Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00119) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Ribostamycin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ribostamycin; Vistamycin; Hetangmycin; Xylostatin; Antibiotic SF 733; Ribostamycinum; Ribostamicina; Ribostamycine; Ribastamin; Dekamycin IV; SF 733; 25546-65-0; ribostamycin A; Ribostamycin [INN:BAN]; Bu 1709; Ribostamycine [INN-French]; Ribostamycinum [INN-Latin]; UNII-2Q5JOU7T53; SF-733; Ribostamicina [INN-Spanish]; C17H34N4O10; EINECS 247-091-5; NSC 138925; BRN 1357280; 2Q5JOU7T53; CHEBI:45257; NSC138925; O-2,6-Diamino-2,6-dideoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->4)-O-(beta-D-ribofuranosyl-(1->5))-2-deoxystreptamine
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
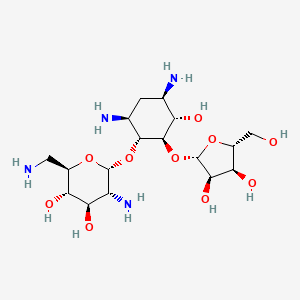
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(5 diseases)
[2]
[1]
[3]
[1]
[3]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA (Bact 16S rRNA) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C17H34N4O10
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1N)O[C@@H]2[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)CN)O)O)N)O[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O3)CO)O)O)O)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C17H34N4O10/c18-2-6-10(24)12(26)8(21)16(28-6)30-14-5(20)1-4(19)9(23)15(14)31-17-13(27)11(25)7(3-22)29-17/h4-17,22-27H,1-3,18-21H2/t4-,5+,6-,7-,8-,9+,10-,11-,12-,13-,14-,15-,16-,17+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
NSKGQURZWSPSBC-VVPCINPTSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (A3AP) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Serratia marcescens infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli C41(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs144 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs150 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs151 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 83-125 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 83-75 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain JM83 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain JM83(pRPG101) | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain M8820Mu | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain MC1065 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain MC1065(pRPG101) | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain POII1681 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain PRC930(pAO43::Tn9O3) | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains | 573 | |||
| Serratia marcescens strains | 615 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Restriction enzyme treating assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cation-supplemented Mueller-Hinton broth assay; agar dilution with MH agar assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Serratia marcescens at a hospital that had used amikacin as its principal aminoglycoside for the preceding 42 months demonstrated high-level resistance to amikacin (greater than or equal to 256 micrograms/ml), kanamycin (greater than or equal to 256 micrograms/ml), gentamicin (greater than or equal to 64 micrograms/ml), netilmicin (64 micrograms/ml), and tobramycin (greater than or equal to 16 micrograms/ml). The clinical isolates and transformants produced a novel 3'-phosphotransferase, APH(3'), that modified amikacin and kanamycin in vitro. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (A3AP) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli HB101 | 634468 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain JM103 | 83333 | |||
| Bacillus circulans strain | 1397 | |||
| Streptomyces lividans strain 66 | 1200984 | |||
| Streptomyces lividans strain M180 | 1916 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Semi-quantitative phosphocellulose-paper binding assay method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The previous demonstration that the APH gene of B. circulans could be expressed in E.coli. These contained a 5.5kb Hind3-digest insert (pCH4) or a 2.7kb Sal1-digest insert (pCH5) at the corresponding site in pBR322. Both these derivatives expressed ampicillin and ribostamycin resistance in E.coli. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (A3AP) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptomyces lividans infection [ICD-11: 1C43.8] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli HB101 | 634468 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain JM103 | 83333 | |||
| Bacillus circulans strain | 1397 | |||
| Streptomyces lividans strain 66 | 1200984 | |||
| Streptomyces lividans strain M180 | 1916 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Semi-quantitative phosphocellulose-paper binding assay method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In attempts to express the B. circulans APH gene in Strep. lividans 66,the 2.7kb Sal1-digest insert of pCH5 was transferred to the Streptomyces vector SLP1.2 by ligating a mixture of a Sal1-digest of pCH5 (1ug) and a partial digest of SLP1.2 (0.5ug) cut at one or two sites of its three Sal1 sites. After incubation, 51 patches of drug-resistant growth were seen. This demonstrated that the ribostamycin-resistance is linked to the plasmid. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (A3AP) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Streptomyces ribosidificus infection [ICD-11: 1C43.14] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Streptomyces lividans strain 66 | 1200984 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain DH-SCY | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain k-12 | 83333 | |||
| Streptomyces hygroscopicus strain SF1084 | 1912 | |||
| Streptomyces ribosidificus strain SF733 | 80859 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Northern hybridization assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Gradient-plate technique of Szybalski assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The rph gene conferring ribostamycin 3'-O-phosphorylation was isolated from a ribostamycin producer, S. ribosidifcus SF733. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (A3AP) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Infection by Bacillus circulans [ICD-11: 1C4Y.12] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli HB101 | 634468 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain JM103 | 83333 | |||
| Bacillus circulans strain | 1397 | |||
| Streptomyces lividans strain 66 | 1200984 | |||
| Streptomyces lividans strain M180 | 1916 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Semi-quantitative phosphocellulose-paper binding assay method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | We have elucidated the full nucleotide sequence of the aminoglycoside phosphotransferase (APH) gene from Bacillus circulans, which produces the aminoglycoside antibiotic butirosin. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (A3AP) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli C41(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs144 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs150 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs151 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 83-125 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 83-75 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain JM83 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain JM83(pRPG101) | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain M8820Mu | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain MC1065 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain MC1065(pRPG101) | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain POII1681 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain PRC930(pAO43::Tn9O3) | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains | 573 | |||
| Serratia marcescens strains | 615 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Restriction enzyme treating assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cation-supplemented Mueller-Hinton broth assay; agar dilution with MH agar assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Serratia marcescens at a hospital that had used amikacin as its principal aminoglycoside for the preceding 42 months demonstrated high-level resistance to amikacin (greater than or equal to 256 micrograms/ml), kanamycin (greater than or equal to 256 micrograms/ml), gentamicin (greater than or equal to 64 micrograms/ml), netilmicin (64 micrograms/ml), and tobramycin (greater than or equal to 16 micrograms/ml). The clinical isolates and transformants produced a novel 3'-phosphotransferase, APH(3'), that modified amikacin and kanamycin in vitro. | |||
ICD-X: Extension Codes
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside O-phosphotransferase APH(3')-Ie | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | citrobacter gillenii infection [ICD-11: XN0FZ] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Drug susceptibility testing | |||
| Mechanism Description | A novel aminoglycoside resistance gene, designated aph(3')-Ie, which confers resistance to ribostamycin, kanamycin, sisomicin and paromomycin, was identified in the chromosome of the animal bacterium Citrobacter gillenii DW61, which exhibited a multidrug resistance phenotype. APH(3')-Ie showed the highest amino acid identity of 74.90% with the functionally characterized enzyme APH(3')-Ia. Enzyme kinetics analysis demonstrated that it had phosphorylation activity toward four aminoglycoside substrates, exhibiting the highest affinity (K m, 4.22 ± 0.88 uM) and the highest catalytic efficiency [k cat/K m, (32.27 ± 8.14) x 104] for ribomycin. Similar to the other APH(3') proteins, APH(3')-Ie contained all the conserved functional sites of the APH family. The aph(3')-Ie homologous genes were present in C. gillenii isolates from different sources, including some of clinical significance. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
