Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00084) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Posaconazole
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Noxafil; Spriafil; Posaconazole SP; Posaconazole in combination with MGCD290; SCH56592; Sch 56592; X2N; Noxafil (TN); Noxafil, Posaconazole; SCH-56592; Posaconazole (USAN/INN); Posaconazole [USAN:INN:BAN]; 1-((1S,2S)-1-Ethyl-2-hydroxypropyl)-4-{4-[4-(4-{[(5S,3R)-5-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-(1,2,4-triazolylmethyl)oxolan-3-yl]methoxy}phenyl)piperazinyl]phenyl}-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one; 4-(p-(4-(p-(((3R,5R)-5-(2,4-Difluorophenyl)tetrahydro-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-3-furyl)methoxy)phenyl)-1-piperazinyl)phenyl)-1-((1S,2S)-1-ethyl-2-hydroxypropyl)-delta(sup 2)-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one; 4-[4-[4-[4-[[(3R,5R)-5-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)oxolan-3-yl]methoxy]phenyl]piperazin-1-yl]phenyl]-2-[(2S,3S)-2-hydroxypentan-3-yl]-1,2,4-triazol-3-one; 4-[4-[4-[4-[[(5R)-5-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-5-(1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)oxolan-3-yl]methoxy]phenyl]piperazin-1-yl]phenyl]-2-[(2S,3S)-2-hydroxypentan-3-yl]-1,2,4-triazol-3-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
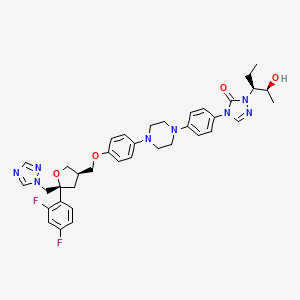
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[2]
[3]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[4]
|
||||
| Target | Candida Cytochrome P450 51 (Candi ERG11) | CP51_CANAL | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C37H42F2N8O4
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC[C@@H]([C@H](C)O)N1C(=O)N(C=N1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)N3CCN(CC3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)OC[C@H]5C[C@](OC5)(CN6C=NC=N6)C7=C(C=C(C=C7)F)F
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C37H42F2N8O4/c1-3-35(26(2)48)47-36(49)46(25-42-47)31-7-5-29(6-8-31)43-14-16-44(17-15-43)30-9-11-32(12-10-30)50-20-27-19-37(51-21-27,22-45-24-40-23-41-45)33-13-4-28(38)18-34(33)39/h4-13,18,23-27,35,48H,3,14-17,19-22H2,1-2H3/t26-,27+,35-,37-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
RAGOYPUPXAKGKH-XAKZXMRKSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aspergillus fumigatus infection [ICD-11: 1F20.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F46Y+p.M172V+p.N248T+p.D255E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EUCAST broth dilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Interestingly, the F46Y/M172V/N248T/D255E/E427k mutation, which has been reported to be associated with azole resistance (37), was detected in one clinical isolate from Shanghai and in one environmental isolate from Xinjiang, respectively. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aspergillus fumigatus infection [ICD-11: 1F20.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G54W |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In the four isolates exhibiting moderate levels of POS resistance glycine 54 was mutated to either glutamate or arginine. In the mutant with a high level of POS resistance glycine 54 was mutated to tryptophan. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aspergillus fumigatus infection [ICD-11: 1F20.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G138C |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Multivariate analysis of overall survival or disease-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Each single mutationad a measurable effect on the affinity of the target enzyme for specific azole derivatives. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G54E |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain RIT | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
NCCLS M38-P microdilution methodology assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Itraconazole resistance has been tightly linked to cyp51A mutations in the codon for Gly54, resulting in five different amino substitutions (G54k, G54V, G54R, G54E, and G54W). | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G54K |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain RIT | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
NCCLS M38-P microdilution methodology assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The G54k amino acid change conferred cross-resistance to both itraconazole and posaconazole (26). The replacement of the wild-type chromosomal cyp51A allele by mutant allele bearing the G161A nucleotide change in codon 54 led to the acquisition of resistance to itraconazole de novo. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Aspergillus niger infection [ICD-11: 1F20.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R228Q |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus niger strain | 5061 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Amino acid changes in ERG11 may contribute to Candida albicans emerging posaconazole resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.P216L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EUCAST method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Four novel mutations were found (H147Y, P216L, Y431C, and G434C). The isolate bearing the P216L mutation was resistant to itraconazole and posaconazole, whereas the isolates with Y431C and G434C showed pan-azole resistance phenotypes. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G434C |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EUCAST method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Four novel mutations were found (H147Y, P216L, Y431C, and G434C). The isolate bearing the P216L mutation was resistant to itraconazole and posaconazole, whereas the isolates with Y431C and G434C showed pan-azole resistance phenotypes. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y431C |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
EUCAST method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Four novel mutations were found (H147Y, P216L, Y431C, and G434C). The isolate bearing the P216L mutation was resistant to itraconazole and posaconazole, whereas the isolates with Y431C and G434C showed pan-azole resistance phenotypes. | |||
| Key Molecule: Sterol 14-alpha demethylase cyp51A (CYP51A) | [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Invasive aspergillosis [ICD-11: 1F20.6] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y121F+p.T289A+p.G448S+p.M172I |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Aspergillus fumigatus strain TR463 | 746128 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | In addition, to compare the susceptibility of TR463 with those of TR34 and TR46, the high resistance of TR463/Y121F/M172I/T289A/G448S was confirmed by MIC testing, displaying a pan-triazole-resistant phenotype to posaconazole, itraconazole, and voriconazole, indicating no in vitro activity of itraconazole and voriconazole (MIC, >16 mg/liter). | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Candida auris infection [ICD-11: 1F23.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y132F |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida auris strain | 498019 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CLSI broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overall, among 45% (n = 20) of isolates that had Y132F and k143R substitutions, 16 showed cross-resistance to one or more azoles namely voriconazole, isavuconazole and posaconazole and four were pan-azole resistant. | |||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (ERG11) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Candida auris infection [ICD-11: 1F23.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.K143R |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Candida auris strain | 498019 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
DNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CLSI broth microdilution method assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overall, among 45% (n = 20) of isolates that had Y132F and k143R substitutions, 16 showed cross-resistance to one or more azoles namely voriconazole, isavuconazole and posaconazole and four were pan-azole resistant. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase (CYP51A1) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Cystic fibrosis [ICD-11: CA25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | S. minutisporum | 41687 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Fluorescent reporter assay; GC-MS | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Antifungal susceptibility assay; Membrane fluidity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | SCFM increases Scedosporium/Lomentospora azole tolerance.Azole resistance is partially due to the efflux pump activity.SCFM leads to decrease in sterol membrane content and increase in membrane fluidity.Scedosporium/Lomentospora species undergo cellular adaptations in SCFM that favours their growth in face of the challenges imposed by azole antifungals. | |||
| Key Molecule: Ergosterol | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Cystic fibrosis [ICD-11: CA25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | S. minutisporum | 41687 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Fluorescent reporter assay; GC-MS | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Antifungal susceptibility assay; Membrane fluidity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | SCFM increases Scedosporium/Lomentospora azole tolerance.Azole resistance is partially due to the efflux pump activity.SCFM leads to decrease in sterol membrane content and increase in membrane fluidity.Scedosporium/Lomentospora species undergo cellular adaptations in SCFM that favours their growth in face of the challenges imposed by azole antifungals. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Calcium-transporting ATPase type 2C member 1 | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Cystic fibrosis [ICD-11: CA25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | S. minutisporum | 41687 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Fluorescent reporter assay; GC-MS | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Antifungal susceptibility assay; Membrane fluidity assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | SCFM increases Scedosporium/Lomentospora azole tolerance.Azole resistance is partially due to the efflux pump activity.SCFM leads to decrease in sterol membrane content and increase in membrane fluidity.Scedosporium/Lomentospora species undergo cellular adaptations in SCFM that favours their growth in face of the challenges imposed by azole antifungals. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
