Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00833) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Reserpine
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Reserpine; 50-55-5; Serpalan; Serpasil; Apoplon; Serpivite; Hypersil; Alserin; Elserpine; Hiserpia; Raunervil; Raupasil; Rausedil; Rausedyl; Rauwasedin; Reserpin; Serpanray; Resine; Rivasin; Sandril; Serpate; (-)-Reserpine; Rau-Sed; Ascoserpina; Austrapine; Bioserpine; Enipresser; Eskaserpine; Helfoserpin; Hiposerpil; Maviserpin; Mayserpine; Mephaserpin; Purserpine; Rauserpine; Reserpamed; Reserpanca; Alkarau; Apsical; Banasil; Benazyl; Carditivo; Carrserp; Escaspere; Eserpine; Eskaserp; Hypersine; Idsoserp; Interpina; Lemiserp; Loweserp; Neoserfin; Neoserp; Quiescin; Raudiford; Raudixoid; Rauloydin; Raumorine; Raunorine; Raupoid; Raurine; Rausedan; Rauserpol; Rausingle; Rautrin; Rauvlid; Rauwilid; Rauwipur; Rauwoleaf; Rawilid; Resedrex; Reserbal; Resercaps; Resercen; Reserjen; Reserlor; Reserpal; Reserpene; Reserpex; Reserpil; Reserpina; Reserpoid; Respital; Restran; Riserpa; Roxinoid; Kitine; Raucap; Raugal; Raulen; Rausan; Reserp; Key-serpine; 3P Reserp; Crystoserpine; Neo-antitensol; Rauserpin-Alk; Deserpine; Reserpinum; Ryser; Reserfia; 3,4,5-Trimethoxybenzoyl methyl reserpate; V-Serp; Carpacil; Gilucard; Klimanosid; Resaltex; Resedril; Reserpidefe; Recipin; Serpine; ENT 50146; Raunova; Residin; Serpivate; Rese-lar; Reser-ar; NCI-C50157; H 520; UNII-8B1QWR724A; Sedaraupina; Temposerpine; Eberpine; Raudixin; Reserpur; Residine; Resocalm; Resperine; Rezerpin; Sandron; Sedaraupin; Sedserp; Serfolia; Serolfia; Serpaloid; Serpasol; Serpazol; Serpena; Serpentil; Serpentina; Serpicon; Serpiloid; Serpogen; Serpoid; Serpone; Sertabs; Sertens; Sertina; Triserpin; Unilord; Serfin; Serpen; Roxel; Vio-Serpine; SK-Reserpine; Renese R; T-Serp; C33H40N2O9; CHEMBL772; Broserpine; R-e-s; Sederaupin; Serpaneurona; Tefaserpina; Tenserpinie; Tepserpine; Eberspine; Reserpka; Resiatric; Resperin; Rivased; Rolserp; Roxynoid; Serpazil; Serpedin; Serpentin; Serpipur; Serpyrit; Sertensin; Serpil; Tempo-Reserpina; 8B1QWR724A; 50-55-5 (free); Mallopress; Rcra waste number U200; Hydropine; Hydroserp; Rauwita; .gamma.-Serpine; CHEBI:28487; Hydromox-R; Diurese-R; NSC59272; Metatensin #2; Metatensin #4; MFCD00005091; NSC-59272; component of Naquival; component of Regroton; Hydropres 25; Hydropres 50; Hydrosine 25; NSC-237659; (3beta,16beta,17alpha,18beta,20alpha)-11,17-dimethoxy-18-[(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy]yohimban-16-carboxylic acid methyl ester; methyl (1S,2R,3R,4aS,13bR,14aS)-2,11-dimethoxy-3-((3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy)-1,2,3,4,4a,5,7,8,13,13b,14,14a-dodecahydroindolo[2',3':3,4]pyrido[1,2-b]isoquinoline-1-carboxylate; methyl (3beta,16beta,17alpha,18beta,20alpha)-11,17-dimethoxy-18-[(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy]yohimban-16-carboxylate; Usaf cb-27; component of Renese R; component of Metatensin; NCGC00091250-04; Hydroserpalan; Diupres 250; Diupres 500; l-Carpserp; component of Butiserpazide; DSSTox_CID_1237; Hydroserpine Plus; Hydroserpine #1; DSSTox_RID_76029; DSSTox_GSID_21237; Chloroserp-250; Chloroserp-500; Chloroserpin-250; Yohimban-16-carboxylic acid,11,17-dimethoxy-18-[(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy]-, methyl ester,(3b,16b,17a,18b,20a)-; Serpasil premix; Chloroserpine-500; Hydro-Reserpine-25; Hydro-Reserpine-50; Hydro-Fluserpine #1; l -Carpserp; Caswell No. 722A; Serp-AFD; Reserpina [INN-Spanish]; 3,5-Trimethoxybenzoyl methyl reserpate; Yohimban-16-carboxylic acid, 11,17-dimethoxy-18-((3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy)-, methyl ester, (3beta,16beta,17alpha,18beta,20alpha)-; (1S,2R,3R,4aS,13bR,14aS)-methyl 2,11-dimethoxy-3-((3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy)-1,2,3,4,4a,5,7,8,13,13b,14,14a-dodecahydroindolo[2',3':3,4]pyrido[1,2-b]isoquinoline-1-carboxylate; methyl (1R,15S,17R,18R,19S,20S)-6,18-dimethoxy-17-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy-1,3,11,12,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21-dodecahydroyohimban-19-carboxylate; methyl (3beta,16beta,17alpha,18beta,20alpha)-11,17-bis(methyloxy)-18-({[3,4,5-tris(methyloxy)phenyl]carbonyl}oxy)yohimban-16-carboxylate; SMR000059122; Apoplon (TN); CCRIS 550; Serpine (pharmaceutical); HSDB 213; Methyl reserpate 3,5-trimethyloxybenzoic acid; 11,17-Dimethoxy-18-((3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy)yohimban-16-carboxylic acid methyl ester; Methyl reserpate 3,5-trimethoxybenzoic acid ester; EINECS 200-047-9; RCRA waste no. U200; EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 123101; NSC 237659; BRN 0102014; AI3-50146; WLN: T F6 D5 C666 EM ON&&TTTJ HO1 SOVR CO1 DO1 EO1& TO1 UVO1; Reserpine [USP:INN:BAN:JAN]; CAS-50-55-5; Reserpine,(S); Serpalan (TN); 3-.beta., 18-.beta.-hydroxy-11,17-.alpha.-dimethoxy-,methyl ester, 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate (ester); 3.beta., 18.beta.-hydroxy-11,17.alpha.-dimethoxy- methyl ester 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate (ester); Benz[g]indolo[2, 1,2,3,4,4a,5,7,8,13,13b,14,14a-dodecahydro-3-hydroxy-2,11-dimethoxy-, methyl ester, 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate; methyl (3beta,16beta,17alpha,18beta,20alpha)-11,17-dimethoxy-18-{[(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)carbonyl]oxy}yohimban-16-carboxylate; Yohimban-16-carboxylic acid,17-dimethoxy-18-[(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy]-, methyl ester, (3.beta.,16.beta.,17.alpha.,18.beta.,20.alpha.)-; Prestwick_147; Methyl reserpate 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoic acid ester; Reserpine, 99%; Spectrum_000109; Reserpic acid methyl ester 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate (ester); 79 more names available; 1263-94-1; Prestwick0_000875; Prestwick1_000875; Prestwick2_000875; Prestwick3_000875; Spectrum3_000894; Spectrum4_000989; Spectrum5_001415; R 0875; SCHEMBL2589; Lopac0_000073; BSPBio_000949; KBioGR_001397; KBioSS_000549; 4-25-00-01319 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); Methyl 18beta-hydroxy-11,17alpha-dimethoxy-3beta,20alpha-yohimban-16beta-carboxylate 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate (ester); methyl dimethoxy-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy-[ ]carboxylate; MLS002154046; MLS006011754; DivK1c_000012; SPECTRUM1500526; SPBio_002870; Reserpine (JP17/USP/INN); AMY591; BPBio1_001045; GTPL4823; MEGxp0_001904; DTXSID7021237; ACon1_000086; HMS500A14; KBio1_000012; KBio2_000549; KBio2_003117; KBio2_005685; KBio3_001808; AOB5791; NINDS_000012; HMS1570P11; HMS1920P04; HMS2092G05; HMS2097P11; HMS2234E24; HMS3260O07; HMS3413D20; HMS3677D20; HMS3714P11; HMS3884I21; Pharmakon1600-01500526; HY-N0480; Reserpine, Vetec(TM) reagent grade; RKL10049; ZINC3938746; Tox21_111107; Tox21_202395; Tox21_300537; Tox21_500073; BBL028800; BDBM50017712; ENT-50146; NSC237659; NSC757309; STK801975; AKOS000277559; Tox21_111107_1; CCG-204168; CS-1913; DB00206; KS-5106; LP00073; MCULE-9131256292; MCULE-9946449258; NSC-757309; SDCCGSBI-0050061.P005; IDI1_000012; NCGC00091250-01; NCGC00091250-02; NCGC00091250-03; NCGC00091250-05; NCGC00091250-06; NCGC00091250-07; NCGC00091250-08; NCGC00091250-09; NCGC00091250-10; NCGC00091250-12; NCGC00091250-14; NCGC00091250-25; NCGC00254489-01; NCGC00259944-01; NCGC00260758-01; 3-beta,20-alpha-Yohimban-16-beta-carboxylic acid, 18-beta-hydroxy-11,17-alpha-dimethoxy-, methyl ester, 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate (ester); AC-13142; AC-34405; BR164333; methyl (1R,15S,17R,18R,19S,20S)-6,18-dimethoxy-17-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyloxy)-3,13-diazapentacyclo[11.8.0.0^{2,10}.0^{4,9}.0^{15,20}]henicosa-2(10),4,6,8-tetraene-19-carboxylate; NCI60_004446; SBI-0050061.P004; EU-0100073; Reserpine, crystallized, >=99.0% (HPLC); SW196458-3; UNM000011053801; C06539; D00197; J10192; AB01562943_01; 005R091; A913268; Q407841; Q-100566; BRD-K95921201-001-07-0; Methyl reserpate; 3,4,5-Trimethoxybenzoic acid ester; Reserpine, certified reference material, TraceCERT(R); Reserpine solution, 1 pg/muL in methanol: water (1:1); Reserpine, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Reserpine Standard for LC-MS, analytical standard, for LC-MS; Reserpine, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; Reserpine, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material; (3 ,16 ,17 ,18 ,20 )-11,17-Dimethoxy-18-[(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy]yohimban-16-carboxylic acid methyl ester; (3beta,16beta,17alpha,18beta,20alpha)-11,17-Dimethoxy-18- [(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy]yohimban-16-carboxyl ic acid methyl ester; 3beta,20alpha-Yohimban-16beta-carboxylic acid, 18beta-hydroxy-11,17alpha-dimethoxy- methyl ester 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate (ester) (8CI); methyl (1R,15S,17R,18R,19S,20S)-6,18-dimethoxy-17-[(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)carbonyloxy]-3,13-diazapentacyclo[11.8.0.0^{2,10}.0^{4,9}.0^{15,20}]henicosa-2(10),4,6,8-tetraene-19-carboxylate; Yohimban-16-carboxylic acid, 11,17-dimethoxy-18-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy-, methyl ester, (3.beta.,16.beta.,17.alpha.,18.beta.,20.alpha.)-
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
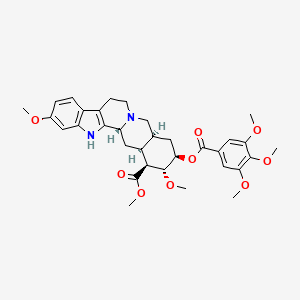
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Synaptic vesicle amine transporter (SLC18A2) | VMAT2_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C33H40N2O9
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CO[C@H]1[C@@H](C[C@@H]2CN3CCC4=C([C@H]3C[C@@H]2[C@@H]1C(=O)OC)NC5=C4C=CC(=C5)OC)OC(=O)C6=CC(=C(C(=C6)OC)OC)OC
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C33H40N2O9/c1-38-19-7-8-20-21-9-10-35-16-18-13-27(44-32(36)17-11-25(39-2)30(41-4)26(12-17)40-3)31(42-5)28(33(37)43-6)22(18)15-24(35)29(21)34-23(20)14-19/h7-8,11-12,14,18,22,24,27-28,31,34H,9-10,13,15-16H2,1-6H3/t18-,22+,24-,27-,28+,31+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
QEVHRUUCFGRFIF-MDEJGZGSSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: MAPK/ERK kinase 1 (MEK1) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Salmonella enterica infection [ICD-11: 1A09.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Activation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | T cell receptor signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| EGFR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa01521 | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04150 | ||
| MEK1/2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | ||
| In Vivo Model | Chicken ceca explant model | Gallus gallus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Chicken-specific kinome peptide array | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Bactericidal assays against Salmonella | |||
| Mechanism Description | Reserpine treatment induced T cell activation, reduced CTLA-4 gene expression, and deactivated metabolic pathways like epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling, which were linked to antimicrobial responses. MEK1/2 activation plays a central role in reserpine-induced antimicrobial activities. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
