Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00804) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Rabeprazole
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Rabeprazole; 117976-89-3; Aciphex; Habeprazole; Pariets; 2-(((4-(3-Methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl)methyl)sulfinyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole; 2-[[4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl]methylsulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole; CHEBI:8768; LY307640; 2-({[4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl]methyl}sulfinyl)-1H-benzimidazole; Rabeprazole [INN:BAN]; 1H-Benzimidazole, 2-[[[4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methyl-2-pyridinyl]methyl]sulfinyl]-; 2-({[4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl]methane}sulfinyl)-1H-1,3-benzodiazole; pariprazole; rabeprazol; Rabeloc; Eraloc; 1H-Benzimidazole, 2-(((4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methyl-2-pyridinyl)methyl)sulfinyl)-; Rabeprazole (INN); Eraloc (TN); HSDB 7321; 2-[{4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl}methylsulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole; 2-{[4-(3-Methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl]methylsulfinyl}-1H-benzimidazole; 2-(((4-(3-Methoxypropoxy)-3-methyl-2-pyridinyl)methyl)sulfinyl)-1H-benzimidazole; 2--1H-benzimidazole; 2-((4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl)methylsulfinyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole; LY 307640; CHEMBL1219; SCHEMBL23336; MLS001401446; BIDD:GT0019; GTPL7290; DTXSID3044122; HMS2052P03; HMS3394P03; AMY10338; BCP06638; HY-B0656; BDBM50070209; E-3810 (PPI); MFCD00868879; s4845; STL186112; AKOS015895259; CCG-101158; DB01129; MCULE-7848941080; NC00408; PB21725; 2-{[4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl]methanesulfinyl}-1H-1,3-benzodiazole; NCGC00388029-07; NCGC00388029-09; AS-34993; SMR000469174; SBI-0206867.P001; DB-020298; DS-002860; FT-0602569; FT-0674301; FT-0674302; Q3515; C07864; D08463; AB00698237-06; 976R893; A803856; SR-01000763041; J-003691; SR-01000763041-3; BRD-A39390670-236-04-0; (R)-2-(((4-(3-Methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl)methyl)sulfinyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole; (S)-2-(((4-(3-Methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl)methyl)sulfinyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole; 1H-benzimidazole,2-[(r)-[[4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methyl-2-pyridinyl]methyl]sulfinyl]-; 2-[[[4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methyl-2-pyridinyl]-methyl] sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole; 2-[[[4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methyl-2-pyridinyl]-methyl]sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole; 2-[[4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-3-methyl-2-pyridyl]methylsulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole;Rabeprazole; 2-{[(3-Methyl-4-(3-methoxypropoxy)-2-pyridinyl)methyl]sulphinyl}1H-benzimidazole; 2-{4-(3-Methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridine-2-yl}methylsulfinyl-1H-benzimidazole
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
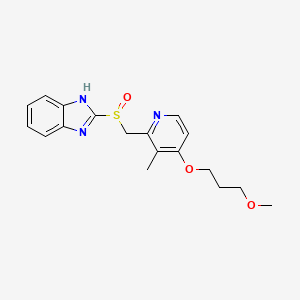
|
||||
| Target | Gastric H(+)/K(+) ATPase alpha (ATP4A) | ATP4A_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C18H21N3O3S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC1=C(C=CN=C1CS(=O)C2=NC3=CC=CC=C3N2)OCCCOC
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C18H21N3O3S/c1-13-16(19-9-8-17(13)24-11-5-10-23-2)12-25(22)18-20-14-6-3-4-7-15(14)21-18/h3-4,6-9H,5,10-12H2,1-2H3,(H,20,21)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
YREYEVIYCVEVJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.94E-11 Fold-change: 9.69E-01 Z-score: 1.04E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT/GSK3beta signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04931 | |
| NF-KappaB signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04064 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-231 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| MJ cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1414 | |
| MMQ cells | Pituitary gland | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | CVCL_2117 | |
| MOLM-13 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2119 | |
| In Vivo Model | Male Wistar rats-Stereotaxic glioma model | Rattus norvegicus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Gene expression analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Scratch wound healing migration assay; Transwell invasion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) is pivotal in embryonic development and wound healing, whereas in cancer it inflicts malignancy and drug resistance. Rabeprazole has efficacy per se and reduces resistance to temozolomide in glioma via EMT inhibition. Rabeprazole suppressed EMT by impeding AKT/GSK3beta phosphorylation and/or NF-kappaB signaling and sensitized temozolomide resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Vimentin (VIM) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.32E-25 Fold-change: 1.45E+00 Z-score: 2.27E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT/GSK3beta signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04931 | |
| NF-KappaB signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04064 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-231 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| MJ cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1414 | |
| MMQ cells | Pituitary gland | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | CVCL_2117 | |
| MOLM-13 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2119 | |
| In Vivo Model | Male Wistar rats-Stereotaxic glioma model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Gene expression analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Scratch wound healing migration assay; Transwell invasion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) is pivotal in embryonic development and wound healing, whereas in cancer it inflicts malignancy and drug resistance. Rabeprazole has efficacy per se and reduces resistance to temozolomide in glioma via EMT inhibition. Rabeprazole suppressed EMT by impeding AKT/GSK3beta phosphorylation and/or NF-kappaB signaling and sensitized temozolomide resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Dishevelled binding antagonist of beta catenin 1 (DACT1) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT/GSK3beta signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04931 | |
| NF-KappaB signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04064 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-231 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| MJ cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1414 | |
| MMQ cells | Pituitary gland | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | CVCL_2117 | |
| MOLM-13 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2119 | |
| In Vivo Model | Male Wistar rats-Stereotaxic glioma model | Rattus norvegicus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; Gene expression analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Scratch wound healing migration assay; Transwell invasion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) is pivotal in embryonic development and wound healing, whereas in cancer it inflicts malignancy and drug resistance. Rabeprazole has efficacy per se and reduces resistance to temozolomide in glioma via EMT inhibition. Rabeprazole suppressed EMT by impeding AKT/GSK3beta phosphorylation and/or NF-kappaB signaling and sensitized temozolomide resistance. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
