Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01493) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Pyridone 6
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Pyridone 6; 457081-03-7; JAK Inhibitor I; Merck-5; CMP 6; Merck 5; CMP-6; 2-tert-butyl-9-fluoro-3H-benzo[h]imidazo[4,5-f]isoquinolin-7(6H)-one; LDX3F0CCST; UNII-LDX3F0CCST; CHEMBL21156; 2-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-9-fluoro-3,6-dihydro-7H-benz[h]-imidaz[4,5-f]isoquinolin-7-one; CHEBI:87103; Compound # 2; 2-(1,1-DIMETHYLETHYL)9-FLUORO-3,6-DIHYDRO-7H-BENZ[H]-IMIDAZ[4,5-F]ISOQUINOLIN-7-ONE; 2-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-9-fluoro-1,6-dihydro-7H-benz[h]imidazo[4,5-f]isoquinolin-7-one; 2-TERT-BUTYL-9-FLUORO-3,6-DIHYDRO-7H-BENZ[H]-IMIDAZ[4,5-F]ISOQUINOLINE-7-ONE; C18H16FN3O; JAK Inhibitor; 2-tert-butyl-9-fluoro-1,6-dihydrobenzo[h]imidazo[4,5-f]isoquinolin-7-one; 2-tert-butyl-9-fluoro-3,6-dihydro-7H-benzo[h]imidazo[4,5-f]isoquinolin-7-one; JAK I inhibitor; Jak Inhibitor 1; PDK1 inhibitor, 1; Kinome_3740; pan-JAK inhibitor P6; 2b7a; Merck-5;CMP 6; Tetracyclic Pyridone, 1; JAK Inhibitor I(Merck 5); SCHEMBL904545; GTPL5992; STO185; SCHEMBL23199918; BDBM26198; DTXSID40420526; EX-A123; SYN1054; BCPP000167; HMS3229G07; HMS3244K21; HMS3244K22; HMS3244L21; BCP01959; Janus-Associated Kinase Inhibitor I; 3809AH; MFCD17019334; ZINC12504479; AKOS026750650; AKOS030240416; AKOS032949970; BCP9000906; CCG-206761; CS-1056; DB04716; SB18936; 2-tert-butyl-9-fluoro-3,6-dihydro-7H-benz(h)imidazo(4,5-f)isoquinoline-7-one; NCGC00345828-01; NCGC00345828-07; AM806646; AS-16211; HY-14435; QC-10171; FT-0700310; Y0239; H11177; K00013; K00225; SR-03000000978-1; Q27096425; 2-(tert-butyl)-9-fluoro-3H-benzo[h]imidazo[4,5-f]isoquinolin-7(6H)-one; 2-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-9-fluoro-3,6-dihydro-7h-benz [h]-imidazo [4,5-f]isoquinolin-7-one; 2-tert-butyl-9-fluoro-1,6-dihydro-7h-benz[h]imidazo[4,5-f]isoquinolin-7-one; 2-tert-butyl-9-fluoro-1,6-dihydro-7h-benzo[h]imidazo[4,5-f]isoquinolin-7-one; 4-tert-butyl-15-fluoro-3,5,10-triazatetracyclo[11.4.0.0(2),.0,(1)(2)]heptadeca-1(13),2(6),4,7(12),8,14,16-heptaen-11-one; 4-tert-butyl-15-fluoro-3,5,10-triazatetracyclo[11.4.0.0,.0,]heptadeca-1(13),2(6),4,7(12),8,14,16-heptaen-11-one; 4-tert-butyl-15-fluoro-3,5,10-triazatetracyclo[11.4.0.0^{2,6.0^{7,12]heptadeca-1(13),2(6),4,7(12),8,14,16-heptaen-11-one; 4-tert-butyl-15-fluoro-3,5,10-triazatetracyclo[11.4.0.0^{2,6}.0^{7,12}]heptadeca-1(13),2(6),3,7(12),8,14,16-heptaen-11-one; 4-tert-butyl-15-fluoro-3,5,10-triazatetracyclo[11.4.0.0^{2,6}.0^{7,12}]heptadeca-1(17),2(6),4,7(12),8,13,15-heptaen-11-one; 4-tert-butyl-15-fluoro-3,5,10-triazatetracyclo[11.4.0.02,6.07,12]heptadeca-1(13),2(6),4,7(12),8,14,16-heptaen-11-one; JAK Inhibitor I; 2-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-9-fluoro-3,6-dihydro-7H-benz[h]-imidaz[4,5-f]isoquinolin-7-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
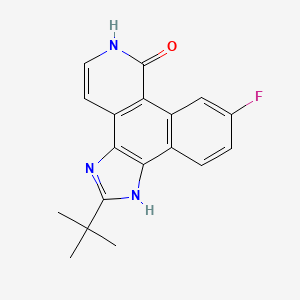
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial Penicillin binding protein (Bact PBP) | NOUNIPROTAC | [2] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
1
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC(C)(C)C1=NC2=C(N1)C3=C(C=C(C=C3)F)C4=C2C=CNC4=O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C18H16FN3O/c1-18(2,3)17-21-14-10-5-4-9(19)8-12(10)13-11(15(14)22-17)6-7-20-16(13)23/h4-8H,1-3H3,(H,20,23)(H,21,22)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
VNDWQCSOSCCWIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Adenylate cyclase-stimulating G alpha protein (GNAS) | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R201L (c.602G>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Human liver cancer tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.R201L (c.602G>T) in gene GNAS cause the sensitivity of JAK inhibitors by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | |||
| Key Molecule: Adenylate cyclase-stimulating G alpha protein (GNAS) | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R201H (c.602G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Human liver cancer tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.R201H (c.602G>A) in gene GNAS cause the sensitivity of JAK inhibitors by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL (CBL) | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Myeloproliferative neoplasm [ICD-11: 2A22.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C384R (c.1150T>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | TF-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0559 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
XTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.C384R (c.1150T>C) in gene CBL cause the sensitivity of JAK inhibitors by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | |||
| Key Molecule: Thrombopoietin receptor (TPOR) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Myeloproliferative neoplasm [ICD-11: 2A22.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.W515F (c.1544_1545delGGinsTT) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Bone marrow | N.A. | ||
| In Vivo Model | Balb/C donor mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
In vitro colony-forming assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.W515F (c.1544_1545delGGinsTT) in gene MPL cause the sensitivity of JAK inhibitors by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 (JAK3) | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q501H (c.1503G>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q501H (c.1503G>T) in gene JAK3 cause the sensitivity of JAK inhibitors by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Key Molecule: Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 (JAK3) | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R657Q (c.1970G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.R657Q (c.1970G>A) in gene JAK3 cause the sensitivity of JAK inhibitors by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Key Molecule: Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 (JAK3) | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I87T (c.260T>C) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.I87T (c.260T>C) in gene JAK3 cause the sensitivity of JAK inhibitors by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 (JAK3) | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90- 2A85] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A572V (c.1715C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NK-S1 cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.A572V (c.1715C>T) in gene JAK3 cause the sensitivity of JAK inhibitors by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Key Molecule: Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 (JAK3) | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90- 2A85] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A573V (c.1718C>T) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NK-S1 cells | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.A573V (c.1718C>T) in gene JAK3 cause the sensitivity of JAK inhibitors by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 (JAK3) | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Copy number gain | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAKT/STAT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04630 | |
| In Vitro Model | HCC70 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1270 |
| HCC1954 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1259 | |
| MDA-231 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| MDA-MB-436 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0623 | |
| SUM159PT cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5423/CVCL_5590 | |
| HCC38 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1267 | |
| HCC1143 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1245 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
SRB assay | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
