA Y288C is resistant to PDGFR inhibitors, such as crenolanib, but sensitive to PI3K/mTOR and MEK inhibitors, such as omipalisib, consistent with pathway activation results. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf (BRAF) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V600E (c.1799T>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.55 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 3.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
420
|
M
M
D
D
R
R
G
G
S
S
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
430
|
H
H
G
G
S
S
E
E
D
D
R
R
N
N
R
R
M
M
K
K
440
|
T
T
L
L
G
G
R
R
R
R
D
D
S
S
S
S
D
D
D
D
450
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
P
P
D
D
G
G
Q
Q
I
I
T
T
V
V
460
|
G
G
Q
Q
R
R
I
I
G
G
S
S
G
G
S
S
F
F
G
G
470
|
T
T
V
V
Y
Y
K
K
G
G
K
K
W
W
H
H
G
G
D
D
480
|
V
V
A
A
V
V
K
K
M
M
L
L
N
N
V
V
T
T
A
A
490
|
P
P
T
T
P
P
Q
Q
Q
Q
L
L
Q
Q
A
A
F
F
K
K
500
|
N
N
E
E
V
V
G
G
V
V
L
L
R
R
K
K
T
T
R
R
510
|
H
H
V
V
N
N
I
I
L
L
L
L
F
F
M
M
G
G
Y
Y
520
|
S
S
T
T
K
K
P
P
Q
Q
L
L
A
A
I
I
V
V
T
T
530
|
Q
Q
W
W
C
C
E
E
G
G
S
S
S
S
L
L
Y
Y
H
H
540
|
H
H
L
L
H
H
I
I
I
I
E
E
T
T
K
K
F
F
E
E
550
|
M
M
I
I
K
K
L
L
I
I
D
D
I
I
A
A
R
R
Q
Q
560
|
T
T
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
M
M
D
D
Y
Y
L
L
H
H
A
A
570
|
K
K
S
S
I
I
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
580
|
N
N
N
N
I
I
F
F
L
L
H
H
E
E
D
D
L
L
T
T
590
|
V
V
K
K
I
I
G
G
D
D
F
F
G
G
L
L
A
A
T
T
600
|
V
E
K
K
S
S
R
R
W
W
S
S
G
G
S
S
H
H
Q
Q
610
|
F
F
E
E
Q
Q
L
L
S
S
G
G
S
S
I
I
L
L
W
W
620
|
M
M
A
A
P
P
E
E
V
V
I
I
R
R
M
M
Q
Q
D
D
630
|
K
K
N
N
P
P
Y
Y
S
S
F
F
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
V
V
640
|
Y
Y
A
A
F
F
G
G
I
I
V
V
L
L
Y
Y
E
E
L
L
650
|
M
M
T
T
G
G
Q
Q
L
L
P
P
Y
Y
S
S
N
N
I
I
660
|
N
N
N
N
R
R
D
D
Q
Q
I
I
I
I
F
F
M
M
V
V
670
|
G
G
R
R
G
G
Y
Y
L
L
S
S
P
P
D
D
L
L
S
S
680
|
K
K
V
V
R
R
S
S
N
N
C
C
P
P
K
K
A
A
M
M
690
|
K
K
R
R
L
L
M
M
A
A
E
E
C
C
L
L
K
K
K
K
700
|
K
K
R
R
D
D
E
E
R
R
P
P
L
L
F
F
P
P
Q
Q
710
|
I
I
L
L
A
A
S
S
I
I
E
E
L
L
L
L
A
A
R
R
720
|
S
S
L
L
P
P
K
K
I
I
H
H
R
R
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.V600E (c.1799T>A) in gene BRAF cause the sensitivity of Omipalisib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-raf (BRAF) | [2] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V600K (c.1798_1799delGTinsAA) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | A375 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0132 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.V600K (c.1798_1799delGTinsAA) in gene BRAF cause the sensitivity of Omipalisib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
