Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00201) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Oxytetracycline
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Adamycin; Biostat; Dabicycline; Dalimycin; Fanterrin; Geomycin; Geotilin; Hydroxytetracycline; Imperacin; Lenocycline; Macocyn; OTC; Oksisyklin; Ossitetraciclina; Oxacycline; Oxitetraciclina; Oxitetracyclin; Oxitetracycline; Oxitetracyclinum; Oxymycin; Oxymykoin; Oxypam; Oxyterracin; Oxyterracine; Oxyterracyne; Oxytetracid; Oxytetracyclin; Oxytetracyclinum; Proteroxyna; Riomitsin; Ryomycin; Solkaciclina; Tarocyn; Tarosin; Teravit; Terrafungine; Terramitsin; Terramycin; Tetran; Unimycin; Ursocyclin; Ursocycline; Vendarcin; Biostat PA; Ossitetraciclina [DCIT]; Oxytetracycline HCl; Oxytetracycline [INN]; Oxytetracycline amphoteric; Oxytetracycline anhydrous; Oxytetracycline calcium; Terramycin im; Antibiotic TM 25; LA 200; Liquamycin LA 200; Mycoshield TMQTHC 20; Pennox 200; TM 5; Terramycin Q50; Geomycin (Streptomyces vimosus); OTC (antibiotic); Oxitetraciclina [INN-Spanish]; Oxytetracycline (anhydrous); Oxytetracycline (internal use); Oxytetracyclinum [INN-Latin]; Terramycin, Liquamycin, Oxytetracycline; (2E,4S,4aR,5S,5aR,6S,12aS)-2-[amino(hydroxy)methylidene]-4-(dimethylamino)-5,6,10,11,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-4,4a,5,5a-tetrahydrotetracene-1,3,12-trione; (2E,4S,6S,12aS)-2-[amino(hydroxy)methylidene]-4-(dimethylamino)-5,6,10,11,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-4,4a,5,5a-tetrahydrotetracene-1,3,12-trione; (2Z)-2-[amino(hydroxy)methylidene]-4-(dimethylamino)-5,6,10,11,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-4,4a,5,5a-tetrahydrotetracene-1,3,12-trione; (2Z,4S,4aR,5S,5aR,6S,12aS)-2-[amino(hydroxy)methylidene]-4-(dimethylamino)-5,6,10,11,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-4,4a,5,5a-tetrahydrotetracene-1,3,12-trione; (4S,4aR,5S,5aR,6S,12aS)-4-(dimethylamino)-3,5,6,10,12,12a-hexahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide; 5-Hydroxytetracycline
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
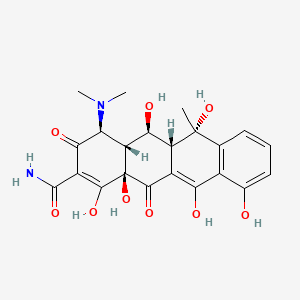
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[2]
[3]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Staphylococcus 30S ribosomal subunit (Stap-coc pbp2) | F4NA87_STAAU | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C22H24N2O9
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C[C@@]1([C@H]2[C@@H]([C@H]3[C@@H](C(=O)C(=C([C@]3(C(=O)C2=C(C4=C1C=CC=C4O)O)O)O)C(=O)N)N(C)C)O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C22H24N2O9/c1-21(32)7-5-4-6-8(25)9(7)15(26)10-12(21)17(28)13-14(24(2)3)16(27)11(20(23)31)19(30)22(13,33)18(10)29/h4-6,12-14,17,25-26,28,30,32-33H,1-3H3,(H2,23,31)/t12-,13-,14+,17+,21-,22+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
OWFJMIVZYSDULZ-PXOLEDIWSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Tetracycline resistance protein tet(59) (TET59) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli EPI-300 | 562 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Tet(59) is preceded by a homolog of the tetracycline repressor tetR typically found upstream of tet genes encoding efflux pumps and include the two palindromic operator sequences present in all regulatory regions of the tet(A)-tet(R) family (33), suggesting that tet(59) probably belongs to the efflux pump family. | |||
| Key Molecule: Putative ABC transporter ATP-binding component (OTRC) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli ET12567 (pUZ8002) | 562 | |||
| Streptomyces rimosus M4018 | 1927 | |||
| Streptomyces rimosus SR16 | 1927 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | OtrC is a multidrug resistance protein based on an ATP hydrolysis-dependent active efflux mechanism.OtrC is a multidrug resistance protein based on an ATP hydrolysis-dependent active efflux mechanism. | |||
| Key Molecule: Tetracycline resistance protein class A (TETA) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Corynebacterium striatum infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Corynebacterium glutamicum strain ATCC 13032 | 196627 | ||
| Corynebacterium striatum strain M82B | 43770 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain DH5alphaMCR | 668369 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The large multiresistance plasmid pTP10 was initially identified in the clinical isolate C. striatum M82B. This 51-kb R-plasmid was shown to carry the determinants for resistance to the antibiotics chloramphenicol, erythomycin, kanamycin, and tetracycline by ethidium bromide-based curing experiments. The tetracycline and oxacillin resistance region is part of a DNA segment structurally similar to the chromosome of the human pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A resistance assay in C. glutamicum demonstrated that the tetAB gene pair of pTP10 is necessary to confer resistance to the antibiotics tetracycline and oxytetracycline. | |||
| Key Molecule: Tetracycline resistance protein class A (TETA) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Corynebacterium glutamicum infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Corynebacterium glutamicum strain ATCC 13032 | 196627 | ||
| Corynebacterium striatum strain M82B | 43770 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain DH5alphaMCR | 668369 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The large multiresistance plasmid pTP10 was initially identified in the clinical isolate C. striatum M82B. This 51-kb R-plasmid was shown to carry the determinants for resistance to the antibiotics chloramphenicol, erythomycin, kanamycin, and tetracycline by ethidium bromide-based curing experiments. Both resistance genes are located on mobile DNA elements that are capable of transposition into the chromosome of the non-pathogenic soil bacteriumC. glutamicum. A resistance assay in C. glutamicum demonstrated that the tetAB gene pair of pTP10 is necessary to confer resistance to the antibiotics tetracycline and oxytetracycline. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Tetracycline resistance protein TetQ (TETQ) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacteroides spp infection [ICD-11: 1C4Y.9] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; Dot blot and Southern blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Tet36 is a new class of ribosome protection type tetracycline resistance protein and lead to drug resistance. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
