Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00094) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Netilmicin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
NTL; Netilmicina; Netilmicine; Netilmicinum; Netilyn; Netira; Nettacin; Vectacin; NETILMICIN SULFATE; Sch 20569; Netilmicin (INN); Netilmicin [INN:BAN]; Netilmicina [INN-Spanish]; Netilmicine [INN-French]; Netilmicinum [INN-Latin]; Netira (TN); Nettacin (TN); Sch-20569; O-(2,6-Diamino-2,3,4,6-tetradesoxy-alpha-glycero-4-hexenopyranosyl-(1-4)-O-(3-desoxy-4-C-methyl-3-methylamino-beta-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1-6)-2-desoxy-N1-ethyl-D-streptamin; (2R,3R,4R,5R)-2-[(1S,2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-amino-3-[[(2S,3R)-3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy]-6-(ethylamino)-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)oxane-3,5-diol; (2R,3R,4R,5R)-2-[(1S,2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-amino-3-[[3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy]-6-(ethylamino)-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)oxane-3,5-diol; (2R,3S,4S,5S)-2-[(1S,2R,3S,4S,6R)-4-amino-3-[[(2S,3R)-3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy]-6-(ethylamino)-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)oxane-3,5-diol; 1-N-Aethylsisomicin; 1-N-Ethylsisomicin; 2-[4-amino-3-[[3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy]-6-(ethylamino)-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)oxane-3,5-diol; 4-amino-3-{[3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydro-2h-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-6-(ethylamino)-2-hydroxycyclohexyl 3-deoxy-4-c-methyl-3-(methylamino)pentopyranoside
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
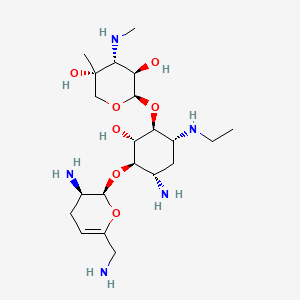
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(6 diseases)
[3]
[3]
[5]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[4]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[6]
[7]
|
||||
| Target | Staphylococcus 30S ribosomal subunit (Stap-coc pbp2) | F4NA87_STAAU | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C21H41N5O7
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CCN[C@@H]1C[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1O[C@@H]2[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@](CO2)(C)O)NC)O)O)O[C@@H]3[C@@H](CC=C(O3)CN)N)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C21H41N5O7/c1-4-26-13-7-12(24)16(32-19-11(23)6-5-10(8-22)31-19)14(27)17(13)33-20-15(28)18(25-3)21(2,29)9-30-20/h5,11-20,25-29H,4,6-9,22-24H2,1-3H3/t11-,12+,13-,14+,15-,16-,17+,18-,19-,20-,21+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
CIDUJQMULVCIBT-MQDUPKMGSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase (AACC2) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 1322345 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Various aminoglycoside modifying enzymes were associated with overlapping phenotypes: 36.5% strains produced AAC(6')-I with either a serine (GEN-TOB-NET) or a leucine (TOB-NET-AMk) at position 119, or both variants (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk); 21.2% expressed ANT(2")-I (GEN-TOB), 7.7% AAC(3)-II (GEN-TOB-NET), 5.8% AAC(3)-I (GEN) and 1.9% AAC(6')-II (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk) or AACA7 (TOB-NET-AMk). | |||
| Key Molecule: Acetylpolyamine amidohydrolase (APAH) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Achromobacter xylosoxydans infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Achromobacter xylosoxydans subsp. denitrificans AX-22 | 85698 | |||
| Escherichia coli MkD-135 | 562 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 10145/3 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA extraction and Sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The aphA15 gene is the first example of an aph-like gene carried on a mobile gene cassette, and its product exhibits close similarity to the APH(3')-IIa aminoglycoside phosphotransferase encoded by Tn5 (36% amino acid identity) and to an APH(3')-IIb enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (38% amino acid identity). Expression of the cloned aphA15 gene in Escherichia coli reduced the susceptibility to kanamycin and neomycin as well as (slightly) to amikacin, netilmicin, and streptomycin. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N-acetyltransferase AAC(6')-IAP | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lactobacillus casei infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | S. maltophilia JUNP350 | N.A. | ||
| Mechanism Description | Compared with vector control,?E. coli?expressing AAC(6')-Iap showed decreased susceptibilities to arbekacin, amikacin, dibekacin, isepamicin, neomycin, netilmicin, sisomicin, and tobramycin. Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) analysis revealed that all the aminoglycosides tested, except for apramycin and paromomycin, were acetylated by AAC(6')-Iap. These results indicated that?aac(6')-Iap?is a functional acetyltransferase that modifies the 6'-NH2?position of aminoglycosides and is involved in aminoglycoside resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside acetyltransferase (AAC) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | ||
| Escherichia coli SCH92111602 | 562 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Dot blot hybridizations assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Standard broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Escherichia coli SCH92111602 expresses an aminoglycoside resistance profile similar to that conferred by the aac(6')-Ie-aph(2")-Ia gene found in gram-positive cocci and was found to contain the aminoglycoside resistance genes aph(2")-Ib and aac(6')-Im (only 44 nucleotides apart). SCH92111602 is an Escherichia coli clinical isolate resistant to a number of aminoglycoside antibiotics, including gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin, and contains an approximately 50-kb plasmid. | |||
| Key Molecule: Acetylpolyamine amidohydrolase (APAH) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Achromobacter xylosoxydans subsp. denitrificans AX-22 | 85698 | |||
| Escherichia coli MkD-135 | 562 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa 10145/3 | 287 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA extraction and Sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Macrodilution broth method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The aphA15 gene is the first example of an aph-like gene carried on a mobile gene cassette, and its product exhibits close similarity to the APH(3')-IIa aminoglycoside phosphotransferase encoded by Tn5 (36% amino acid identity) and to an APH(3')-IIb enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (38% amino acid identity). Expression of the cloned aphA15 gene in Escherichia coli reduced the susceptibility to kanamycin and neomycin as well as (slightly) to amikacin, netilmicin, and streptomycin. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 2'-N-acetyltransferase (A2NA) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain DH5a | 668369 | ||
| Escherichia coli strain XLI-Blue | 562 | |||
| Providencia stuartii strain PR50 | 588 | |||
| Providencia stuartii strain SCH75082831A | 588 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Microdilution plates assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | E.coli DH5alpha/pR 1000 demonstrated an AAC(2')-Ia resistance profile,with gentamicin, tobramycin, netilmicin, and 6'-Nethylnetilmicin MICs increased over those seen with E.coli DH5alpha. In addition, E.coli DH5alpha/pR 1000 did not show an elevated 2'-N-ethylnetilmicin MIC (MIC was 0.25ug/ml). Therefore, pR1000 encoded an enzyme capable of acetylating 6'-N-ethylnetilmicin but not 2'-N-ethylnetilmicin, suggesting 2'-N-acetyltransferase activity. DH5alpha/pSCH4500, which contains a subcloned 1.3-kb fragment, also demonstrated an AAC(2')-Ia resistance profile. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 2'-N-acetyltransferase (A2NA) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli strain DH5a | 668369 | ||
| Mycolicibacterium smegmatis strain EP10 | 1772 | |||
| Mycolicibacterium smegmatis strain mc2155 | 246196 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blot hybridizations assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar macrodilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The introduction of a plasmid-located copy of either the aac (2')-Ib or the aac (2')-Id genes into M. smegmatis mc2155 produces an increase in the level of resistance over those values observed in M. smegmatis mc2155. However, the introduction of the plasmid-located aac (2') Ic gene did not lead to an increase in the MICs. In this experiment, an increase of at least two dilutions in the MIC values over those observed in M. smegmatismc2155 with the vector pSUM36 has been assumed to be due to the increase in the activity of the AAC (2') enzyme. The MICs for the 2'-ethylnetilmicin do not change since this aminoglycoside is not a substrate of the AAC (2') enzyme. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 2'-N-acetyltransferase (A2NA) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Mycobacterium smegmatis infection [ICD-11: 1B2Z.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Acquired |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli XL1-Blue | 562 | ||
| Streptomyces lividans strain 1326 | 1200984 | |||
| Mycolicibacterium fortuitum strain FC1k | 1766 | |||
| Mycolicibacterium smegmatis strain mc2 155 | 246196 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Southern blot hybridizations assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Twofold dilution of antibiotics assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The aac(2')-Ib gene cloned in a mycobacterial plasmid and introduced in Mycobacterium smegmatis conferred resistance to gentamicin, tobramycin, dibekacin, netilmicin, and 6'-N-ethylnetilmicin. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase (AACC2) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Folliculitis [ICD-11: 1B74.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 1322345 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Various aminoglycoside modifying enzymes were associated with overlapping phenotypes: 36.5% strains produced AAC(6')-I with either a serine (GEN-TOB-NET) or a leucine (TOB-NET-AMk) at position 119, or both variants (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk); 21.2% expressed ANT(2")-I (GEN-TOB), 7.7% AAC(3)-II (GEN-TOB-NET), 5.8% AAC(3)-I (GEN) and 1.9% AAC(6')-II (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk) or AACA7 (TOB-NET-AMk). | |||
ICD-09: Visual system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase (AACC2) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Corneal ulcers [ICD-11: 9A76.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 1322345 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Various aminoglycoside modifying enzymes were associated with overlapping phenotypes: 36.5% strains produced AAC(6')-I with either a serine (GEN-TOB-NET) or a leucine (TOB-NET-AMk) at position 119, or both variants (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk); 21.2% expressed ANT(2")-I (GEN-TOB), 7.7% AAC(3)-II (GEN-TOB-NET), 5.8% AAC(3)-I (GEN) and 1.9% AAC(6')-II (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk) or AACA7 (TOB-NET-AMk). | |||
ICD-10: Ear/mastoid process diseasess
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside N(3)-acetyltransferase (AACC2) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 1322345 | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 287 | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates | 287 | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 1280 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Agar dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Various aminoglycoside modifying enzymes were associated with overlapping phenotypes: 36.5% strains produced AAC(6')-I with either a serine (GEN-TOB-NET) or a leucine (TOB-NET-AMk) at position 119, or both variants (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk); 21.2% expressed ANT(2")-I (GEN-TOB), 7.7% AAC(3)-II (GEN-TOB-NET), 5.8% AAC(3)-I (GEN) and 1.9% AAC(6')-II (GEN-TOB-NET-AMk) or AACA7 (TOB-NET-AMk). | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
