Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00318) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Moxifloxacin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Avelox; MFX; MXF; MXFX; Vigamox; Avalox (TN); Avelon (TN); Avelox (TN); Moxifloxacin [INN:BAN]; Vigamox (TN); Avelox I.V.; Actira (*Hydrochloride*); Avelox (*Hydrochloride*); (1'S,6'S)-1-Cyclopropyl-7-(2,8-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-8-yl)-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-8-methoxy-7-((4aS,7aS)-octahydro-6H-pyrrolo(3,4-b)pyridin-6-yl)-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; 7-[(4aS,7aS)-1,2,3,4,4a,5,7,7a-octahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
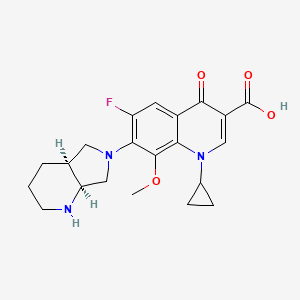
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(6 diseases)
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[8]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial DNA gyrase (Bact gyrase) |
GYRA_STAAU
; GYRB_STAAU |
[1] | ||
| Staphylococcus Topoisomerase IV (Stap-coc parC) | PARC_STAAS | [1] | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C21H24FN3O4
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
COC1=C2C(=CC(=C1N3C[C@@H]4CCCN[C@@H]4C3)F)C(=O)C(=CN2C5CC5)C(=O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C21H24FN3O4/c1-29-20-17-13(19(26)14(21(27)28)9-25(17)12-4-5-12)7-15(22)18(20)24-8-11-3-2-6-23-16(11)10-24/h7,9,11-12,16,23H,2-6,8,10H2,1H3,(H,27,28)/t11-,16+/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
FABPRXSRWADJSP-MEDUHNTESA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Quinolone efflux pump (QEPA2) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A99G+p.V134I |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence alignments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Disk diffusion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | QepA confers decreased susceptibility to hydrophilic fluoroquinolones (e.g., norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and enrofloxacin) with a 32- to 64-fold increase of MICs. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit B (PARE) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Leprosy [ICD-11: 1B20.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D464N |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli Rosetta-gami 2 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli TOP-10 | 83333 | |||
| Mycobacterium leprae Thai-53 | 1769 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
DNA supercoiling assay; DNA cleavage assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | FQs are known to interact with both A and B subunits of DNA gyrase and inhibit supercoiling activity of this enzyme.The FQ-inhibited supercoiling assay and FQ-induced cleavage assay demonstrated the important roles of these amino acid substitutions in reduced sensitivity to FQ with marked influence by amino acid substitution, especially at position 502. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit B (PARE) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Leprosy [ICD-11: 1B20.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N502D |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli Rosetta-gami 2 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli TOP-10 | 83333 | |||
| Mycobacterium leprae Thai-53 | 1769 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
DNA supercoiling assay; DNA cleavage assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | FQs are known to interact with both A and B subunits of DNA gyrase and inhibit supercoiling activity of this enzyme.The FQ-inhibited supercoiling assay and FQ-induced cleavage assay demonstrated the important roles of these amino acid substitutions in reduced sensitivity to FQ with marked influence by amino acid substitution, especially at position 502. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit B (PARE) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Leprosy [ICD-11: 1B20.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E504V |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli Rosetta-gami 2 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli TOP-10 | 83333 | |||
| Mycobacterium leprae Thai-53 | 1769 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
DNA supercoiling assay; DNA cleavage assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | FQs are known to interact with both A and B subunits of DNA gyrase and inhibit supercoiling activity of this enzyme.The FQ-inhibited supercoiling assay and FQ-induced cleavage assay demonstrated the important roles of these amino acid substitutions in reduced sensitivity to FQ with marked influence by amino acid substitution, especially at position 502. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Quinolone resistance protein NorB (NORB) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA microarray hybridization assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Serial twofold agar dilutions assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MgrA was an indirect regulator of norB expression. The mgrA norB double mutant was reproducibly twofold more susceptible to the tested quinolones than the mgrA mutant. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: HTH-type transcriptional regulator MgrA (MGRA) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA microarray hybridization assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Serial twofold agar dilutions assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MgrA was an indirect regulator of norB expression. The mgrA norB double mutant was reproducibly twofold more susceptible to the tested quinolones than the mgrA mutant. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: DNA gyrase subunit A (GYRA) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Anthrax [ICD-11: 1B97.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | p.S85+p.S85F+p.E89K+p.E89A |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain | 562 | ||
| Bacillus anthracis strain | 1392 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA cleavage assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The most common gyrase mutations in quinolone-resistant strains of B. anthracis are found at the conserved serine and glutamic acid residues (GyrAS85 and GyrAE89). In laboratory strains selected for resistance against ciprofloxacin and/or moxifloxacin (two widely prescribed quinolone antibacterials), approximately 80% of the isolates carried a GyrAS85L mutation (either alone or in combination with other gyrase/topoisomerase IV amino acid changes). The only other mutation reported to cause resistance without any other gyrase/topoisomerase IV changes was a GyrAE89K substitution. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit B (PARE) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HIV-infected patients with tuberculosis [ICD-11: 1C60.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.N538D |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Escherichia coli HB101 | 634468 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis LR222 | 1772 | |||
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis MLB 262 | 1773 | |||
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates | 1773 | |||
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis liquid | 1773 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; disk diffusion test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | DNA gyrase consists of two GyrA and two GyrB subunits encoded by gyrA and gyrB, respectively.Fluoroquinolone belong to the quinolone class of antibiotics which inhibit bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV.Certain gyrA and gyrB mutations reported to confer cross-resistance to different FQ antibiotics based on clinical data have not yet been characterized in well-studied M. tuberculosis backgrounds. | |||
| Key Molecule: DNA topoisomerase 4 subunit B (PARE) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | HIV-infected patients with tuberculosis [ICD-11: 1C60.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E540D |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Escherichia coli HB101 | 634468 | |||
| Mycobacterium smegmatis LR222 | 1772 | |||
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis MLB 262 | 1773 | |||
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates | 1773 | |||
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis liquid | 1773 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay; disk diffusion test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | DNA gyrase consists of two GyrA and two GyrB subunits encoded by gyrA and gyrB, respectively.Fluoroquinolone belong to the quinolone class of antibiotics which inhibit bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV.Certain gyrA and gyrB mutations reported to confer cross-resistance to different FQ antibiotics based on clinical data have not yet been characterized in well-studied M. tuberculosis backgrounds. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
