Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00376) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Streptothricin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
STREPTOTHRICINS; Streptothricin; 54003-27-9; EINECS 258-911-6; DTXSID60202321; [6-[[(3aS,7R,7aS)-7-hydroxy-4-oxo-1,3a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydroimidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-2-yl]amino]-5-(3,6-diaminohexanoylamino)-4-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl] carbamate; [6-[(E)-[(3aS,7R,7aS)-7-hydroxy-4-oxo-3,3a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-2-ylidene]amino]-5-(3,6-diaminohexanoylamino)-4-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydropyran-3-yl] carbamate
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
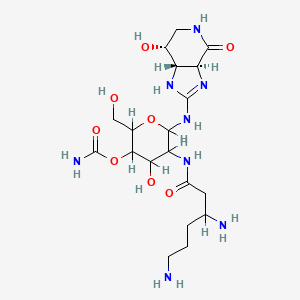
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[2]
[2]
[2]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C19H34N8O8
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1[C@H]([C@@H]2[C@@H](C(=O)N1)N=C(N2)NC3C(C(C(C(O3)CO)OC(=O)N)O)NC(=O)CC(CCCN)N)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C19H34N8O8/c20-3-1-2-7(21)4-10(30)24-13-14(31)15(35-18(22)33)9(6-28)34-17(13)27-19-25-11-8(29)5-23-16(32)12(11)26-19/h7-9,11-15,17,28-29,31H,1-6,20-21H2,(H2,22,33)(H,23,32)(H,24,30)(H2,25,26,27)/t7 ,8-,9 ,11-,12+,13 ,14 ,15 ,17 /m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
NRAUADCLPJTGSF-WJPMJIHPSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Streptothricin acetyltransferase (STA) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Streptomyces lividans strain Tk21 | 1916 | ||
| Bacillus subtilis strain RM141 | 1423 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 5131-5 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
[a-32P] dCTP by the dideoxynucleoside triphosphate chain termination method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The nucleotide sequence of the streptothricin acetyltransferase (STAT) gene from streptothricin-producing Streptomyces lavendulae predicts a 189-amino-acid protein of molecular weight 20,000, which is consistent with that determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the purified enzyme. By addition of promoter signals and a synthetic ribosome-binding (Shine-Dalgarno) sequence at an appropriate position upstream of the STAT translational start codon, the STAT gene confers streptothricin resistance on Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Streptothricin N-acetyltransferase Sat4 (SAT4) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Campylobacter fetus infection [ICD-11: 1C40.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Campylobacter coli strain BE/G4 | 195 | ||
| Campylobacter coli strain BE5698 | 195 | |||
| Campylobacter coli strain BE6361 | 195 | |||
| Campylobacter coli strain BM2509 | 195 | |||
| Campylobacter coli strain Ck196 | 195 | |||
| Campylobacter coli strain Ck197 | 195 | |||
| Campylobacter coli strain Ck199 | 195 | |||
| Campylobacter coli strain Ck204 | 195 | |||
| Campylobacter jejuni strain Ck194 | 197 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain SURE | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain SURE (pAT132) | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
SDS-polyacrylamide gel assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The sat 4 streptothricin resistance gene from Campylobacter coli BE/G4 was cloned into pUC18, and its nucleotide sequence was determined. Streptothricin acetyltransferase activity was detected in Escherichia coli cells containing recombinant plasmid pAT132 which carries the sat4 gene as an insert. The deduced amino acid sequence displayed 21-27% amino acid identity with streptothricin acetyltransferases from Escherichia coli and streptothricin producers Streptomyces lavendulae and Streptomyces noursei. The sat 4 gene was detected by hybridization in clinical and environmental isolates of Campylobacter spp. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Streptothricin acetyltransferase (STA) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptomyces lavendulae infection [ICD-11: 1C43.13] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Streptomyces lividans strain Tk21 | 1916 | ||
| Bacillus subtilis strain RM141 | 1423 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 5131-5 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
[a-32P] dCTP by the dideoxynucleoside triphosphate chain termination method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The nucleotide sequence of the streptothricin acetyltransferase (STAT) gene from streptothricin-producing Streptomyces lavendulae predicts a 189-amino-acid protein of molecular weight 20,000, which is consistent with that determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the purified enzyme. By addition of promoter signals and a synthetic ribosome-binding (Shine-Dalgarno) sequence at an appropriate position upstream of the STAT translational start codon, the STAT gene confers streptothricin resistance on Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Streptothricin acetyltransferase (STA) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacillus subtilis infection [ICD-11: 1G40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Streptomyces lividans strain Tk21 | 1916 | ||
| Bacillus subtilis strain RM141 | 1423 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 5131-5 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
[a-32P] dCTP by the dideoxynucleoside triphosphate chain termination method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The nucleotide sequence of the streptothricin acetyltransferase (STAT) gene from streptothricin-producing Streptomyces lavendulae predicts a 189-amino-acid protein of molecular weight 20,000, which is consistent with that determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the purified enzyme. By addition of promoter signals and a synthetic ribosome-binding (Shine-Dalgarno) sequence at an appropriate position upstream of the STAT translational start codon, the STAT gene confers streptothricin resistance on Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
