Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00316) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Tyrphostin AG-1478
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
AG-1478; 153436-53-4; Tyrphostin AG 1478; N-(3-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-amine; 175178-82-2; Tyrphostin AG-1478; 4-(3-Chloroanilino)-6,7-dimethoxyquinazoline; AG 1478; AG1478; TYRPHOSTIN; 4-Quinazolinamine, N-(3-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dimethoxy-; UNII-SUH0SEZ9HY; SUH0SEZ9HY; AG-1478 hydrochloride; AG-1478 (Tyrphostin AG-1478); CHEMBL7917; CHEBI:75404; N-(3-Chlorophenyl)-6,7-dimethoxy-4-quinazolinamine; NSC-693255; AK-63142; N-(3-chlorophenyl)-6,7-dimethoxy-quinazolin-4-amine; BRD6408; BRD-6408; SR-01000076156; NSC693255
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
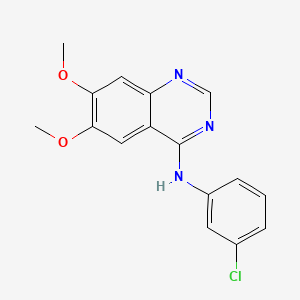
|
||||
| Target | Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | EGFR_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Stress-activated protein kinase 2a (p38 alpha) | MK14_HUMAN | [1] | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C16H14ClN3O2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
COC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)C(=NC=N2)NC3=CC(=CC=C3)Cl)OC
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C16H14ClN3O2/c1-21-14-7-12-13(8-15(14)22-2)18-9-19-16(12)20-11-5-3-4-10(17)6-11/h3-9H,1-2H3,(H,18,19,20)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
GFNNBHLJANVSQV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Protransforming growth factor alpha (TGFA) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.36E-10 Fold-change: 1.90E-01 Z-score: 6.41E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| EGFR/RAS signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01521 | ||
| In Vitro Model | DU-145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The induction of bone metastasis and TkI resistance require miR-203 down-regulation, activation of the EGFR pathway via altered expression of EGFR ligands (EREG and TGFA) and anti-apoptotic proteins (API5, BIRC2, and TRIAP1). Importantly, a sufficient reconstitution of invasiveness and resistance to TkIs treatment was observed in cells transfected with anti-miR-203. In prostate cancer patients, miR-203 levels were inversely correlated with the expression of two EGFR ligands, EREG and TGFA, and an EGFR dependent gene signature. | |||
| Key Molecule: Proepiregulin (EREG) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.31E-11 Fold-change: 7.13E-01 Z-score: 6.92E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| EGFR/RAS signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01521 | ||
| In Vitro Model | DU-145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The induction of bone metastasis and TkI resistance require miR-203 down-regulation, activation of the EGFR pathway via altered expression of EGFR ligands (EREG and TGFA) and anti-apoptotic proteins (API5, BIRC2, and TRIAP1). Importantly, a sufficient reconstitution of invasiveness and resistance to TkIs treatment was observed in cells transfected with anti-miR-203. In prostate cancer patients, miR-203 levels were inversely correlated with the expression of two EGFR ligands, EREG and TGFA, and an EGFR dependent gene signature. | |||
| Key Molecule: Amphiregulin (AREG) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Prostate cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.10E-17 Fold-change: 3.99E-01 Z-score: 9.35E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| EGFR/RAS signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01521 | ||
| In Vitro Model | DU-145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The induction of bone metastasis and TkI resistance require miR-203 down-regulation, activation of the EGFR pathway via altered expression of EGFR ligands (EREG and TGFA) and anti-apoptotic proteins (API5, BIRC2, and TRIAP1). Importantly, a sufficient reconstitution of invasiveness and resistance to TkIs treatment was observed in cells transfected with anti-miR-203. In prostate cancer patients, miR-203 levels were inversely correlated with the expression of two EGFR ligands, EREG and TGFA, and an EGFR dependent gene signature. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: hsa-mir-203 | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| EGFR/RAS signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01521 | ||
| In Vitro Model | DU-145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The induction of bone metastasis and TkI resistance require miR-203 down-regulation, activation of the EGFR pathway via altered expression of EGFR ligands (EREG and TGFA) and anti-apoptotic proteins (API5, BIRC2, and TRIAP1). Importantly, a sufficient reconstitution of invasiveness and resistance to TkIs treatment was observed in cells transfected with anti-miR-203. In prostate cancer patients, miR-203 levels were inversely correlated with the expression of two EGFR ligands, EREG and TGFA, and an EGFR dependent gene signature. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
