Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00314)
| Name |
CXC chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
CXCR4
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr2:136114349-136119177[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MEGISIYTSDNYTEEMGSGDYDSMKEPCFREENANFNKIFLPTIYSIIFLTGIVGNGLVI
LVMGYQKKLRSMTDKYRLHLSVADLLFVITLPFWAVDAVANWYFGNFLCKAVHVIYTVNL YSSVLILAFISLDRYLAIVHATNSQRPRKLLAEKVVYVGVWIPALLLTIPDFIFANVSEA DDRYICDRFYPNDLWVVVFQFQHIMVGLILPGIVILSCYCIIISKLSHSKGHQKRKALKT TVILILAFFACWLPYYIGISIDSFILLEIIKQGCEFENTVHKWISITEALAFFHCCLNPI LYAFLGAKFKTSAQHALTSVSRGSSLKILSKGKRGGHSSVSTESESSSFHSS Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Receptor for the C-X-C chemokine CXCL12/SDF-1 that transduces a signal by increasing intracellular calcium ion levels and enhancing MAPK1/MAPK3 activation. Involved in the AKT signaling cascade. Plays a role in regulation of cell migration, e.g. during wound healing. Acts as a receptor for extracellular ubiquitin; leading to enhanced intracellular calcium ions and reduced cellular cAMP levels. Binds bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) et mediates LPS-induced inflammatory response, including TNF secretion by monocytes. Involved in hematopoiesis and in cardiac ventricular septum formation. Also plays an essential role in vascularization of the gastrointestinal tract, probably by regulating vascular branching and/or remodeling processes in endothelial cells. Involved in cerebellar development. In the CNS, could mediate hippocampal-neuron survival.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
7 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10.3] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Pancreas | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.90E-02 Fold-change: 1.57E-01 Z-score: 1.95E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | CXCR4/let-7a/HMGA2 pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | HPDE6-C7 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0P38 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Transwell assay; Flow cytometric analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | CXCR4/Let-7a axis regulates metastasis and chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer cells through targeting HMGA2. overexpression of HMGA2 restores cell proliferation, metastasis and chemosensitivity of gem inhibited by let-7a. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Bendamustine hydrochloride | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | CXCR4 mutation led to bendamustine in the waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Bortezomib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | CXCR4 mutation led to bortezomib in the waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A60.3] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04061 | |
| In Vitro Model | MyLa cells | Embryo | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
XTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MF-Fs promote migration and chemoresistance of MyLa cells through CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling. Through the entire range of Doxo concentrations, MyLa cells cocultured with MF-Fs were significantly more resistant than MyLa cells cocultured with N-Fs. | |||
| Disease Class: Mycosis fungoides [ICD-11: 2B01.0] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycosis fungoides [ICD-11: 2B01.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycosis fungoides tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
XTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MF cultures yielded significantly increased levels of FAPalpha, a CAF marker, and CAF-associated genes and proteins: CXCL12 (ligand of CXCR4 expressed on MF cells), collagen XI, and matrix metalloproteinase 2. Cultured MF fibroblasts showed greater proliferation than normal fibroblasts in ex vivo experiments. A coculture with MyLa cells (MF cell line) increased normal fibroblast growth, reduced the sensitivity of MyLa cells to doxorubicin, and enhanced their migration. Inhibiting the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis increased doxorubicin-induced apoptosis of MyLa cells and reduced MyLa cell motility. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Fludarabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | CXCR4 mutation led to fludarabine in the waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Ibrutinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | CXCR4 mutation led to ibrutinib in the waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. | |||
| Disease Class: Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Ibrutinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | p.S338X |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Mechanism Description | CXCR4 is a transmembrance chemokine receptor that is internalized upon binding to its ligand CXCL12 and subsequently signals through G-proteins to activate the AKT and ERK pathways. The CXCR4 pathway plays an important role in lymphocyte migration and homing. CXCR4WHIM-like are prevalent somatic mutations, present in 30% of patients with WM. It was recently demonstrated that CXCR4S338X, the most common WHIM-like mutation, reduces CXCR4 receptor internalization and allows for sustained enzymatic activity of AKT and ERK and subsequent increased cell survival. When cells are exposed to ibrutinb, CXCR4S338X-carrying WM cells, compared to CXCR4WT cells, exhibit reduced apoptosis. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia [ICD-11: 2A85.4] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Idelalisib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | CXCR4 mutation led to idelalisib in the waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Pancreas | |
| The Specified Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.90E-02; Fold-change: 1.38E+00; Z-score: 7.23E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.66E-03; Fold-change: 1.08E+00; Z-score: 5.26E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
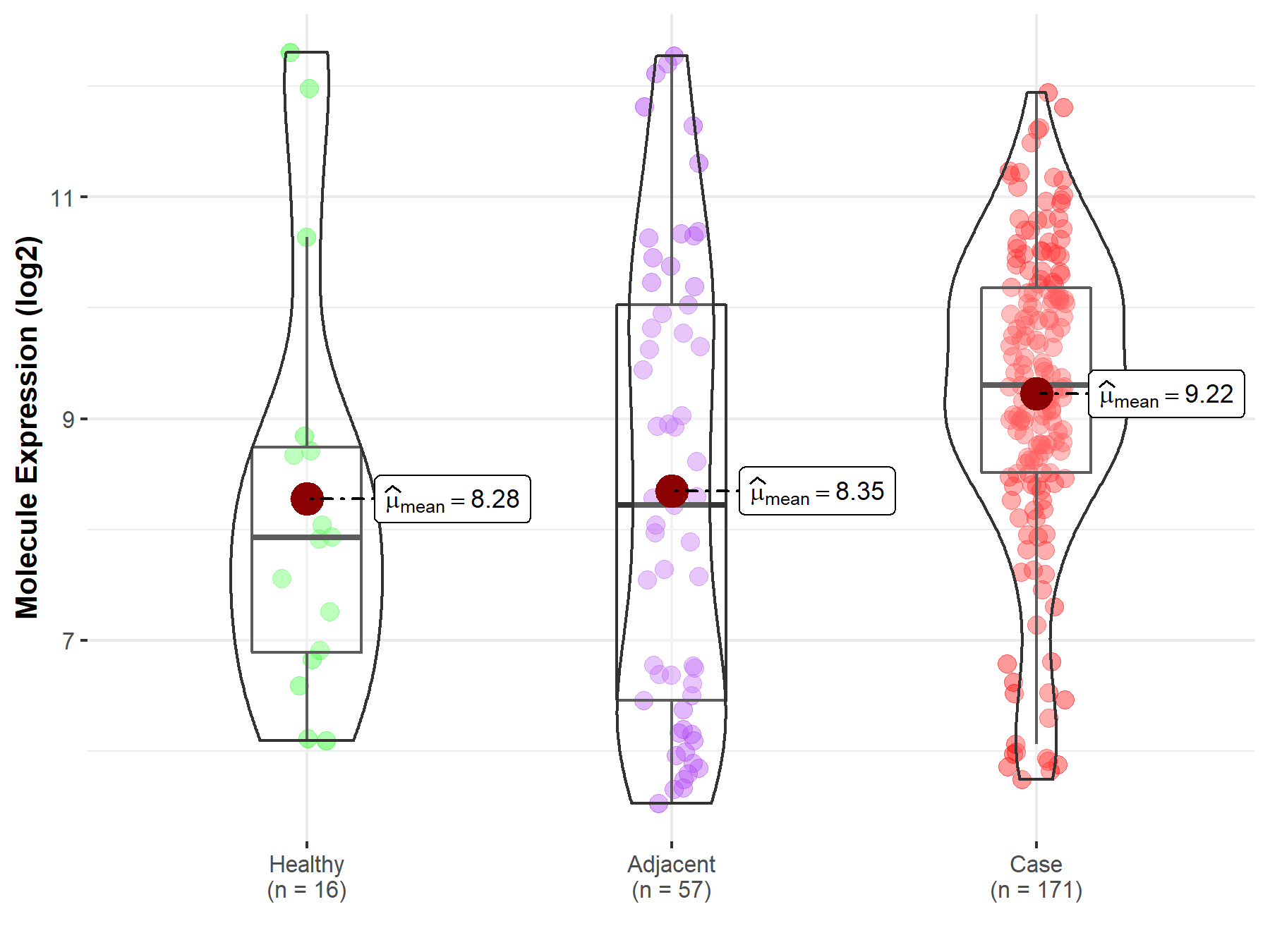
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

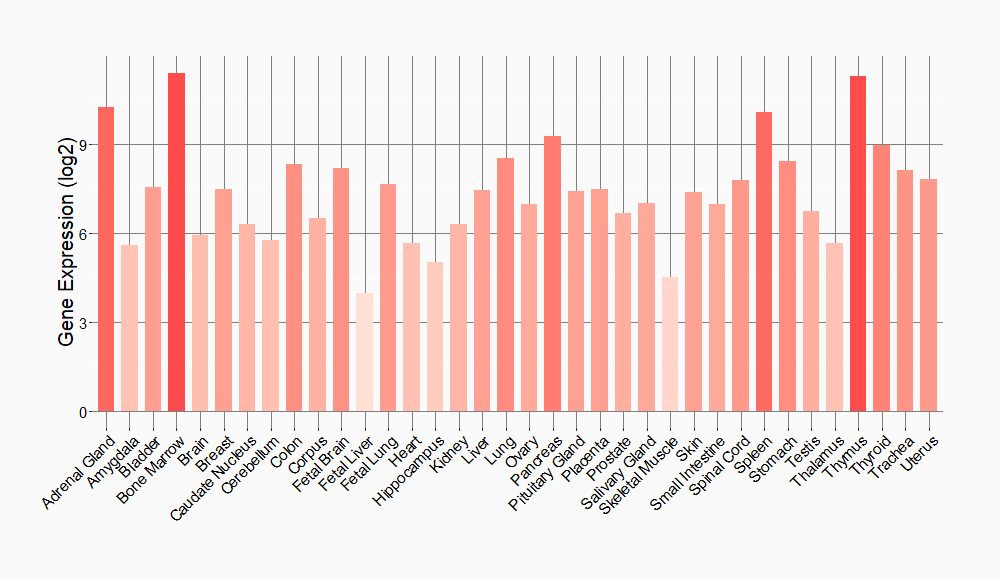
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
